C#线程1---Thread基础
1. thread 不带参数 (Main和Thread都在同步处理)(注意using static 和System.Console的使用)

using static System.Console; namespace Recipe1 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Thread t = new Thread(PrintNumber); t.Start(); PrintNumber(); Read(); } static void PrintNumber() { WriteLine("Starting..."); for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) { WriteLine( i); Thread.Sleep(100); } } } }
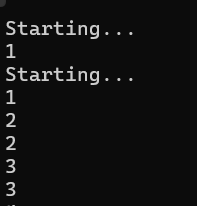
2. 暂停(休眠)线程,展示如何让一个线程等待一段时间而不用消耗操作系统资源,虽然先启动,但还是后运行。(sleep当线程处于休眠状态时,它会占用尽可能少的CPU时间)

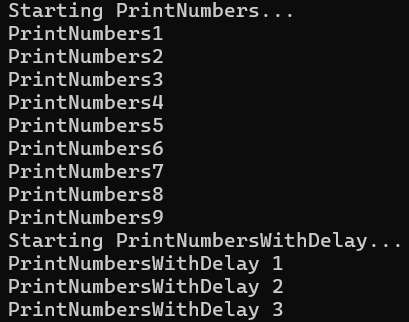
class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { Thread t = new Thread(PrintNumbersWithDelay); t.Start(); PrintNumbers(); } static void PrintNumbers() { WriteLine("Starting PrintNumbers..."); for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) { WriteLine("PrintNumbers"+i); } } static void PrintNumbersWithDelay() { WriteLine("Starting PrintNumbersWithDelay..."); for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) { Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); WriteLine("PrintNumbersWithDelay "+i); } } }
3. 等待线程完成,再往下走(t.Join() ,主线程处于阻塞状态(啥也不干),等待t这个线程完成,当线程t完成 时,主程序会继续运行

class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { WriteLine("Starting program..."); Thread t = new Thread(PrintNumbersWithDelay); t.Start(); t.Join(); WriteLine("Thread completed"); } static void PrintNumbersWithDelay() { WriteLine("Starting..."); for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) { Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); WriteLine(i); } } }
4. 线程中途中止(t.Start();Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(6));t.Abort(); 我们等待6秒后对线程调用了 t.Abort方法 这给线程注入了 ThreadAbortException方法,导致线程被终结。这非常危险,因为该异常可 以在任何时刻发生并可能彻底摧毁应用程序;另外,使用该技术也不一定总能终止线程。目 标线程可以通过处理该异常并调用Thread.ResetAbort方法来拒绝被终止因此并不推荐使用 Abort方法来关闭线程°可优先使用一些其他方法.比如提供一个CancellationToken方法来 取消线程的执行

class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { WriteLine("Starting program..."); Thread t = new Thread(PrintNumbersWithDelay); t.Start(); Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(6)); t.Abort(); WriteLine("A thread has been aborted"); } static void PrintNumbersWithDelay() { WriteLine("Starting..."); for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) { Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); WriteLine(i); } } }
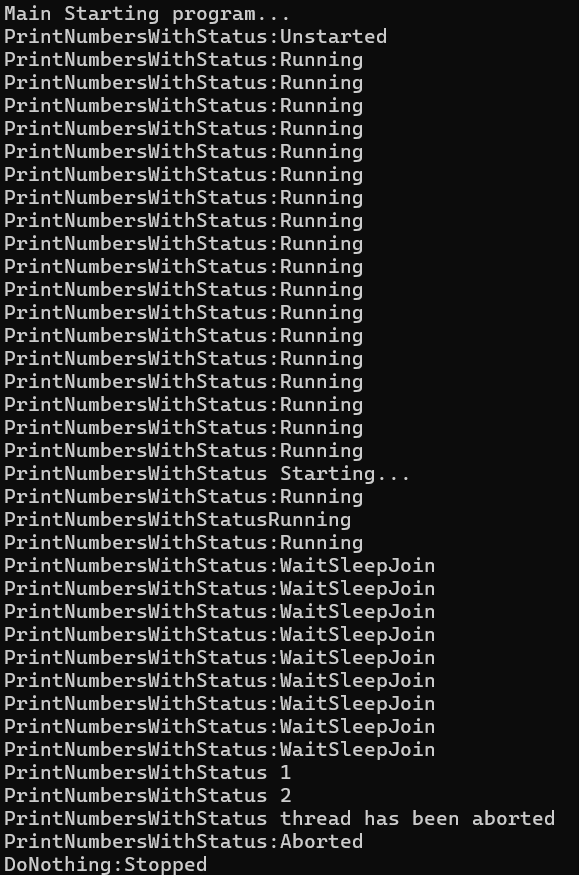
5. 描述一个线程可能会有哪些状态.获取线程是否已经启动或是否处于阻塞状态等(状态位于Thread对象的ThreadState属性中 ThreadState属性是一个C#枚举对象)

1 static void Main(string[] args) 2 { 3 WriteLine("Main Starting program..."); 4 Thread t = new Thread(PrintNumbersWithStatus); 5 Thread t2 = new Thread(DoNothing); 6 WriteLine("PrintNumbersWithStatus:"+t.ThreadState.ToString()); 7 t2.Start(); 8 t.Start(); 9 for (int i = 1; i < 30; i++) 10 { 11 WriteLine("PrintNumbersWithStatus:"+t.ThreadState.ToString()); 12 } 13 Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(6)); 14 t.Abort(); 15 WriteLine("PrintNumbersWithStatus thread has been aborted"); 16 WriteLine("PrintNumbersWithStatus:"+t.ThreadState.ToString()); 17 WriteLine("DoNothing:"+t2.ThreadState.ToString()); 18 Read(); 19 } 20 21 static void DoNothing() 22 { 23 Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); 24 } 25 26 static void PrintNumbersWithStatus() 27 { 28 WriteLine("PrintNumbersWithStatus Starting..."); 29 WriteLine("PrintNumbersWithStatus"+CurrentThread.ThreadState.ToString()); 30 for (int i = 1; i < 10; i++) 31 { 32 Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); 33 WriteLine("PrintNumbersWithStatus "+i); 34 } 35 }
如果拥有一个 以上的计算核心,将在两秒钟内得到初步结果,两个值应该很接近〉然而,如果有其他程序占用了所有的CPU核心运行负载,CPU核心大部分时间在运行高优先级的线程,只留给剩下的线程很少的时间来 运行,为了模拟该情形,我们设置了 ProcessorAffinity选项,止操作系统将所有的线程运 行在单个CPU核心(第一个核心)上。

class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { WriteLine($"Current thread priority: {CurrentThread.Priority}"); WriteLine("Running on all cores available"); RunThreads(); Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); WriteLine("Running on a single core"); GetCurrentProcess().ProcessorAffinity = new IntPtr(1); RunThreads(); } static void RunThreads() { var sample = new ThreadSample(); var threadOne = new Thread(sample.CountNumbers); threadOne.Name = "ThreadOne"; var threadTwo = new Thread(sample.CountNumbers); threadTwo.Name = "ThreadTwo"; threadOne.Priority = ThreadPriority.Highest; threadTwo.Priority = ThreadPriority.Lowest; threadOne.Start(); threadTwo.Start(); Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); sample.Stop(); } class ThreadSample { private bool _isStopped = false; public void Stop() { _isStopped = true; } public void CountNumbers() { long counter = 0; while (!_isStopped) { counter++; } WriteLine($"{CurrentThread.Name} with " + $"{CurrentThread.Priority,11} priority " + $"has a count = {counter,13:N0}"); } } }
7. 前台线程和后台线程(进程会等待所有的前台线程完成后再结束工作,但是如果只剩下后台线程,则会直接结 束工作)

static void Main(string[] args) { var sampleForeground = new ThreadSample(10); var sampleBackground = new ThreadSample(20); var threadOne = new Thread(sampleForeground.CountNumbers); threadOne.Name = "ForegroundThread"; var threadTwo = new Thread(sampleBackground.CountNumbers); threadTwo.Name = "BackgroundThread"; threadTwo.IsBackground = true; threadOne.Start(); threadTwo.Start(); } class ThreadSample { private readonly int _iterations; public ThreadSample(int iterations) { _iterations = iterations; } public void CountNumbers() { for (int i = 0; i < _iterations; i++) { Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(0.5)); WriteLine($"{CurrentThread.Name} prints {i}"); } } }
8. 向线程传递参数

using static System.Threading.Thread; namespace Recipe1 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { //通过ThreadSample对象的构造函数传入,再启动线程 var sample = new ThreadSample(10); var threadOne = new Thread(sample.CountNumbers); threadOne.Name = "ThreadOne"; threadOne.Start(); threadOne.Join(); WriteLine("--------------------------"); //使用Thread.Start方法接收一个对象给线程。必须接受object类型的单个参数 var threadTwo = new Thread(Count); threadTwo.Name = "ThreadTwo"; threadTwo.Start(8); threadTwo.Join(); WriteLine("--------------------------"); //lambda表达式定义了一个不属于任何类的方法。 该方法使用需要的参数调用了另一个方法,并在另一个线程中运行该方法 var threadThree = new Thread(() => CountNumbers(12)); threadThree.Name = "ThreadThree"; threadThree.Start(); threadThree.Join(); WriteLine("--------------------------"); int i = 10; var threadFour = new Thread(() => PrintNumber(i)); i = 20; var threadFive = new Thread(() => PrintNumber(i)); threadFour.Start(); threadFive.Start(); Read(); } static void Count(object iterations) { CountNumbers((int)iterations); } static void CountNumbers(int iterations) { for (int i = 1; i <= iterations; i++) { Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(0.5)); WriteLine($"{CurrentThread.Name} prints {i}"); } } static void PrintNumber(int number) { WriteLine(number); } class ThreadSample { private readonly int _iterations; public ThreadSample(int iterations) { _iterations = iterations; } public void CountNumbers() { for (int i = 1; i <= _iterations; i++) { Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(0.5)); WriteLine($"{CurrentThread.Name} prints {i}"); } } } } }
9. 线程中的锁(产生死锁)
三个线程共享同一个counter实例,在一个周期 中进行一次递增和一次递减。这将导致不确定的结果(这是因为Counter类并不是线程安全的。当多个线程同时访问counter对象时,第一个 线程得到的counter值10并增加为1"然后第二个线程得到的值是11并增加为12。第一个 线程得到counter值12,但是递减操作发生前,第二个线程得到的counter值也是12。然后 第一个线程将12递减为11并保存回counter中,同时第二个线程进行了同样的操作。结果 我们进行了两次递增操作但是只有一次递减操作,这显然不对)
为了确保不会发生以上情形,必须保证当有线程操作counter对象时,所有其他线程必 须等待直到当前线程完成操作。我们可以使用lock关键字来实现这种行为。如果锁定了一个 对象,需要访问该对象的所有其他线程则会处于阻塞状态,并等待直到该对象解除锁定。这 可能会导致严重的性能问题

using System; using System.Threading; using static System.Console; namespace Chapter1.Recipe9 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { WriteLine("Incorrect counter"); var c = new Counter(); var t1 = new Thread(() => TestCounter(c)); var t2 = new Thread(() => TestCounter(c)); var t3 = new Thread(() => TestCounter(c)); t1.Start(); t2.Start(); t3.Start(); t1.Join(); t2.Join(); t3.Join(); WriteLine($"Total count: {c.Count}"); WriteLine("--------------------------"); WriteLine("Correct counter"); var c1 = new CounterWithLock(); t1 = new Thread(() => TestCounter(c1)); t2 = new Thread(() => TestCounter(c1)); t3 = new Thread(() => TestCounter(c1)); t1.Start(); t2.Start(); t3.Start(); t1.Join(); t2.Join(); t3.Join(); WriteLine($"Total count: {c1.Count}"); Read(); } static void TestCounter(CounterBase c) { for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) { c.Increment(); c.Decrement(); } } class Counter : CounterBase { public int Count { get; private set; } public override void Increment() { Count++; } public override void Decrement() { Count--; } } class CounterWithLock : CounterBase { private readonly object _syncRoot = new Object(); public int Count { get; private set; } public override void Increment() { lock (_syncRoot) { Count++; } } public override void Decrement() { lock (_syncRoot) { Count--; } } } abstract class CounterBase { public abstract void Increment(); public abstract void Decrement(); } } }
10. Monitor类锁定资源(避免死锁)
产生死锁的过程:在该方法中我们先锁定了第一个对象,等待一秒后锁定了 第二个对象。然后在另一个线程中启动该方法。最后尝试在主线程中先后锁定第二个和第一 个对象。
如果像该示例的第二部分一样使用lock关键字,将会造成死锁。第一个线程保持对 lockl对象的锁定,等待直到lock2对象被释放。主线程保持对lock2对象的锁定并等待直到 lockl对象被释放,但lockl对象永远不会被释放。
我们可以直接使用Monitor类。其拥有TryEnter方法,该方法接受一个超时参 数。如果在我们能够获取被lock保护的资源之前,超时参数过期,则该方法会返回false

using System; using System.Threading; using static System.Console; using static System.Threading.Thread; namespace Chapter1.Recipe10 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { object lock1 = new object(); object lock2 = new object(); new Thread(() => LockTooMuch(lock1, lock2)).Start(); lock (lock2) { Thread.Sleep(1000); WriteLine("Monitor.TryEnter allows not to get stuck, returning false after a specified timeout is elapsed"); if (Monitor.TryEnter(lock1, TimeSpan.FromSeconds(5))) { WriteLine("Acquired a protected resource succesfully"); } else { WriteLine("Timeout acquiring a resource!"); } } new Thread(() => LockTooMuch(lock1, lock2)).Start(); WriteLine("----------------------------------"); lock (lock2) { WriteLine("This will be a deadlock!"); Sleep(1000); lock (lock1) { WriteLine("Acquired a protected resource succesfully"); } } } static void LockTooMuch(object lock1, object lock2) { lock (lock1) { Sleep(1000); lock (lock2); } } } }
11.线程中处理异常
当主程序启动时,定义了两个将会抛出异常的线程。其中一个对异常进行了处理,另 一个则没有。可以看到第二个异常没有被包裹启动线程的try/catch代码块捕获到。所以 如果直接使用线程,一般来说不要在线程中抛出异常,而是在线程代码中使用try/catch 代码块

using System; using System.Threading; using static System.Console; using static System.Threading.Thread; namespace Chapter1.Recipe11 { class Program { static void Main(string[] args) { var t = new Thread(FaultyThread); t.Start(); t.Join(); try { t = new Thread(BadFaultyThread); t.Start(); } catch (Exception ex) { WriteLine("We won't get here!"); } } static void BadFaultyThread() { WriteLine("Starting a faulty thread..."); Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(2)); throw new Exception("Boom!"); } static void FaultyThread() { try { WriteLine("Starting a faulty thread..."); Sleep(TimeSpan.FromSeconds(1)); throw new Exception("Boom!"); } catch (Exception ex) { WriteLine($"Exception handled: {ex.Message}"); } } } }







【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 【自荐】一款简洁、开源的在线白板工具 Drawnix
· 没有Manus邀请码?试试免邀请码的MGX或者开源的OpenManus吧
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· C#/.NET/.NET Core优秀项目和框架2025年2月简报
· DeepSeek在M芯片Mac上本地化部署