容器之分类与各种测试(四)——unordered_set和unordered_map
关于set和map的区别前面已经说过,这里仅是用hashtable将其实现,所以不做过多说明,直接看程序
unordered_set
#include<stdexcept>
#include<string>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<ctime>
#include<unordered_set>
using namespace std;
long get_a_target_long()
{
long target = 0;
cout<<"target(0~"<<RAND_MAX<<"):";
cin>>target;
return target;
}
string get_a_target_string()
{
long target = 0;
char buf[10];
cout<<"target(0~"<<RAND_MAX<<"):";
cin>>target;
snprintf(buf, 10, "%ld", target);
return string(buf);
}
int compareLongs(const void* a, const void* b)
{
return (*(long*)a - *(long*)b);
}
int compareStrings(const void *a, const void *b)
{
if(*(string*)a > *(string*)b)
return 1;
else if(*(string*)a < *(string*)b)
return -1;
else
return 0;
}
void test_unordered_set(long& value)
{
cout << "\ntest_unordered_set().......... \n";
unordered_set<string> c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i=0; i< value; ++i)
{
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
c.insert(string(buf));
}
catch(exception& p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
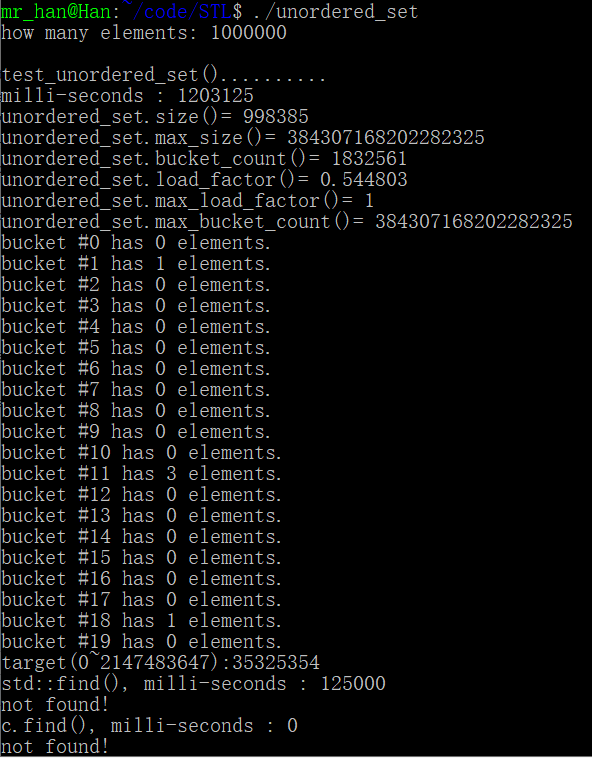
cout << "unordered_set.size()= " << c.size() << endl; //元素个数
cout << "unordered_set.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl; //
cout << "unordered_set.bucket_count()= " << c.bucket_count() << endl;//篮子个数
cout << "unordered_set.load_factor()= " << c.load_factor() << endl; //负载
cout << "unordered_set.max_load_factor()= " << c.max_load_factor() << endl;//最大负载
cout << "unordered_set.max_bucket_count()= " << c.max_bucket_count() << endl; //
for (unsigned i=0; i< 20; ++i) {
cout << "bucket #" << i << " has " << c.bucket_size(i) << " elements.\n";
}
string target = get_a_target_string();
{
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = find(c.begin(), c.end(), target); //比 c.find(...) 慢很多
cout << "std::find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
}
{
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = c.find(target); //比 std::find(...) 快很多
cout << "c.find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
long int value;
cout<<"how many elements: ";
cin>>value;
test_unordered_set(value);
return 0;
}
运行结果
unordered_map
#include<stdexcept>
#include<string>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<iostream>
#include<ctime>
#include<unordered_map>
using namespace std;
long get_a_target_long()
{
long target = 0;
cout<<"target(0~"<<RAND_MAX<<"):";
cin>>target;
return target;
}
string get_a_target_string()
{
long target = 0;
char buf[10];
cout<<"target(0~"<<RAND_MAX<<"):";
cin>>target;
snprintf(buf, 10, "%ld", target);
return string(buf);
}
int compareLongs(const void* a, const void* b)
{
return (*(long*)a - *(long*)b);
}
int compareStrings(const void *a, const void *b)
{
if(*(string*)a > *(string*)b)
return 1;
else if(*(string*)a < *(string*)b)
return -1;
else
return 0;
}
void test_unordered_map(long& value)
{
cout << "\ntest_unordered_map().......... \n";
unordered_map<long, string> c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i=0; i< value; ++i)
{
try {
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
c[i] = string(buf); //特殊的插入方式
}
catch(exception& p) {
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
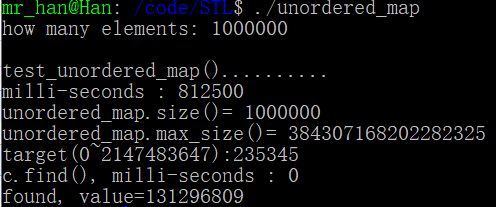
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
cout << "unordered_map.size()= " << c.size() << endl; //元素个数
cout << "unordered_map.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl;
long target = get_a_target_long();
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = c.find(target);//map 不用 std::find()
cout << "c.find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, value=" << (*pItem).second << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
}
int main()
{
long int value;
cout<<"how many elements: ";
cin>>value;
test_unordered_map(value);
return 0;
}
运行结果
不积小流无以成江河




