[bbk5129]第13集 - Chapter 06- Working with Composite Data Types(Collection)
Associative Arrays(INDEX BY Tables)
An associative array is a PL/SQL collection with two columns:
- Primary Key of integer or string data type(主键可以使整型值,可以使字符串值)
- Column of scalar or record data type
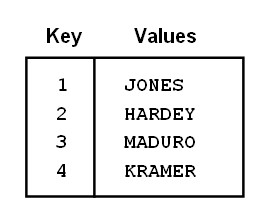
IOT表表示存储在数据库中的一种数据类型.INDEX BY Table只能用在PL/SQL中,不能存储在数据库中.
Associative Array Structure
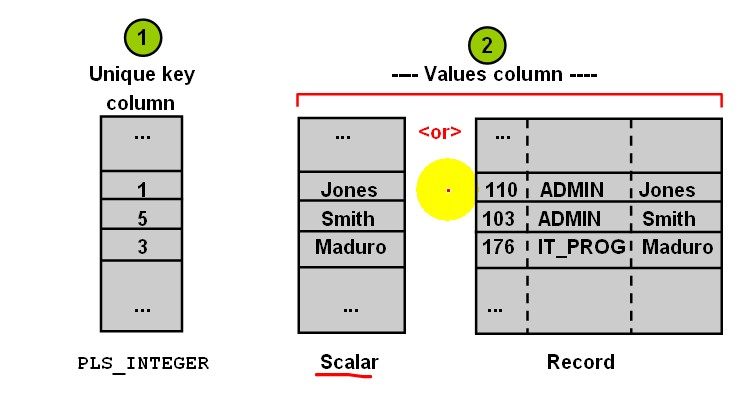
The Order of Associative Arrays
- The subscripts of an associative array can be either strings or integers.
- Subscripts are stored in sort order,not creation order.
- For strings,sort order is determined by the initialization parameters NLS_SORT and NLS_COMP.
- Like a database table,an associative array:
- -Is empty(but not null) until you populate it.
- -Can hold an arbitrary number of elements,which you can access without knkowing their postions.
- Unlike a database table,an associative array:
- -Does not need disk space or network operations.
- -Cannot be manipulated with DML statements.
访问关联数组,可以直接通过下标去访问,或者从头到尾的去遍历.
Steps to Create an Associative Array
Syntax:
TYPE type_name IS TABLE OF {column_type | variable%TYPE | table.column%TYPE} [NOT NULL] | table%ROWTYPE | INDEX BY PLS_INTEGER | BINARY_INTEGER | VARCHAR2(<size>); identifier type_name;
Creating and Accessing Associative Arrays
DECLARE TYPE ename_table_type IS TABLE OF employees.last_name%TYPE INDEX BY PLS_INTEGER; TYPE hiredate_table_type IS TABLE OF DATE INDEX BY PLS_INTEGER; ename_table ename_table_type; hiredate_table hiredate_table_type; BEGIN ename_table(1) := 'CAMERON'; hiredate_table(8) := SYSDATE + 7; NULL; END; /
SET SERVEROUT ON; DECLARE TYPE list_of_names_t IS TABLE OF employees.first_name%TYPE INDEX BY PLS_INTEGER; happlyfamily list_of_names_t; l_row PLS_INTEGER; BEGIN happlyfamily(2020020202) := 'Eli'; happlyfamily(-15070) := 'Steven'; happlyfamily(-90900) := 'Chris'; happlyfamily(88) := 'Veva'; l_row := happlyfamily.FIRST; WHILE (l_row IS NOT NULL) LOOP DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(l_row || '-->' || happlyfamily(l_row)); l_row := happlyfamily.NEXT(l_row); END LOOP; l_row := 88; IF happlyfamily.EXISTS(l_row) THEN DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('It is here!-->' || happlyfamily(l_row)); ELSE DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE('It is not here!-->' || happlyfamily(l_row)); END IF; END; /
下标可以随意的使用,只要符合数据类型的规定;
Using INDEX BY Table Methods
The following methods make asscociative arrays easier to user:
- EXISTS
- COUNT
- PRIOR
- FIRST
- NEXT
- LAST
- DELETE
INDEX BY Table of Records Option
Define an associative array to hold an entire row form a table.
DECLARE TYPE dept_table_type IS TABLE OF departments%ROWTYPE INDEX BY PLS_INTEGER; dept_table dept_table_type; --each element of dept_table is a record BEGIN SELECT * INTO dept_table(1) FROM departments WHERE department_id = 10; DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(dept_table(1).department_id || '->' || dept_table(1).department_name || '->' || dept_table(1).manager_id ); END; /
DECLARE TYPE emp_table_type IS TABLE OF employees%ROWTYPE INDEX BY PLS_INTEGER; emp_table emp_table_type; max_count NUMBER := 104; BEGIN FOR i IN 100..max_count LOOP SELECT * INTO emp_table(i) FROM employees WHERE employee_id = i; END LOOP; FOR i IN emp_table.FIRST..emp_table.LAST LOOP DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(emp_table(i).employee_id || '->' || emp_table(i).last_name); END LOOP; END; /
增强版
DECLARE TYPE emp_table_type IS TABLE OF employees%ROWTYPE INDEX BY PLS_INTEGER; emp_table emp_table_type; --max_count NUMBER := 104; BEGIN --FOR i IN 100..max_count --LOOP -- SELECT * INTO emp_table(i) FROM employees WHERE employee_id = i; --END LOOP; SELECT * BULK COLLECT INTO emp_table FROM employees WHERE employee_id IN (100,101,102,103,104,105); FOR i IN emp_table.FIRST..emp_table.LAST LOOP DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(emp_table(i).employee_id || '->' || emp_table(i).last_name); END LOOP; END; /
Index By Integer or String?
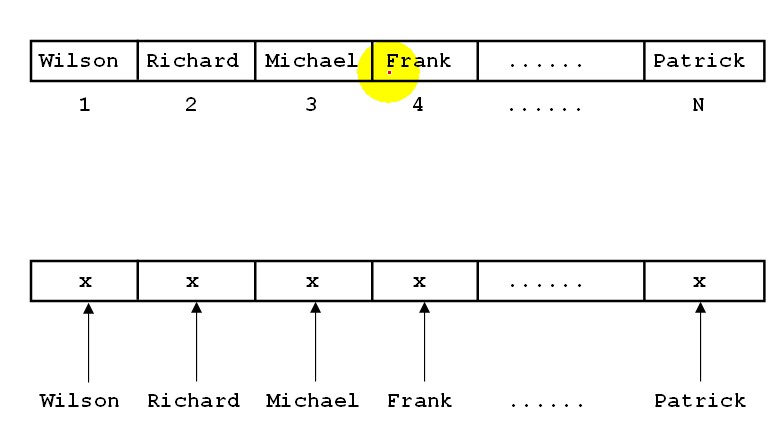
使用PLS_INTEGER作为索引下标与使用String作为索引下标,在查询过程中,String类型的索引性能是最高的.二者在算法上有着本质的区别.






