[bbk4998]第11集 - Chapter 06- Working with Composite Data Types -00-4998(Record)
Objectives
After completing this lesson,you should be able to do the following:
- Describe PL/SQL collections and records
- Create user-defined PL/SQL records
- Create a PL/SQL record with the %ROWTYPE attribute
- Create associative arrays
Oracle数据库中,复合数据类型包含:集合(collections)、记录(records)
Oracle数据库中,集合的类型:(关联数组、嵌套表、可变长度数组)
Agenda
- Introducing composite data types
- Using PL/SQL records
- -Manipulating data with PL/SQL records
- -Advantages of the %ROWTYPE attribute
- Using PL/SQL collections
- -Examining associative arrays(重点介绍)
- -Introducing nested tables
- -Introducing VARRAY
Composite Data Types
- Can hold multiple values (unlike scalar types)
- Are of two types:
- -PL/SQL records
- -PL/SQL collections
- -Associate array(INDEX BY TABLE;以前称之为索引表)
- -Nested table
- -VARRAY
PL/SQL Records or Collections?
- Use PL/SQL records when you want to store values of different data types but only one occurrence at a time.
- Use PL/SQL collections when you want to store values of the same data type.

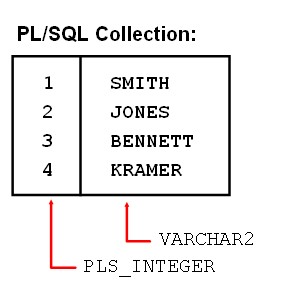
Record相当于C语言里面的Struct
Collection类似于C语言里的Array
对于Record里面的每个组成部分,称为field,对于Collection里面的每个组成部分称之为element。
PL/SQL Records
- Must contain one or more components(called fields) of any sclar,RECORD,or INDEX BY table data type
- Are similar to structures in most third-generation languages (including C and C++)
- Are user-defined and can be a subset of a row in a table
- Treat a collection of fields as a logical unit
- Are convenient for fetching a row of data from a table for processing.
Creating a PL/SQL Record
Syntax:
TYPE type_name IS RECORD (filed_declaration[,filed_declaration]...); identify type_name; filed_declaration: filed_name {filed_type | variable%TYPE | table.column%TYPE | table%ROWTYPE} [[NOT NULL] {:= | DEFAULT} expr]
Creating a PL/SQL Record:Example
SET SERVEROUT ON; DECLARE TYPE t_rec IS RECORD ( v_sal number(8), v_minsal number(8) default 1000, v_hire_date employees.hire_date%type, v_rec1 employees%rowtype ); v_myrec t_rec; BEGIN v_myrec.v_sal := v_myrec.v_minsal + 500; v_myrec.v_hire_date := sysdate; SELECT * INTO v_myrec.v_rec1 FROM employees WHERE employee_id = 100; DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(v_myrec.v_rec1.last_name || '-->' || TO_CHAR(v_myrec.v_hire_date,'YYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS') || '->' || TO_CHAR(v_myrec.v_sal)); END; /
声明一个类型,是不占内存的;而根据这个类型创建一个变量,是占内存的.
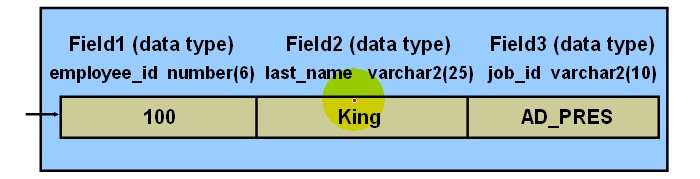
PL/SQL Record Structure
Field declarations:

Example:
%ROWTYPE Statement
- Declare a variable according to a collection of columns in a database table or view.
- Prefix %ROWTYPE with the database table or view.
- Fields in the record take their names and data types from the columns of the table or view.
Syntax:
DECLARE identifier reference%ROWTYPE;
SET SERVEROUT ON; DECLARE TYPE myrec IS RECORD ( id number(8), name varchar2(20) default 'ArcerZhang', birthday DATE ); person myrec; BEGIN person.id := 123456; person.birthday := SYSDATE; DBMS_OUTPUT.PUT_LINE(person.id || '-->' || person.name || '->' || TO_CHAR(person.birthday,'YYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS')); END; /
Advantage of Using the %ROWTYPE Attribute
- The number and data types of the underlying database columns need not be known-and ,in fact,might change at run time.
- The %ROWTYPE attribute is useful when you want to retrieve a row with:
- -The SELECT * statement
- -Row-level INSERT and UPDATE statements
当使用%ROWTYPE进行record的定义时(假设基于table的定义),一旦table的结构发生变化,那么record所在的过程或者函数将失效,此时必须要重新编译.






