容器的分类与各种测试(三)——deque
deque是双端队列,其表象看起来是可以双端扩充,但实际上是通过内存映射管理来营造可以双端扩充的假象,如图所示
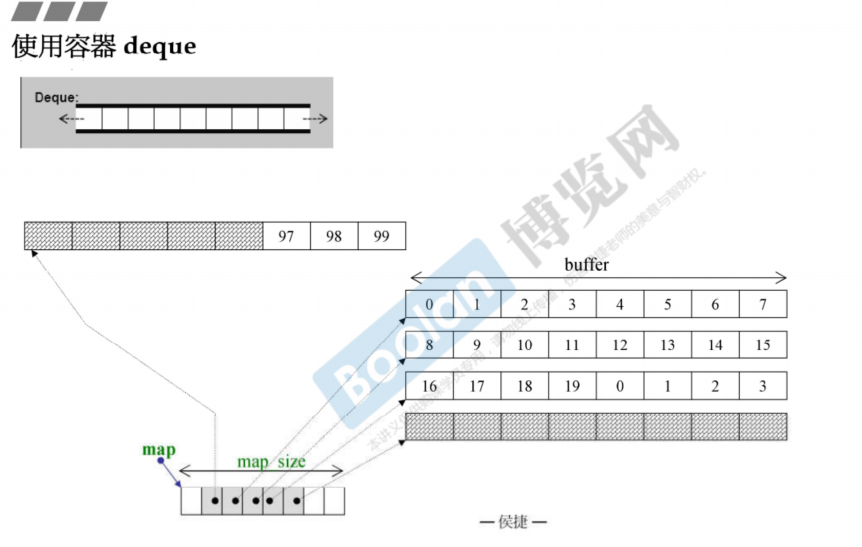
比如,用户将最左端的buff用光时,map会自动向左扩充,继续申请并映射一个新的buff,右端同理。
例程
#include<stdexcept>
#include<string>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<algorithm>//sort,qsort
#include<iostream>
#include<ctime>
#include<deque>
using namespace std;
long get_a_target_long()
{
long target = 0;
cout<<"target(0~"<<RAND_MAX<<"):";
cin>>target;
return target;
}
string get_a_target_string()
{
long target = 0;
char buf[10];
cout<<"target(0~"<<RAND_MAX<<"):";
cin>>target;
snprintf(buf, 10, "%ld", target);
return string(buf);
}
int compareLongs(const void* a, const void* b)
{
return (*(long*)a - *(long*)b);
}
int compareStrings(const void *a, const void *b)
{
if(*(string*)a > *(string*)b)
return 1;
else if(*(string*)a < *(string*)b)
return -1;
else
return 0;
}
void test_deque(long& value)
{
cout << "\ntest_deque().......... \n";
deque<string> c;
char buf[10];
clock_t timeStart = clock();
for(long i=0; i< value; ++i)
{
try
{
snprintf(buf, 10, "%d", rand());
c.push_front(string(buf));
}
catch(exception& p)
{
cout << "i=" << i << " " << p.what() << endl;
abort();
}
}
cout << "milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
cout << "deque.size()= " << c.size() << endl;
cout << "deque.front()= " << c.front() << endl;
cout << "deque.back()= " << c.back() << endl;
cout << "deque.max_size()= " << c.max_size() << endl;
string target = get_a_target_string();
timeStart = clock();
auto pItem = ::find(c.begin(), c.end(), target);// 显示指明使用#include<algorithm>中的find() or sort()
cout << "std::find(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
if (pItem != c.end())
cout << "found, " << *pItem << endl;
else
cout << "not found! " << endl;
timeStart = clock();
::sort(c.begin(), c.end()); // 显示指明使用#include<algorithm>中的find() or sort()
cout << "c.sort(), milli-seconds : " << (clock()-timeStart) << endl;
c.clear();
}
int main()
{
long int value;
cout<<"how many elements:";
cin>>value;
test_deque(value);
return 0;
}
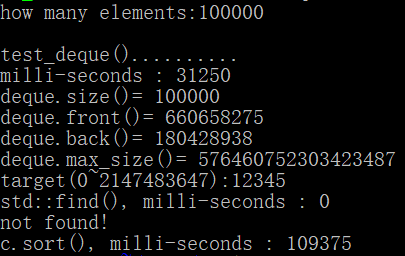
运行结果
不积小流无以成江河




