最小堆
堆:一种支持数据插入删除,能方便的从中取出最大最小数据的一种高效数据结构。
假定在各个数据记录中存在一个能够标识数据记录的数据项,并将该数据项对数据进行组织,则可称此数据项为关键码。//其实对这个关键码的感念还是不太理解
如果有一个关键码的集合K={k0, k1,k2......,kn-1},把它的所有元素按完全二叉树的顺序存储方式放在一个一维数组中,并且满足k i <= k 2i+1且k i <= k 2i+2(或者k i >= k 2i+1且k i >= k 2i+2)i = 0,1,2.....(n-2)/2 (向下取整),则称这个集合为最小堆(或最大堆)。
如图
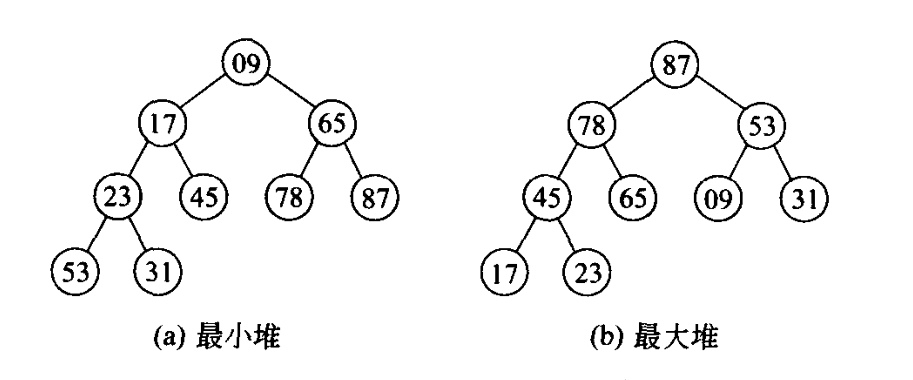
前者任意节点的关键码均小于或者等于它的左,右子女的关键码,位于堆顶的结点的关键码是整个集合最小的,所以称他为最小堆。(反之就是最大堆啦)
在我个人理解,堆,就是一种半排序的数据结构,它仅需要维持各个小分堆的堆特性,就可以保证自己的堆顶的合法性。
代码如下
//header.h #define DefaultSize 10 #include<iostream> using namespace std; template<class T, class E> class MinHeap { private: E *heap; int currentSize; int maxHeapSize; void siftDown(int start, int m); void siftUp(int start); public: MinHeap(int sz = DefaultSize); MinHeap(E arr[], int n); ~MinHeap(){delete []heap;} bool Insert(const E& x); bool RemoveMin(E& x); bool IsEmpty()const{return (this->currentSize == 0 ? true : false);} bool IsFull()const{return (this->currentSize == this->maxHeapSize ? true : false);} void MakeEmpty(){currentSize = 0;} void ShowHeap(); }; template<class T, class E> MinHeap<T, E>::MinHeap(int sz) { this->maxHeapSize = (DefaultSize < sz) ? sz : DefaultSize; this->heap = new E[this->maxHeapSize]; if(this->heap == NULL) { cout<<"heap application memory failed!"<<endl; exit(1); } this->currentSize = 0; } template<class T, class E> MinHeap<T, E>::MinHeap(E arr[], int n) { this->maxHeapSize = (DefaultSize < n) ? n : DefaultSize; this->heap = new E[this->maxHeapSize]; if(this->heap == NULL) { cout<<"heap application memory failed!"<<endl; exit(1); } for(int i=0; i<n; ++i) this->heap[i] = arr[i]; this->currentSize = n; int currentPos = (this->currentSize-2)/2; while(currentPos >= 0) { siftDown(currentPos, this->currentSize-1); --currentPos; } } template<class T, class E> void MinHeap<T, E>::siftDown(int start, int m)//下滑调整 { int i = start, j = 2*i + 1; E temp = this->heap[i]; while(j <= m) { if(i<m && this->heap[j]>this->heap[j+1])//找子节点中娇小的 ++j; if(temp <= this->heap[j])//与子节点较小的进行比较,发现没问题就退出 break; else //当前堆顶比子节点大,把子节点换上来 { this->heap[i] = this->heap[j]; i = j; j = 2*j+1; } } this->heap[i] = temp; //交换结束,将temp放到自己合适的位置 } template<class T, class E> void MinHeap<T, E>::siftUp(int start)//从下到上调整 { if(start>this->currentSize) { cout<<"start number biger than current heap size!"<<endl; return; } int j = start, i = (j-1)/2; E temp = this->heap[j]; while(j >= 0) { if(this->heap[i] <= temp) break; else { this->heap[j] = heap[i]; j = i; i = (i-1)/2; } } this->heap[j] = temp; } template<class T, class E> bool MinHeap<T, E>::Insert(const E& x) { if(this->currentSize == this->maxHeapSize) //发现书中的堆太小,且不能自动扩容,加入了自动扩容功能 { cerr<<"Heap Full,try application Memory!"<<endl; E *p = new E[this->currentSize+DefaultSize]; if(p==NULL) { cerr<<"application memory failed!"<<endl; return false; } for(int i=0; i<this->currentSize; ++i) { p[i] = this->heap[i]; }
delete []this->heap; //扩容后记得删除原来无用空间 this->heap = p; this->maxHeapSize = this->currentSize+DefaultSize; } this->heap[currentSize] = x; siftDown(0, this->currentSize-1); ++this->currentSize; return true; } template<class T, class E> bool MinHeap<T, E>::RemoveMin(E& x) { if(!this->currentSize) { cout<<"Heap empty"<<endl; return false; } x = this->heap[0]; this->heap[0] = this->heap[currentSize-1]; siftDown(0, this->currentSize-1); return true; } template<class T, class E> void MinHeap<T, E>::ShowHeap() { cout<<"Heap[] = "; for(int i=0; i<this->currentSize; ++i) { cout<<this->heap[i]<<" "; } cout<<endl; }
#include"header.h"
int main()
{
int ar[] = {9,8,7,6,5,4,3,2,1,0};
MinHeap<int, int> MH(ar, 10);
MH.ShowHeap();
for(int i=30; i<41; ++i)
MH.Insert(i);
MH.ShowHeap();
}
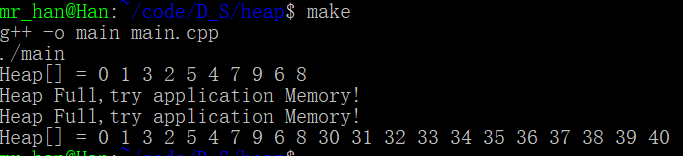
运行效果
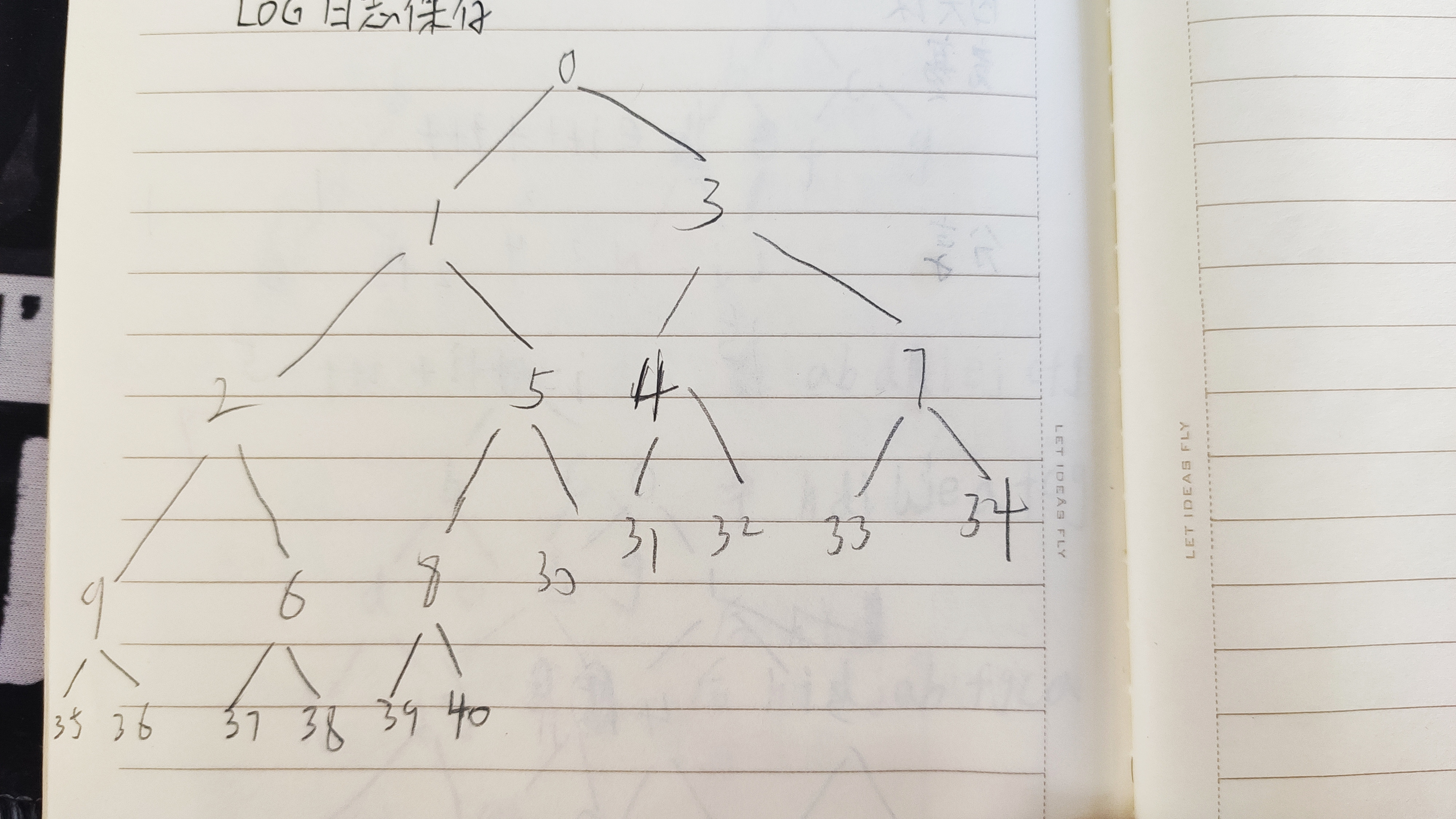
我们将这个堆的抽象结构画出来,是这样子的
不积小流无以成江河




