类的继承访问
首先说两点:①无论何种继承方式,子类都无法继承父类的构造和析构函数
②保护方法只能在类作用域内被调用,任何对象都无法直接调用保护方法。
共有public、protected、private三种继承方法
1.子类作public继承时,可以通过对象直接调用自己和父类的公有方法
父类的保护成员只能在类作用域内调用,而不能在外部通过对象调用
父类的私有数据成员不可在子类中直接调用,只能通过父类的公用或保护方法调用
2.子类作protected继承时,子类把父类的保护和公用方法都当作自己的保护方法,私有仍为子类自己不可直接调用的私有
因此这样继承的子类实例化的对象都无法直接使用父类的所有方法
3.子类作private继承时,子类会将父类的公有和保护方法当作自己的私有数据成员(子类的保护和公用方法可调用),
私有仍为子类自己不可直接调用的私有,子类实例化的对象更不可能直接使用父类的方法
//Test1.h
#include<iostream> using namespace std; class Father { private: double f; protected: void Show_F(); public: Father():f(0) {} ~Father() {} void Print_F(); }; class Son1 : public Father { private: int s; protected: void Show_S1(); public: Son1():s(0) {} ~Son1() {} void Print_S1(); }; class Son2 : protected Father { private: int s; protected: void Show_S2(); public: Son2():s(0) {} ~Son2() {} void Print_S2(); }; class Son3 : private Father //等价 class Son3 : Father { private: int s; protected: void Show_S3(); public: Son3():s(0) {} ~Son3() {} void Print_S3(); }; void Father::Show_F() { cout<<"It's father protected. "<<endl; } void Father::Print_F() { cout<<"It's father public. "<<endl; } void Son1::Show_S1() { cout<<"It's son1 protected. "<<endl; this->Show_F(); this->Print_F(); } void Son1::Print_S1() { cout<<"It's son1 public. "<<endl; this->Show_F(); this->Print_F(); this->Show_S1(); } void Son2::Show_S2() { cout<<"It's son2 protected. "<<endl; this->Show_F(); this->Print_F(); } void Son2::Print_S2() { cout<<"It's son2 public. "<<endl; this->Show_F(); this->Print_F(); this->Show_S2(); } void Son3::Show_S3() { cout<<"It's son3 protected. "<<endl; this->Show_F(); this->Print_F(); } void Son3::Print_S3() { cout<<"It's son3 public. "<<endl; this->Show_F(); this->Print_F(); this->Show_S3(); }
//Test.cpp #include"Test1.h" void main() { Son1 st1; Son2 st2; Son3 st3; st1.Print_F(); cout<<"*****************"<<endl; st1.Print_S1(); cout<<"*****************"<<endl; st1.Print_S1(); cout<<"*****************"<<endl; st3.Print_S3(); }
运行结果如下
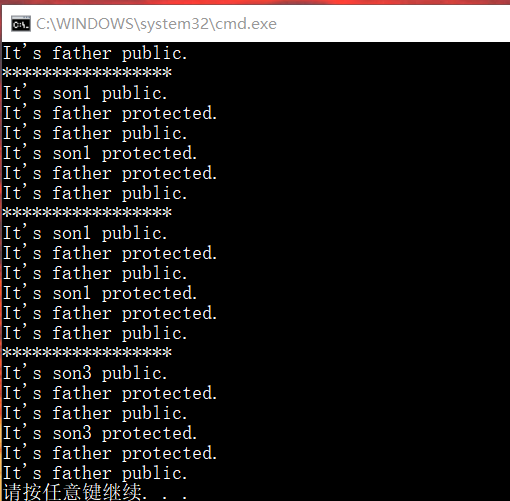
不积小流无以成江河




