[JavaScript] 《JavaScript高级程序设计》笔记
1.|| 和 &&
这两个逻辑运算符和c#是类似的,都是惰性的计算
a() || b() 若a()为真返回a()的结果,此时b()不计算; a()为假则返回b()
a() && b() a()为真返回b()的结果,a()为假返回b()
2.函数声明提升
执行代码前会先读取函数声明,可以把函数声明放在调用语句后面。
sayHi(); function sayHi()
{
alert("Hi!");
}
使用函数表达式创建匿名函数
var funcName = function (arg0, arg1) { }
3.自定义构造函数创建对象
- 创建一个新对象
- 将构造函数的作用于赋给新对象(this指向这个新对象)
- 执行构造函数中的代码(为对象添加属性)
- 返回新对象
function Person(name, age, job) { this.name = name; this.age = age; this.job = job; this.sayName = function() { alert(this.name); }; } var person1 = new Person("Nicholas", 29, "Software Engineer"); var person2 = new Person("Greg", 27, "Doctor");
delete person1.name; //删除person1的实例属性(可用于恢复对原型中属性的访问)
4.原型
所有实例共享原型中的属性和方法(类似static),实例中存在与原型同名属性或方法时将覆盖原型中的
function Person(){ } Person.prototype.name = "Nicholas";
Person.prototype.age = 29;
Person.prototype.job = "Software Engineer";
Person.prototype.sayName = function()
{
alert(this.name);
}; var person1 = new Person(); person1.sayName(); //"Nicholas" var person2 = new Person(); person2.sayName(); //"Nicholas" alert(person1.sayName == person2.sayName); //true
Person构造函数、Person原型属性与Person实例的关系
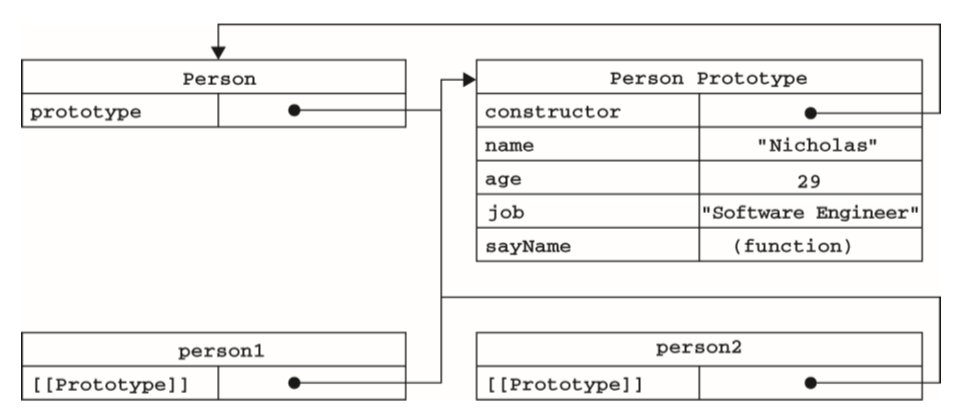
通过isPrototypeOf()判断原型与实例的关系(内部是否有指向特定实例的指针)
alert(Person.prototype.isPrototypeOf(person1)); //true alert(Person.prototype.isPrototypeOf(person2)); //true
返回[[Prototype]]的值
alert(Object.getPrototypeOf(person1) == Person.prototype); //true alert(Object.getPrototypeOf(person1).name); //"Nicholas"
hasOwnProperty() 属性是否是实例属性
alert(person1.hasOwnProperty("name")); //false
in 对象能访问给定属性时返回true (无论属性存在于实例还是原型中)
alert("name" in person1); //tru
Object.keys() 获取对象上所有可枚举的实例属性
var keys = Object.keys(Person.prototype);
alert(keys); //"name,age,job,sayName"
instanceof 判断变量是否是给定引用类型(根据原型链,类似于继承)的实例
alert(person instanceof Object); //true, Everything is Object
使用对象字面量重写整个原型对象
function Person(){ } Person.prototype = { name : "Nicholas", age : 29, job: "Software Engineer", sayName : function () { alert(this.name); } }
5.使用原型链实现继承
function SuperType() { this.property = true; } SuperType.prototype.getSuperValue = function() { return this.property; }; function SubType() { this.subproperty = false; } // SuperType SubType.prototype = new SuperType(); SubType.prototype.getSubValue = function () //不能使用对象字面量创建原型方法,会重写原型链 { return this.subproperty; }; var instance = new SubType(); alert(instance.getSuperValue()); //true

原型链实现继承的问题
- 包含引用类型值的原型属性会被所有实例共享
- 创建子类型的实例时无法向基类型传参
6.借用构造函数
(伪造对象 | 经典继承) (解决原型中包含引用类型值的问题)
function SuperType(name) {
this.name = name; this.colors = ["red", "blue", "green"]; } function SubType() { //继承SuperType SuperType.call(this, "Nicholas");
this.age =20; } var instance1 = new SubType(); instance1.colors.push("black"); alert(instance1.colors); //"red,blue,green,black" var instance2 = new SubType(); alert(instance2.colors); //"red,blue,green"
SuperType.call(this) 在将要创建的SubType实例的环境下调用了SuperType构造函数,在新SubType对象上执行Super Type() 函数定义中的所有对象初始化代码,SubType的每个实例就会具有自己的colors属性的副本。
借用构造函数的问题
- 方法都在构造函数中定义,无法复用函数
7.组合继承
function SuperType(name) { this.name = name; this.colors = ["red", "blue", "green"]; } SuperType.prototype.sayName = function() { alert(this.name); }; function SubType(name, age) { //继承属性 colors SuperType.call(this, name);
this.age = age; } //继承方法 sayAge()
SubType.prototype = new SuperType(); SubType.prototype.constructor = SubType; SubType.prototype.sayAge = function() { alert(this.age); }; var instance1 = new SubType("Nicholas", 29); instance1.colors.push("black"); alert(instance1.colors); //"red,blue,green,black" instance1.sayName(); //"Nicholas"; instance1.sayAge(); //29 var instance2 = new SubType("Greg", 27); alert(instance2.colors); //"red,blue,green" instance2.sayName(); //"Greg"; instance2.sayAge(); //27


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号