Linux RT Patch配置和测试
Linux实时补丁是针对Linux内核进行的一系列修改,以提高其性能,使其更适合实时应用。
1. 内核RT补丁
稳定版本内核地址:
针对linux不同版本的patch列表:
打上RT补丁的内核版本:
已有版本呢5.4.31,结合RT补丁,选择的版本号为:
RT patch:patch-5.4.34-rt21.patch.gz
kernel:v5.4.34
将补丁往内核打:
git clone -b v5.3.34 https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/stable/linux.git
cd linux
zcat ../patch-5.4.34-rt21.patch.gz | patch -p1
然后将打了补丁的内核和linux-stable-rt对比,两者代码一致。
git clone -b v5.4.34-rt21 https://git.kernel.org/pub/scm/linux/kernel/git/rt/linux-stable-rt.git
2 打开关闭RT
抢占模式配置如下,实时性越来越高。其中最后一个是实时系统:
General setup
->Preemption Model
->No Forced Preemption (Server)--主动吞吐量,对时间不敏感场景,比如服务器。
->Voluntary Kernel Preemption (Desktop)--牺牲小部分吞吐量,增加更多抢占点,降低延时提高了响应速度。适用于桌面环境。
->Preemptible Kernel (Low-Latency Desktop)--将非关键部分内核代码都变成可抢占,提高了响应速度。适用于对延时有一定要求的桌面和嵌入式设备。
->Fully Preemptible Kernel (Real-Time)--将内核中不可抢占部分修改,除了底层和关键代码不可抢占以外,全可抢占。适用于需要保证实时性的场景。
3 Linux RT性能测试
rt-tests(v2.3)
cyclicdeadline
cyclictest
使用说明:
cyclictest V 2.30
Usage:
cyclictest <options>
-a [CPUSET] --affinity Run thread #N on processor #N, if possible, or if CPUSET
given, pin threads to that set of processors in round-
robin order. E.g. -a 2 pins all threads to CPU 2,
but -a 3-5,0 -t 5 will run the first and fifth
threads on CPU (0),thread #2 on CPU 3, thread #3
on CPU 4, and thread #5 on CPU 5.
-A USEC --aligned=USEC align thread wakeups to a specific offset
-b USEC --breaktrace=USEC send break trace command when latency > USEC
-c CLOCK --clock=CLOCK select clock
0 = CLOCK_MONOTONIC (default)
1 = CLOCK_REALTIME
--default-system Don't attempt to tune the system from cyclictest.
Power management is not suppressed.
This might give poorer results, but will allow you
to discover if you need to tune the system
-d DIST --distance=DIST distance of thread intervals in us, default=500
-D --duration=TIME specify a length for the test run.
Append 'm', 'h', or 'd' to specify minutes, hours or days.
-F --fifo=<path> create a named pipe at path and write stats to it
-h --histogram=US dump a latency histogram to stdout after the run
US is the max latency time to be tracked in microseconds
This option runs all threads at the same priority.
-H --histofall=US same as -h except with an additional summary column
--histfile=<path> dump the latency histogram to <path> instead of stdout
-i INTV --interval=INTV base interval of thread in us default=1000
--json=FILENAME write final results into FILENAME, JSON formatted
--laptop Save battery when running cyclictest
This will give you poorer realtime results
but will not drain your battery so quickly
--latency=PM_QOS power management latency target value
This value is written to /dev/cpu_dma_latency
and affects c-states. The default is 0
-l LOOPS --loops=LOOPS number of loops: default=0(endless)
--mainaffinity=CPUSET
Run the main thread on CPU #N. This only affects
the main thread and not the measurement threads
-m --mlockall lock current and future memory allocations
-M --refresh_on_max delay updating the screen until a new max
latency is hit. Useful for low bandwidth.
-N --nsecs print results in ns instead of us (default us)
-o RED --oscope=RED oscilloscope mode, reduce verbose output by RED
-p PRIO --priority=PRIO priority of highest prio thread
--policy=NAME policy of measurement thread, where NAME may be one
of: other, normal, batch, idle, fifo or rr.
--priospread spread priority levels starting at specified value
-q --quiet print a summary only on exit
-r --relative use relative timer instead of absolute
-R --resolution check clock resolution, calling clock_gettime() many
times. List of clock_gettime() values will be
reported with -X
--secaligned [USEC] align thread wakeups to the next full second
and apply the optional offset
-s --system use sys_nanosleep and sys_setitimer
-S --smp Standard SMP testing: options -a -t and same priority
of all threads
--spike=<trigger> record all spikes > trigger
--spike-nodes=[num of nodes]
These are the maximum number of spikes we can record.
The default is 1024 if not specified
-t --threads one thread per available processor
-t [NUM] --threads=NUM number of threads:
without NUM, threads = max_cpus
without -t default = 1
--tracemark write a trace mark when -b latency is exceeded
-u --unbuffered force unbuffered output for live processing
-v --verbose output values on stdout for statistics
format: n:c:v n=tasknum c=count v=value in us
--dbg_cyclictest print info useful for debugging cyclictest
-x --posix_timers use POSIX timers instead of clock_nanosleep.
实测命令:
cyclictest -t 5 -p 95 -i 1000 -l 1000 -m -D 1m
测试结果解析
Voluntary:
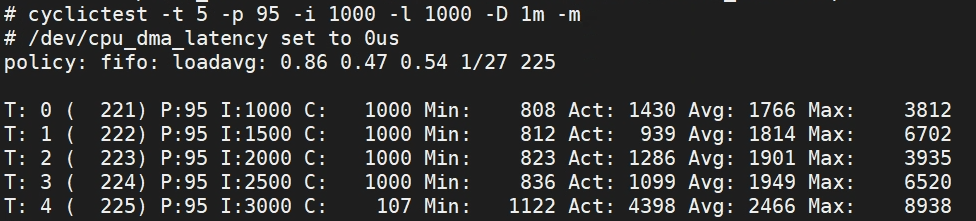
Preemptible:

Fully preemptible:
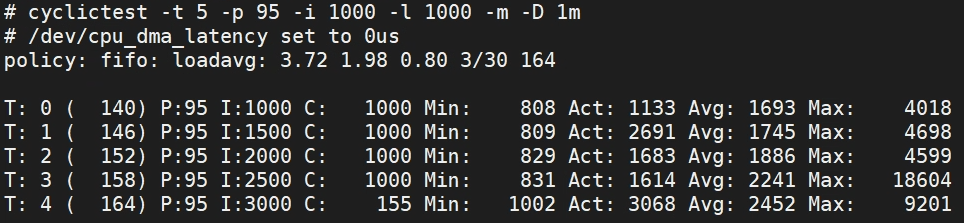
测试结果细节分析参考如下说明:
| Abbreviation | Label | Description |
|---|---|---|
| T | Thread | Thread index and thread ID |
| P | Priority | RT thread priority |
| I | Interval | Intended wake up period for the latency measuring threads (in us) |
| C | Count | Number of times the latency was measured i.e. iteration count |
| Min | Minimum | Minimum latency that was measured (in us) |
| Act | Actual | Latency measured during the latest completed iteration (in us) |
| Avg | Average | 测试结果平均值。 |
| Max | Maximum | Maximum latency that was measured (in us) |
deadline_test
oslat
需要支持frc()函数。
pip_stress
进程Priority Inheritance压力测试。
pi_stress
Priority Inheritance mutex压力测试。
pmqtest
需要支持Message Queue。
ptsematest
queue延时测试。
queuelat
rt-migrate-test
实时任务迁移性能测试。
signaltest
sigwaittest
测试sigwait()延时。
ssdd
svsematest
测试sysv semaphore的延时。
4 相关文档
Blog post series - Shuhao (shuhaowu.com)
(187条消息) Linux RT 进程引发内核频繁卡死的优化方案_边缘计算社区的博客-CSDN博客
realtime:documentation:howto:applications:preemptrt_setup [Wiki] (linuxfoundation.org)
realtime:documentation:howto:applications:application_base [Wiki] (linuxfoundation.org)



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号