Linux死锁检测-Lockdep
关键词:LockDep、spinlock、mutex。
lockdep是内核提供协助发现死锁问题的功能。
本文首先介绍何为lockdep,然后如何在内核使能lockdep,并简单分析内核lockdep相关代码。
最后构造不同死锁用例,并分析如何根据lockdep输出发现问题根源。
1. Lockdep介绍
死锁是指两个或多个进程因争夺资源而造成的互相等待的现象。
常见的死锁有如下两种:
递归死锁:中断等延迟操作中使用了锁,和外面的锁构成了递归死锁。
AB-BA死锁:多个锁因处理不当而引发死锁,多个内核路径上的所处理顺序不一致也会导致死锁。
Linux内核提供死锁调试模块Lockdep,跟踪每个锁的自身状态和各个锁之间的依赖关系,经过一系列的验证规则来确保锁之间依赖关系是正确的。
2. 内核死锁检测Lockdep
2.1 使能Lockdep
Lockdep检测的锁包括spinlock、rwlock、mutex、rwsem的死锁,锁的错误释放,原子操作中睡眠等错误行为。
在内核中配置路径为:Kernel hacking->Lock Debugging (spinlocks, mutexes, etc...)。
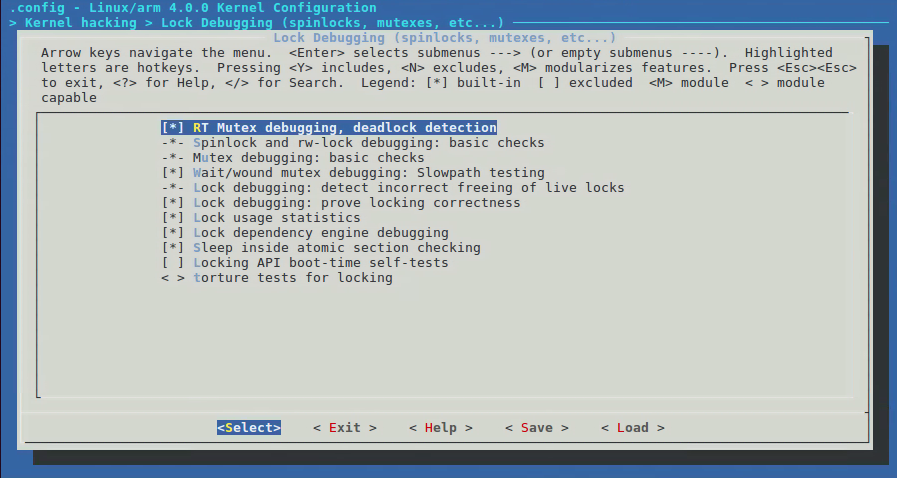
下面是lockcep内核选项及其解释:
CONFIG_DEBUG_RT_MUTEXES=y
检测rt mutex的死锁,并自动报告死锁现场信息。
CONFIG_DEBUG_SPINLOCK=y
检测spinlock的未初始化使用等问题。配合NMI watchdog使用,能发现spinlock死锁。
CONFIG_DEBUG_MUTEXES=y检测并报告mutex错误
CONFIG_DEBUG_WW_MUTEX_SLOWPATH=y
检测wait/wound类型mutex的slowpath测试。
CONFIG_DEBUG_LOCK_ALLOC=y
检测使用中的锁(spinlock/rwlock/mutex/rwsem)被释放,或者使用中的锁被重新初始化,或者在进程退出时持有锁。
CONFIG_PROVE_LOCKING=y
使内核能在死锁发生前报告死锁详细信息。参见/proc/lockdep_chains。
CONFIG_LOCKDEP=y
整个Lockdep的总开关。参见/proc/lockdep、/proc/lockdep_stats。
CONFIG_LOCK_STAT=y记锁持有竞争区域的信息,包括等待时间、持有时间等等信息。参见/proc/lock_stat。
CONFIG_DEBUG_LOCKDEP=y会对Lockdep的使用过程中进行更多的自我检测,会增加很多额外开销。
CONFIG_DEBUG_ATOMIC_SLEEP=y
在atomic section中睡眠可能造成很多不可预测的问题,这些atomic section包括spinlock持锁、rcu读操作、禁止内核抢占部分、中断处理中等等。
2.2 Lock相关内核节点
/proc/sys/kernel/lock_stat------------------------置位则可以查看/proc/lock_stat统计信息,清楚则关闭lockdep统计信息。
/proc/sys/kernel/max_lock_depth--------------
/proc/sys/kernel/prove_locking
/proc/locks
/proc/lock_stat-------------------------------------关于锁的使用统计信息
/proc/lockdep---------------------------------------存在依赖关系的锁
/proc/lockdep_stats------------------------------存在依赖关系锁的统计信息
/proc/lockdep_chains----------------------------依赖关系锁链表
内核还提供了了Tracepoint协助发现锁的使用问题:/sys/kernel/debug/tracing/events/lock。
2.3 lockdep代码简单分析
3. Lockdep测试
3.1 测试spin_lock死锁
构造测试用例代码如下:
void hack_spinAB(void) { printk("hack_lockdep:A->B\n"); spin_lock(&hack_spinA); spin_lock(&hack_spinB); } void hack_spinBA(void) { printk("hack_lockdep:B->A\n"); spin_lock(&hack_spinB); } static int __init lockdep_test_init(void) { printk("al: lockdep error test init\n"); hack_spinAB(); hack_spinBA(); return 0; }
执行insmod data/lock.ko 后,控制台显示如下。
首先从死锁描述大概可以知道死锁类型。
然后详细介绍了产生死锁的点,这时就可以大概知道是哪个锁,有哪些地方调用导致了死锁。
接着是详细的发生死锁的backtrace,有助于分析死锁产生时的栈回溯。
al: lockdep error test init
hack_lockdep:A->B
hack_lockdep:B->A=============================================
[ INFO: possible recursive locking detected ]---------------------------------------------------------------检测到的死锁描述:递归死锁类型
4.0.0+ #87 Tainted: G O
---------------------------------------------
insmod/658 is trying to acquire lock:---------------------------------------------------------------------------死锁细节描述:欲持锁点和已持锁点
(hack_spinB){+.+...}, at: [<bf002030>] lockdep_test_init+0x30/0x3c [lock]--------------------------lockdep_test_init中调用hack_spinBA再次持有hack_spinB锁but task is already holding lock:
(hack_spinB){+.+...}, at: [<bf000038>] hack_spinAB+0x38/0x3c [lock]--------------------------------hack_spinB已经在hack_spinAB函数中被持有other info that might help us debug this:-----------------------------------------------------------------------锁的其它补充信息
Possible unsafe locking scenario:CPU0
----
lock(hack_spinB);
lock(hack_spinB);*** DEADLOCK ***
May be due to missing lock nesting notation
2 locks held by insmod/658:----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------进程共持有两个锁
#0: (hack_spinA){+.+...}, at: [<bf000030>] hack_spinAB+0x30/0x3c [lock]
#1: (hack_spinB){+.+...}, at: [<bf000038>] hack_spinAB+0x38/0x3c [lock]stack backtrace:--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------栈回溯信息:可以看出从lockdep_test_init->_raw_spin_lock->lock_acquire的调用路径。
CPU: 0 PID: 658 Comm: insmod Tainted: G O 4.0.0+ #87
Hardware name: ARM-Versatile Express
[<c00171b4>] (unwind_backtrace) from [<c0012e7c>] (show_stack+0x20/0x24)
[<c0012e7c>] (show_stack) from [<c05ade10>] (dump_stack+0x8c/0xb4)
[<c05ade10>] (dump_stack) from [<c006b988>] (__lock_acquire+0x1aa4/0x1f64)
[<c006b988>] (__lock_acquire) from [<c006c55c>] (lock_acquire+0xf4/0x190)
[<c006c55c>] (lock_acquire) from [<c05b4ec8>] (_raw_spin_lock+0x60/0x98)
[<c05b4ec8>] (_raw_spin_lock) from [<bf002030>] (lockdep_test_init+0x30/0x3c [lock])
[<bf002030>] (lockdep_test_init [lock]) from [<c0008a28>] (do_one_initcall+0x9c/0x1e8)
[<c0008a28>] (do_one_initcall) from [<c05abf30>] (do_init_module+0x70/0x1c0)
[<c05abf30>] (do_init_module) from [<c00a4ddc>] (load_module+0x18b0/0x1f90)
[<c00a4ddc>] (load_module) from [<c00a55fc>] (SyS_init_module+0x140/0x150)
[<c00a55fc>] (SyS_init_module) from [<c000ec80>] (ret_fast_syscall+0x0/0x4c)
INFO: rcu_sched self-detected stall on CPU
0: (2099 ticks this GP) idle=5ed/140000000000001/0 softirq=13024/13024 fqs=1783
(t=2100 jiffies g=-51 c=-52 q=22)
Task dump for CPU 0:
insmod R running 0 658 657 0x00000002
[<c00171b4>] (unwind_backtrace) from [<c0012e7c>] (show_stack+0x20/0x24)
[<c0012e7c>] (show_stack) from [<c0052874>] (sched_show_task+0x128/0x184)
[<c0052874>] (sched_show_task) from [<c0055dd0>] (dump_cpu_task+0x48/0x4c)
[<c0055dd0>] (dump_cpu_task) from [<c0082878>] (rcu_dump_cpu_stacks+0x9c/0xd4)
[<c0082878>] (rcu_dump_cpu_stacks) from [<c008665c>] (rcu_check_callbacks+0x640/0x968)
[<c008665c>] (rcu_check_callbacks) from [<c008b628>] (update_process_times+0x4c/0x74)
[<c008b628>] (update_process_times) from [<c009a1d4>] (tick_periodic+0x54/0xf8)
[<c009a1d4>] (tick_periodic) from [<c009a3d8>] (tick_handle_periodic+0x38/0x98)
[<c009a3d8>] (tick_handle_periodic) from [<c00164a4>] (twd_handler+0x40/0x50)
[<c00164a4>] (twd_handler) from [<c007dfc4>] (handle_percpu_devid_irq+0xd8/0x1dc)
[<c007dfc4>] (handle_percpu_devid_irq) from [<c0079a7c>] (generic_handle_irq+0x3c/0x4c)
[<c0079a7c>] (generic_handle_irq) from [<c0079dc4>] (__handle_domain_irq+0x6c/0xc4)
[<c0079dc4>] (__handle_domain_irq) from [<c0008740>] (gic_handle_irq+0x34/0x6c)
[<c0008740>] (gic_handle_irq) from [<c0013a44>] (__irq_svc+0x44/0x5c)
Exception stack(0xed5c9d18 to 0xed5c9d60)
9d00: 00000000 00010000
9d20: 0000ffff c02f3898 bf0001b0 c0b1d248 123cc000 00000000 0c99b2c5 00000000
9d40: 00000000 ed5c9d84 ed5c9d60 ed5c9d60 c0070cb4 c0070cb4 60000013 ffffffff
[<c0013a44>] (__irq_svc) from [<c0070cb4>] (do_raw_spin_lock+0xf0/0x1e0)
[<c0070cb4>] (do_raw_spin_lock) from [<c05b4eec>] (_raw_spin_lock+0x84/0x98)
[<c05b4eec>] (_raw_spin_lock) from [<bf002030>] (lockdep_test_init+0x30/0x3c [lock])
[<bf002030>] (lockdep_test_init [lock]) from [<c0008a28>] (do_one_initcall+0x9c/0x1e8)
[<c0008a28>] (do_one_initcall) from [<c05abf30>] (do_init_module+0x70/0x1c0)
[<c05abf30>] (do_init_module) from [<c00a4ddc>] (load_module+0x18b0/0x1f90)
[<c00a4ddc>] (load_module) from [<c00a55fc>] (SyS_init_module+0x140/0x150)
[<c00a55fc>] (SyS_init_module) from [<c000ec80>] (ret_fast_syscall+0x0/0x4c)
BUG: spinlock lockup suspected on CPU#0, insmod/658------------------------------------------------------------错误类型是spinlock,下面的backtrace和上面基本一致。
lock: hack_spinB+0x0/0xfffffedc [lock], .magic: dead4ead, .owner: insmod/658, .owner_cpu: 0-----------发生死锁的是hack_spinB
CPU: 0 PID: 658 Comm: insmod Tainted: G O 4.0.0+ #87
Hardware name: ARM-Versatile Express
[<c00171b4>] (unwind_backtrace) from [<c0012e7c>] (show_stack+0x20/0x24)
[<c0012e7c>] (show_stack) from [<c05ade10>] (dump_stack+0x8c/0xb4)
[<c05ade10>] (dump_stack) from [<c0070b2c>] (spin_dump+0x8c/0xd0)
[<c0070b2c>] (spin_dump) from [<c0070cd0>] (do_raw_spin_lock+0x10c/0x1e0)
[<c0070cd0>] (do_raw_spin_lock) from [<c05b4eec>] (_raw_spin_lock+0x84/0x98)
[<c05b4eec>] (_raw_spin_lock) from [<bf002030>] (lockdep_test_init+0x30/0x3c [lock])
[<bf002030>] (lockdep_test_init [lock]) from [<c0008a28>] (do_one_initcall+0x9c/0x1e8)
[<c0008a28>] (do_one_initcall) from [<c05abf30>] (do_init_module+0x70/0x1c0)
[<c05abf30>] (do_init_module) from [<c00a4ddc>] (load_module+0x18b0/0x1f90)
[<c00a4ddc>] (load_module) from [<c00a55fc>] (SyS_init_module+0x140/0x150)
[<c00a55fc>] (SyS_init_module) from [<c000ec80>] (ret_fast_syscall+0x0/0x4c)
3.2 mutex测试
执行insmod /data/mutexlock.ko,稍后结果如下。
首先是死锁类型介绍。
然后是产生死锁的两个点的调用者,再详细给出了两个点的栈回溯。
最后是死锁点的详细栈回溯。
====================================================== [ INFO: possible circular locking dependency detected ] 4.0.0+ #92 Tainted: G O ------------------------------------------------------- kworker/1:1/343 is trying to acquire lock: (mutex_a){+.+...}, at: [<bf000080>] lockdep_test_worker+0x24/0x58 [mutexlock] but task is already holding lock: ((&(&delay_task)->work)){+.+...}, at: [<c0041078>] process_one_work+0x130/0x60c which lock already depends on the new lock. the existing dependency chain (in reverse order) is: -> #1 ((&(&delay_task)->work)){+.+...}: [<c00406f4>] flush_work+0x4c/0x2bc [<c0041cc4>] __cancel_work_timer+0xa8/0x1d0 [<c0041e28>] cancel_delayed_work_sync+0x1c/0x20 [<bf000138>] lockdep_thread+0x84/0xa4 [mutexlock] [<c0046ee0>] kthread+0x100/0x118 [<c000ed50>] ret_from_fork+0x14/0x24 -> #0 (mutex_a){+.+...}: [<c006c55c>] lock_acquire+0xf4/0x190 [<c05b09e4>] mutex_lock_nested+0x90/0x480 [<bf000080>] lockdep_test_worker+0x24/0x58 [mutexlock] [<c0041138>] process_one_work+0x1f0/0x60c [<c0041fd0>] worker_thread+0x54/0x530 [<c0046ee0>] kthread+0x100/0x118 [<c000ed50>] ret_from_fork+0x14/0x24 other info that might help us debug this: Possible unsafe locking scenario: CPU0 CPU1 ---- ---- lock((&(&delay_task)->work)); lock(mutex_a); lock((&(&delay_task)->work)); lock(mutex_a); *** DEADLOCK *** 2 locks held by kworker/1:1/343: #0: ("events"){.+.+.+}, at: [<c0041078>] process_one_work+0x130/0x60c #1: ((&(&delay_task)->work)){+.+...}, at: [<c0041078>] process_one_work+0x130/0x60c stack backtrace: CPU: 1 PID: 343 Comm: kworker/1:1 Tainted: G O 4.0.0+ #92 Hardware name: ARM-Versatile Express Workqueue: events lockdep_test_worker [mutexlock] [<c00171b4>] (unwind_backtrace) from [<c0012e7c>] (show_stack+0x20/0x24) [<c0012e7c>] (show_stack) from [<c05ade10>] (dump_stack+0x8c/0xb4) [<c05ade10>] (dump_stack) from [<c0065e80>] (print_circular_bug+0x21c/0x344) [<c0065e80>] (print_circular_bug) from [<c006be44>] (__lock_acquire+0x1f60/0x1f64) [<c006be44>] (__lock_acquire) from [<c006c55c>] (lock_acquire+0xf4/0x190) [<c006c55c>] (lock_acquire) from [<c05b09e4>] (mutex_lock_nested+0x90/0x480) [<c05b09e4>] (mutex_lock_nested) from [<bf000080>] (lockdep_test_worker+0x24/0x58 [mutexlock]) [<bf000080>] (lockdep_test_worker [mutexlock]) from [<c0041138>] (process_one_work+0x1f0/0x60c) [<c0041138>] (process_one_work) from [<c0041fd0>] (worker_thread+0x54/0x530) [<c0041fd0>] (worker_thread) from [<c0046ee0>] (kthread+0x100/0x118) [<c0046ee0>] (kthread) from [<c000ed50>] (ret_from_fork+0x14/0x24)
上面的backtrace,和下面的代码流程对照,只有在打开CONFIG_PROVE_LOCKING才会打印相关信息。
lockdep_test_worker ->mutex_lock(&mutex_a) ->mutex_lock_nested ->__mutex_lock_common ->mutex_acquire_nest ->lock_acquire_exclusive ->lock_acquire ->__lock_acquire-----------------------------------------下面的validate_chain在打开CONFIG_PROVE_LOCKING才会进行检查。 ->validate_chain->...->print_circular_bug
参考文档



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号