简析Linux镜像生成过程
关键词:vmlinux、objcopy、nm、uboot、gzip等等。
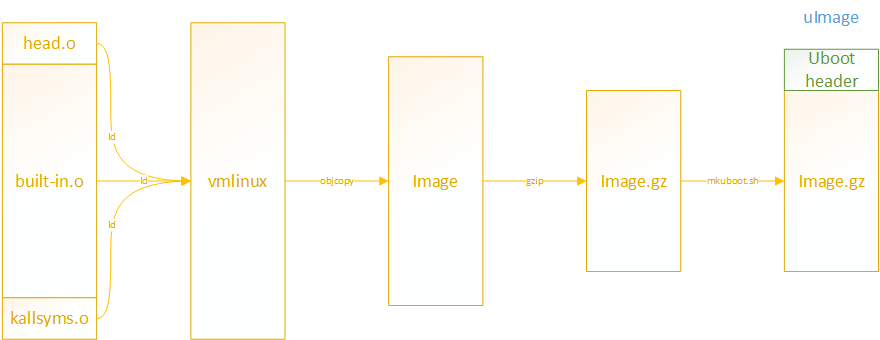
Linux镜像原始输出为vmlinux,后续可能已Image、Image.gz、uImage形式输出。具体过程如下:
1. 通过link-vmlinux.sh生成vmlinux和System.map文件。
2. 通过objcopy移除vmlinux中不必要段,输出binary格式Image。
3. 对Image进行压缩,输出不同格式的压缩文件,比如gzip对应的Image.gz。
4. 对Image.gz加上uboot头信息,生成uImage文件。
1. 生成vmlinux和System.map
根目录Makefile生成.vmlinux.cmd:
cmd_vmlinux := /bin/bash scripts/link-vmlinux.sh aarch64-linux-gnu-ld -EL --no-undefined -X -pie -shared -Bsymbolic --no-apply-dynamic-relocs --fix-cortex-a53-843419 --build-id ; true
link-vmlinux.sh链接head.o和built-in.o,并最终输出vmlinux和System.map文件。
#!/bin/sh set -e # Nice output in kbuild format # Will be supressed by "make -s" info() { if [ "${quiet}" != "silent_" ]; then printf " %-7s %s\n" ${1} ${2} fi } # Thin archive build here makes a final archive with # symbol table and indexes from vmlinux objects, which can be # used as input to linker. # # Traditional incremental style of link does not require this step # # built-in.o output file # archive_builtin() { if [ -n "${CONFIG_THIN_ARCHIVES}" ]; then info AR built-in.o rm -f built-in.o; ${AR} rcsT${KBUILD_ARFLAGS} built-in.o \ ${KBUILD_VMLINUX_INIT} \ ${KBUILD_VMLINUX_MAIN} if [ -n "${CONFIG_LTO_CLANG}" ]; then mv -f built-in.o built-in.o.tmp ${LLVM_AR} rcsT${KBUILD_ARFLAGS} built-in.o $(${AR} t built-in.o.tmp) rm -f built-in.o.tmp fi fi } # If CONFIG_LTO_CLANG is selected, collect generated symbol versions into # .tmp_symversions modversions() { if [ -z "${CONFIG_LTO_CLANG}" ]; then return fi if [ -z "${CONFIG_MODVERSIONS}" ]; then return fi rm -f .tmp_symversions for a in built-in.o ${KBUILD_VMLINUX_LIBS}; do for o in $(${AR} t $a); do if [ -f ${o}.symversions ]; then cat ${o}.symversions >> .tmp_symversions fi done done echo "-T .tmp_symversions" } # Link of vmlinux.o used for section mismatch analysis # ${1} output file modpost_link() { local objects if [ -n "${CONFIG_THIN_ARCHIVES}" ]; then objects="--whole-archive built-in.o" else objects="${KBUILD_VMLINUX_INIT} \ --start-group \ ${KBUILD_VMLINUX_MAIN} \ --end-group" fi if [ -n "${CONFIG_LTO_CLANG}" ]; then # This might take a while, so indicate that we're doing # an LTO link info LTO vmlinux.o else info LD vmlinux.o fi ${LD} ${LDFLAGS} -r -o ${1} $(modversions) ${objects}--------------------------------------链接head.o和built-in.o生成vmlinux.o。 } # If CONFIG_LTO_CLANG is selected, we postpone running recordmcount until # we have compiled LLVM IR to an object file. recordmcount() { if [ -z "${CONFIG_LTO_CLANG}" ]; then return fi if [ -n "${CONFIG_FTRACE_MCOUNT_RECORD}" ]; then scripts/recordmcount ${RECORDMCOUNT_FLAGS} $* fi } # Link of vmlinux # ${1} - optional extra .o files # ${2} - output file vmlinux_link() { local lds="${objtree}/${KBUILD_LDS}" local objects if [ "${SRCARCH}" != "um" ]; then local ld=${LD} local ldflags="${LDFLAGS} ${LDFLAGS_vmlinux}" if [ -n "${LDFINAL_vmlinux}" ]; then ld=${LDFINAL_vmlinux} ldflags="${LDFLAGS_FINAL_vmlinux} ${LDFLAGS_vmlinux}" fi if [[ -n "${CONFIG_THIN_ARCHIVES}" && -z "${CONFIG_LTO_CLANG}" ]]; then objects="--whole-archive built-in.o ${1}" else objects="${KBUILD_VMLINUX_INIT} \ --start-group \ ${KBUILD_VMLINUX_MAIN} \ --end-group \ ${1}" fi ${ld} ${ldflags} -o ${2} -T ${lds} ${objects} else ... fi } # Create ${2} .o file with all symbols from the ${1} object file kallsyms() { info KSYM ${2} local kallsymopt; if [ -n "${CONFIG_HAVE_UNDERSCORE_SYMBOL_PREFIX}" ]; then kallsymopt="${kallsymopt} --symbol-prefix=_" fi if [ -n "${CONFIG_KALLSYMS_ALL}" ]; then kallsymopt="${kallsymopt} --all-symbols" fi if [ -n "${CONFIG_KALLSYMS_ABSOLUTE_PERCPU}" ]; then kallsymopt="${kallsymopt} --absolute-percpu" fi if [ -n "${CONFIG_KALLSYMS_BASE_RELATIVE}" ]; then kallsymopt="${kallsymopt} --base-relative" fi local aflags="${KBUILD_AFLAGS} ${KBUILD_AFLAGS_KERNEL} \ ${NOSTDINC_FLAGS} ${LINUXINCLUDE} ${KBUILD_CPPFLAGS}" local afile="`basename ${2} .o`.S" ${NM} -n ${1} | scripts/kallsyms ${kallsymopt} > ${afile} ${CC} ${aflags} -c -o ${2} ${afile} } # Create map file with all symbols from ${1} # See mksymap for additional details mksysmap() { ${CONFIG_SHELL} "${srctree}/scripts/mksysmap" ${1} ${2} } sortextable() { ${objtree}/scripts/sortextable ${1} } # Delete output files in case of error cleanup() { rm -f .old_version rm -f .tmp_System.map rm -f .tmp_kallsyms* rm -f .tmp_version rm -f .tmp_symversions rm -f .tmp_vmlinux* rm -f built-in.o rm -f System.map rm -f vmlinux rm -f vmlinux.o } on_exit() { if [ $? -ne 0 ]; then cleanup fi } trap on_exit EXIT on_signals() { exit 1 } trap on_signals HUP INT QUIT TERM # # # Use "make V=1" to debug this script case "${KBUILD_VERBOSE}" in *1*) set -x ;; esac if [ "$1" = "clean" ]; then cleanup exit 0 fi # We need access to CONFIG_ symbols case "${KCONFIG_CONFIG}" in */*) . "${KCONFIG_CONFIG}" ;; *) # Force using a file from the current directory . "./${KCONFIG_CONFIG}" esac # Update version info GEN .version if [ ! -r .version ]; then rm -f .version; echo 1 >.version; else mv .version .old_version; expr 0$(cat .old_version) + 1 >.version; fi; archive_builtin #link vmlinux.o modpost_link vmlinux.o-----------------------------------------------生成vmlinux.o文件。 # modpost vmlinux.o to check for section mismatches ${MAKE} -f "${srctree}/scripts/Makefile.modpost" vmlinux.o # final build of init/ ${MAKE} -f "${srctree}/scripts/Makefile.build" obj=init GCC_PLUGINS_CFLAGS="${GCC_PLUGINS_CFLAGS}" if [ -n "${CONFIG_LTO_CLANG}" ]; then # Re-use vmlinux.o, so we can avoid the slow LTO link step in # vmlinux_link KBUILD_VMLINUX_INIT= KBUILD_VMLINUX_MAIN=vmlinux.o # Call recordmcount if needed recordmcount vmlinux.o fi kallsymso="" kallsyms_vmlinux="" if [ -n "${CONFIG_KALLSYMS}" ]; then # kallsyms support # Generate section listing all symbols and add it into vmlinux # It's a three step process: # 1) Link .tmp_vmlinux1 so it has all symbols and sections, # but __kallsyms is empty. # Running kallsyms on that gives us .tmp_kallsyms1.o with # the right size # 2) Link .tmp_vmlinux2 so it now has a __kallsyms section of # the right size, but due to the added section, some # addresses have shifted. # From here, we generate a correct .tmp_kallsyms2.o # 2a) We may use an extra pass as this has been necessary to # woraround some alignment related bugs. # KALLSYMS_EXTRA_PASS=1 is used to trigger this. # 3) The correct ${kallsymso} is linked into the final vmlinux. # # a) Verify that the System.map from vmlinux matches the map from # ${kallsymso}. kallsymso=.tmp_kallsyms2.o kallsyms_vmlinux=.tmp_vmlinux2 # step 1 vmlinux_link "" .tmp_vmlinux1---------------------------------------------生成.tmp_vmlinux1文件。 kallsyms .tmp_vmlinux1 .tmp_kallsyms1.o-----------------------------------生成.tmp_kallsyms1.o文件。 # step 2 vmlinux_link .tmp_kallsyms1.o .tmp_vmlinux2-------------------------------生成.tmp_vmlinux2文件。 kallsyms .tmp_vmlinux2 .tmp_kallsyms2.o-----------------------------------生成.tmp_kallsyms2.o文件。 # step 2a if [ -n "${KALLSYMS_EXTRA_PASS}" ]; then kallsymso=.tmp_kallsyms3.o kallsyms_vmlinux=.tmp_vmlinux3 vmlinux_link .tmp_kallsyms2.o .tmp_vmlinux3 kallsyms .tmp_vmlinux3 .tmp_kallsyms3.o fi fi info LD vmlinux vmlinux_link "${kallsymso}" vmlinux-------------------------------------------生成vmlinux文件。 if [ -n "${CONFIG_BUILDTIME_EXTABLE_SORT}" ]; then info SORTEX vmlinux sortextable vmlinux fi info SYSMAP System.map mksysmap vmlinux System.map---------------------------------------------------从vmlinux生成System.map文件。 # step a (see comment above) if [ -n "${CONFIG_KALLSYMS}" ]; then mksysmap ${kallsyms_vmlinux} .tmp_System.map if ! cmp -s System.map .tmp_System.map; then echo >&2 Inconsistent kallsyms data echo >&2 Try "make KALLSYMS_EXTRA_PASS=1" as a workaround exit 1 fi fi # We made a new kernel - delete old version file rm -f .old_version
mksysmap从vmlinux中解析出ANUW类型的符号,并排除__crc_部分。
#!/bin/sh -x # Based on the vmlinux file create the System.map file # System.map is used by module-init tools and some debugging # tools to retrieve the actual addresses of symbols in the kernel. # # Usage # mksysmap vmlinux System.map ##### # Generate System.map (actual filename passed as second argument) # $NM produces the following output: # f0081e80 T alloc_vfsmnt # The second row specify the type of the symbol: # A = Absolute # B = Uninitialised data (.bss) # C = Common symbol # D = Initialised data # G = Initialised data for small objects # I = Indirect reference to another symbol # N = Debugging symbol # R = Read only # S = Uninitialised data for small objects # T = Text code symbol # U = Undefined symbol # V = Weak symbol # W = Weak symbol # Corresponding small letters are local symbols # For System.map filter away: # a - local absolute symbols # U - undefined global symbols # N - debugging symbols # w - local weak symbols # readprofile starts reading symbols when _stext is found, and # continue until it finds a symbol which is not either of 'T', 't', # 'W' or 'w'. __crc_ are 'A' and placed in the middle # so we just ignore them to let readprofile continue to work. # (At least sparc64 has __crc_ in the middle). $NM -n $1 | grep -v '\( [aNUw] \)\|\(__crc_\)\|\( \$[adt]\)\|\( \.L\)' > $2
2. 生成Image和Image.gz
生成Image命令在arch/arm64/boot/Makefile中定义:
include $(srctree)/arch/arm64/boot/dts/Makefile OBJCOPYFLAGS_Image :=-O binary -R .note -R .note.gnu.build-id -R .comment -S targets := Image Image.bz2 Image.gz Image.lz4 Image.lzma Image.lzo DTB_NAMES := $(subst $\",,$(CONFIG_BUILD_ARM64_APPENDED_DTB_IMAGE_NAMES)) ifneq ($(DTB_NAMES),) DTB_LIST := $(addsuffix .dtb,$(DTB_NAMES)) else DTB_LIST := $(dtb-y) endif DTB_OBJS := $(addprefix $(obj)/dts/,$(DTB_LIST)) $(obj)/Image: vmlinux FORCE $(call if_changed,objcopy) $(obj)/Image.bz2: $(obj)/Image FORCE $(call if_changed,bzip2) $(obj)/Image-dtb: $(obj)/Image $(DTB_OBJS) FORCE $(call if_changed,cat) $(obj)/Image.gz: $(obj)/Image FORCE $(call if_changed,gzip)
...
arch/arm64/boot/.Image.cmd:
cmd_arch/arm64/boot/Image := aarch64-linux-gnu-objcopy -O binary -R .note -R .note.gnu.build-id -R .comment -S vmlinux arch/arm64/boot/Image
移除vmlinux中.note、.note.build-id、.comment段,并且移除所有符号和重定位信息,输出binary格式到Image中。
arch/arm64/boot/.Image.gz.cmd:
cmd_arch/arm64/boot/Image.gz := (cat arch/arm64/boot/Image | gzip -n -f -9 > arch/arm64/boot/Image.gz) || (rm -f arch/arm64/boot/Image.gz ; false)
Image.gz文件就是将Image文件通过gzip进行打包。
3. 生成uImage文件
uImage是对而进行文件加上Uboot头信息,Uboot读取后进行解析,校验并加载到特定位置运行。
在scripts/Makefile.lib中定义了生成uImage命令:
# U-Boot mkimage # --------------------------------------------------------------------------- MKIMAGE := $(srctree)/scripts/mkuboot.sh # SRCARCH just happens to match slightly more than ARCH (on sparc), so reduces # the number of overrides in arch makefiles UIMAGE_ARCH ?= $(SRCARCH) UIMAGE_COMPRESSION ?= $(if $(2),$(2),none) UIMAGE_OPTS-y ?= UIMAGE_TYPE ?= kernel UIMAGE_LOADADDR ?= arch_must_set_this UIMAGE_ENTRYADDR ?= $(UIMAGE_LOADADDR) UIMAGE_NAME ?= 'Linux-$(KERNELRELEASE)' UIMAGE_IN ?= $< UIMAGE_OUT ?= $@ quiet_cmd_uimage = UIMAGE $(UIMAGE_OUT) cmd_uimage = $(CONFIG_SHELL) $(MKIMAGE) -A $(UIMAGE_ARCH) -O linux \ -C $(UIMAGE_COMPRESSION) $(UIMAGE_OPTS-y) \ -T $(UIMAGE_TYPE) \ -a $(UIMAGE_LOADADDR) -e $(UIMAGE_ENTRYADDR) \ -n $(UIMAGE_NAME) -d $(UIMAGE_IN) $(UIMAGE_OUT)



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号