第3天 IDEA 2021简单设置与优化 Java运算符 包机制
IDEA 2021简单设置与优化
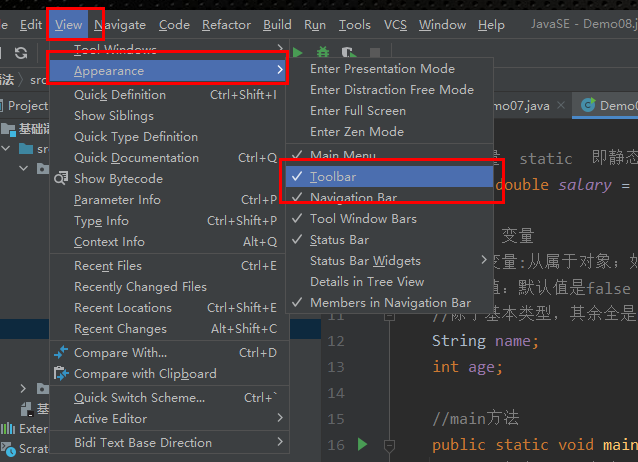
- 将工具条显示在上方
View–>Appearance–>Toolbar
- 鼠标悬停显示
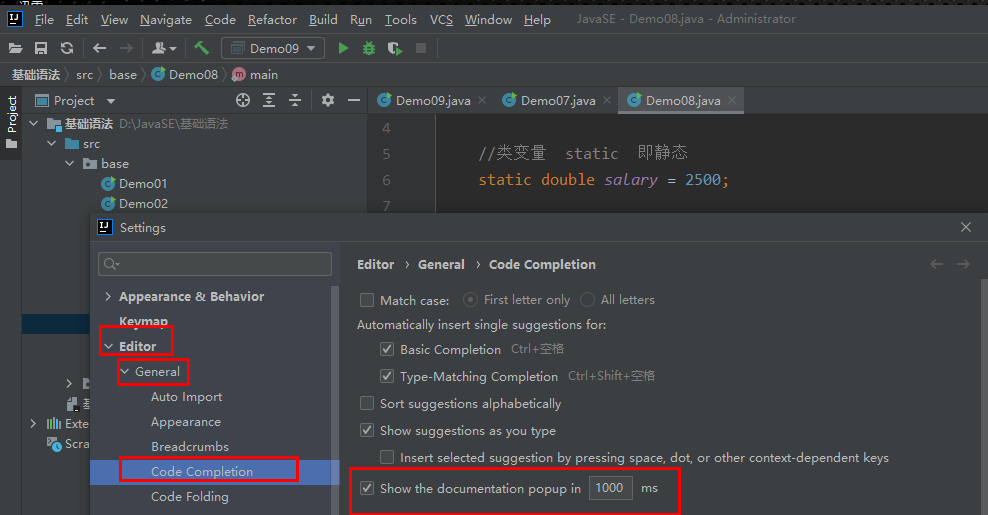
File–>setting–>Editor–>General–>CodeCompletion–>勾选show zhe documentation popup in 1000 ms
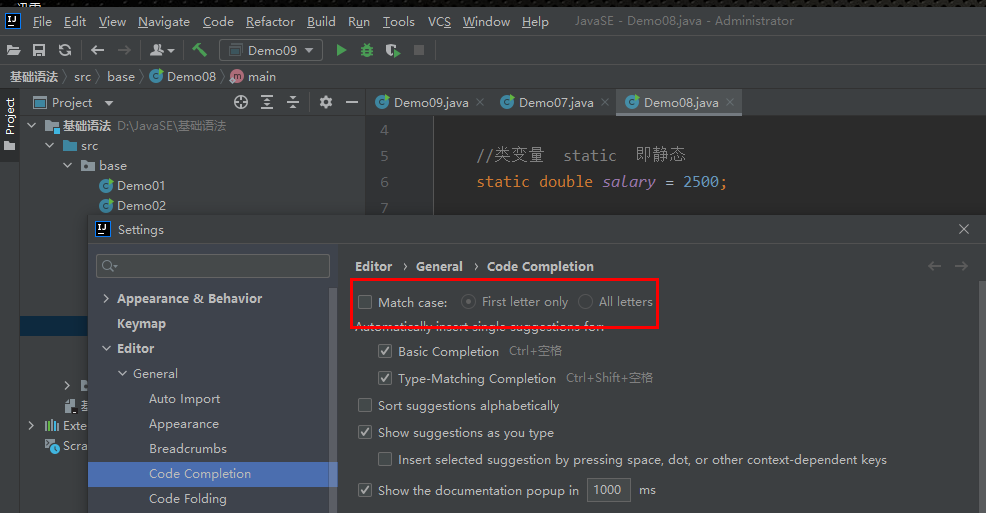
- 忽略大小写
File–>setting–>Editor–>General–>CodeCompletion–>将Match case的勾去掉
-
intellij IDEA中 introduce local variable 快捷键自动补全
解决:Alt+Enter 就会弹出如下界面 选择后 便可以自动补全 -
找到IDEA安装目录 选择idea64.exe.vmoptions文件用notepad++打开并修改
默认的设置太小的
-Xms128m -Xmx750m-XX:ReservedCodeCacheSize=240m
建议电脑4G内存以上的配置为:
-Xms2048m-Xmx2048m-XX:ReservedCodeCacheSize=1024m
需要注意的是,每次更新idea时该配置文件会自动复原,记住每次更新后重新设置一下。
运算符
-
java语言支持如下运算符: 优先级 ()
- 算数运算符:+ - * / % ++ --
- 估值运算符: =
- 关系运算符: < > >= <= == !=(不等于)
-
重点理解下 ++ -- 运算符 知道程序如何运行的
练习:
package operator; public class Demo01 { public static void main(String[] args) { // 二元运算符 //ctrl + D :复制当前行到下一行 int a = 10; int b = 20; int c = 25; int d = 25; System.out.println(a+b); System.out.println(a-b); System.out.println(a*b); System.out.println(a/(double)b); } }package operator; public class Demo02 { public static void main(String[] args) { long a = 123123123123L; int b = 123; short c = 10; byte d = 8; System.out.println(a+b+c+d); //long System.out.println(b+c+d); //int System.out.println(c+d); //int //有一个long输出后即为long 按高级别运算后输出,由double输出即为double,其余全为int } }package operator; public class Demo03 { public static void main(String[] args) { //关系运算符返回结果: 正确 错误 布尔型 int a = 10; int b = 20; int c = 21; System.out.println(c%a); // c/a 21/10.....1 取余数 模运算 System.out.println(a<b); //true System.out.println(a>b); //false System.out.println(a==b); //false System.out.println(a!=b); //true } }package operator; public class Demo04 { public static void main(String[] args) { // ++ -- 自增 自减 一元运算符 int a = 3; int b = a++; //执行完这段代码后,先给b赋值,再自增 //a++ a=a+1 System.out.println(a); //++a a=a+1 int c = ++a;//执行完这段代码前,先自增,再给b赋值 System.out.println(a); System.out.println(b); System.out.println(c); //幂运算 2^3 2*2*2 =8 很多运算类会使用工具类操作 double pow = Math.pow(2, 3); System.out.println(pow); } }- 逻辑运算符: && || ! 即 与 或 非
public class Demo05 { public static void main(String[] args) { // 与(and) 或(or) 非(取反) boolean a = true; boolean b = false; System.out.println("a && b: " + (a&&b));// false 两个变量都为真 结果才为true System.out.println("a || b: " + (a||b));// true 两个变量有一个为真 结果才为true System.out.println("!(a && b): " + !(a&&b));// true 如果是真则为假 如果是假则为真 //短路运算 int c = 5; boolean d = (c<4) && (c++ <4); System.out.println(d); //false 说明直接判断c<4为false后不会在进行c++判断 System.out.println(c); //5 如果判断了则c值不可能是5,即为短路运算 } }- 位运算符 & | …… ~ >> << >>>
package operator; public class Demo06 { public static void main(String[] args) { /* A = 0011 1100 B = 0000 1101 ----------------------- A&B = 0000 1100 A|B = 0011 1101 A^B = 0011 0001 ~B = 1111 0010 ----------------------- 一道面试题: 计算2*8 = 16 如何效率最高? 可拆分为 2*2*2*2 位运算,效率极高!!! << 即 *2 >> 即 /2 0000 0000 0 0000 0001 1 0000 0010 2 0000 0011 3 0000 0100 4 0000 1000 8 0001 0000 16 */ System.out.println(2<<3); //输出 16 } }- 扩展赋值运算符 += -= *= /=
package operator; public class Demo07 { public static void main(String[] args) { int a = 10; int b = 20; a+=b; // a = a+b 偷懒写法 a-=b; // a = a-b 偷懒写法 System.out.println(a); //30 //字符串连接符 + , String System.out.println(a+b); //30 //------------------------------ //一道面试题:计算a+b+"" 和 ""+a+b System.out.println(a+b+""); //30 字符串在后,则先计算在加字符串 System.out.println(""+a+b); //1020 字符串在前 则直接执行字符串连接 } }- 条件运算符 ? :
package operator; public class Demo08 { public static void main(String[] args) { // x ? y : z // 如果x==true 则结果为y,否则结果为z int score = 80; String type = score < 60 ? "不及格 " : "及格"; //必须掌握 // if 也可以做判断 建议用条件运算符 System.out.println(type); //及格 } }
包机制
-
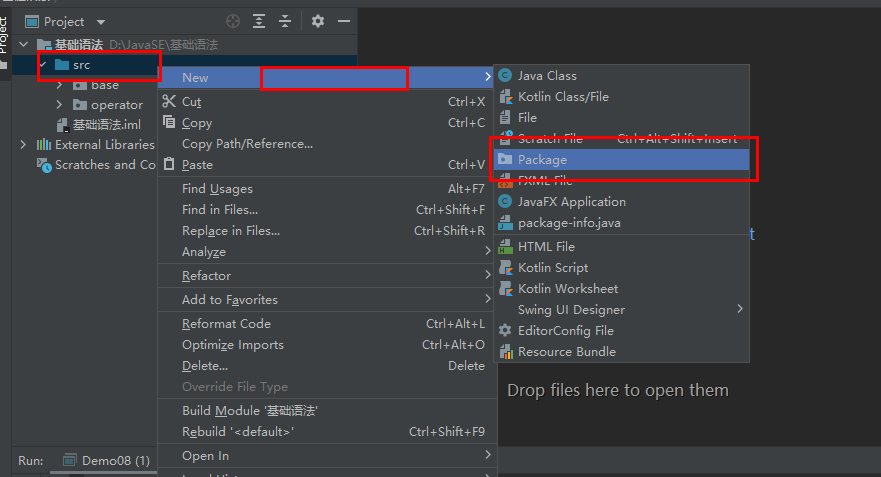
包 即为文件夹
-
一般利用公司域名倒置作为包名: com.kuang.www
![]()
3.例新建com.kuang的包
![]()
![]()
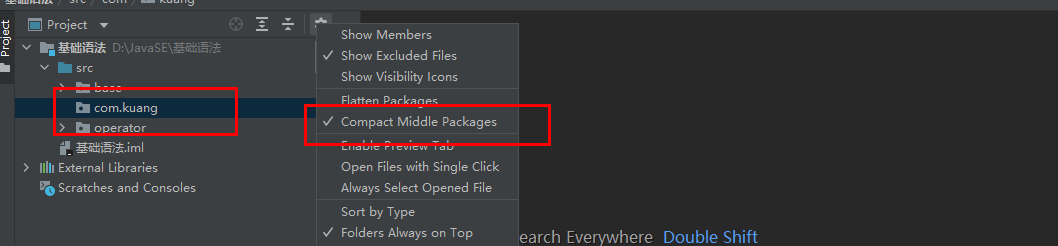
如果是com.kuang一个包则操作如下,取消Compact Middle Package即可
![]()
变为
![]()
-
为了能够使用某一个包的成员,我们需要在java程序中明确导入该包。使用“import”语句即可完成此功能。
import package1[.package2.....].(classname |*);
-
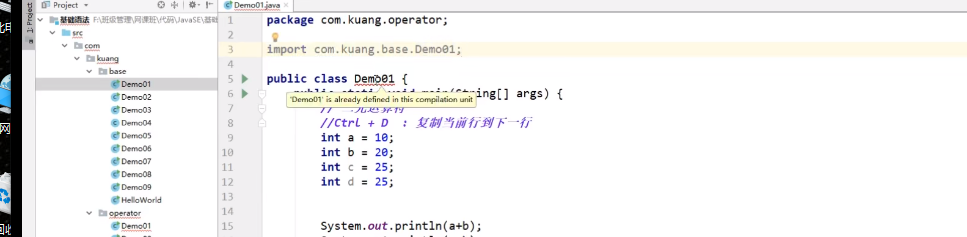
切记包与包内名字不要重复
![]()
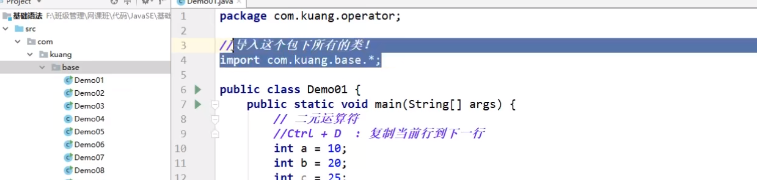
可以直接导入包内的所有文件
![]()





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号