【转载】Java枚举的使用
枚举类型可以取代以往常量的定义方式,即将常量封装在类或接口中。此外,枚举类型还提供了安全检查功能。枚举类型本质上还是以类的形式存在。
1、使用枚举类型设置常量
以往设置常量,通常将常量放置在接口中,这样在程序中就可以直接使用了,并且该常量不能被修改,因为在接口中定义的常量时,该常量的修饰符为final与static。
public interface Constants { public static final int RED = 1; public static final int BLUE = 2; public static final int GREEN = 3; }
使用枚举定义常量的语法如下:
public enum ColorEnum { RED, BLUE, GREEN }
命名规范:
final常量:使用大写字母命名,并且中间使用下划线进行连接。
enum枚举:使用大写字母命名,并且中间使用下划线进行连接。
示例:枚举类型的使用。
public static void doit(ColorEnum c) { switch (c) { case RED: System.out.println("This is RED"); break; case BLUE: System.out.println("This is BLUE"); break; case GREEN: System.out.println("This is GREEN"); break; default: break; } } public static void main(String[] args) { doit(ColorEnum.RED); }
2、深入了解枚举类型
枚举类型较传统定义常量的方式,除了具有参数类型检测的优势之外,还具有其他方面的优势。
2.1 操作枚举类型成员的方法
用户可以将一个枚举类型看作是一个类,它继承于java.lang.Enum类,当定义一个枚举类型时,每一个枚举类型成员都可以看作是枚举类型的一个实例,这些枚举类型成员默认都被final、public、static所修饰,所以当使用枚举类型成员时直接使用枚举类型名称调用枚举类型成员即可。
由于枚举类型对象继承与java.lang.Enum类,所以该类中一些操作枚举类型的方法都可以应用到枚举型中。
枚举类型的常用方法:
方法名称 具体含义 使用方法
values() 该方法可以将枚举类型成员以数组的形式返回 枚举类型名称.values()
valueOf() 该方法可以实现将普通字符串转换为枚举实例 枚举类型名称.valueOf("ABC")
compareTo() 该方法用于比较两个枚举对象在定义时的顺序 枚举对象.compareTo()
ordinal() 该方法用于得到枚举成员的位置索引 枚举对象.ordinal()
(1)values()方法
该方法可以将枚举类型成员以数组的形式返回,也可以通过该方法获取枚举类型的成员。
示例:使用枚举类型中的values()方法获取枚举类型中的成员变量。
/** * 使用枚举类型中的values()方法获取枚举类型中的成员变量 * * @author pan_junbiao * */ public class ShowEnum { enum ColorEnum { RED, BLUE, GREEN } // 循环由values()方法返回的数组 public static void main(String[] args) { System.out.println("方式一:"); for (int i = 0; i < ColorEnum.values().length; i++) { // 将枚举成员变量打印 System.out.println("枚举类型成员变量:" + ColorEnum.values()[i]); } System.out.println("方式二:"); for (ColorEnum c : ColorEnum.values()) { // 将枚举成员变量打印 System.out.println("枚举类型成员变量:" + c); } } }
执行结果:
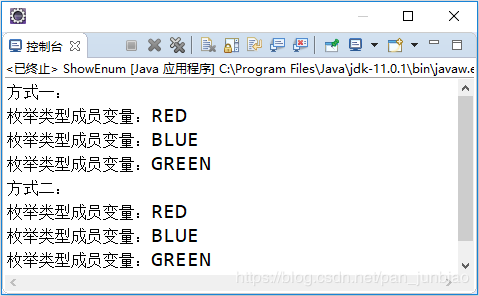
(2)valueOf()与compareTo()方法
枚举类型中静态方法valueOf()可以实现将普通字符串转换为枚举实例,而compareTo()方法用于比较两个枚举对象在定义时的顺序。
示例:枚举中valueOf()与compareTo()方法的使用。
/** * 枚举中valueOf()与compareTo()方法的使用 * * @author pan_junbiao * */ public class EnumMethodTest { enum ColorEnum { RED, BLUE, GREEN } // 定义比较枚举类型方法,参数类型为枚举类型 public static void compare(ColorEnum c) { // 根据values()方法返回的数组做循环操作 for (int i = 0; i < ColorEnum.values().length; i++) { // 将比较结果返回 System.out.println(c + "与" + ColorEnum.values()[i] + "的比较结果为:" + c.compareTo(ColorEnum.values()[i])); } } public static void main(String[] args) { // 使用valueOf()将字符串转换为枚举实例 ColorEnum c = ColorEnum.valueOf("BLUE"); compare(c); } }
执行结果:
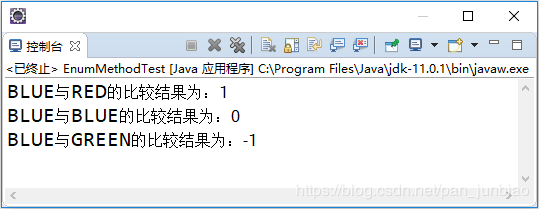
说明:调用compareTo()方法返回的结果,正值代表方法中的参数在调用该方法的枚举对象位置之前;0代表两个相互比较的枚举成员的位置相同;负值代表方法中参数在调用该方法的枚举对象位置之后。
(3)ordinal()方法
该方法用于得到枚举成员的位置索引。
示例:枚举中ordinal()方法的使用。
/** * 枚举中ordinal()方法的使用 * * @author pan_junbiao * */ public class EnumOrdinalTest { public enum ColorEnum { RED, BLUE, GREEN } public static void main(String[] args) { for (int i = 0; i < ColorEnum.values().length; i++) { // 在循环中获取枚举类型成员的索引位置 System.out.println(ColorEnum.values()[i] + "在枚举类型中位置索引值" + ColorEnum.values()[i].ordinal()); } } }
执行结果:

2.2 枚举类型中的构造方法
在枚举类型中,可以添加构造方法,但是规定这个构造方法必须为private修饰符修饰。
示例:在枚举类型中,可以添加构造方法。
/** * 在枚举类型中添加构造方法 * * @author pan_junbiao * */ public class EnumIndexTest { enum ColorEnum { RED(1, "我是红色"), BLUE(2, "我是蓝色"), GREEN(3, "我是绿色"); private final int value; private final String description; private ColorEnum(int value, String description) { this.value = value; this.description = description; } public int getValue() { return this.value; } public String getDescription() { return this.description; } public static ColorEnum valueOf(int value) { switch (value) { case 1: return ColorEnum.RED; case 2: return ColorEnum.BLUE; case 3: return ColorEnum.GREEN; default: return null; } } } public static void main(String[] args) { for (ColorEnum c : ColorEnum.values()) { System.out.println("枚举成员:" + c + " 值:" + c.getValue() + " 描述:" + c.getDescription()); } System.out.println("值转换成枚举:" + ColorEnum.valueOf(2)); System.out.println("字符串转换成枚举:" + ColorEnum.valueOf("GREEN")); } }
执行结果:

2.3 枚举中实现接口
除了可以使用上述示例的方法定义getDescription()方法获取枚举类型成员变量是的描述之外,还可以将这个getDescription()方法放置在接口中,使枚举类型实现接口,然后使每个枚举类型实现接口中的方法。
示例:在项目中创建d接口和枚举类型的AnyEnum类,在枚举类型AnyEnum类中实现带方法的接口,使每个枚举类型成员实现该接口中的方法。
interface d { public int getValue(); public String getDescription(); } /** * 枚举中实现接口 * * @author pan_junbiao * */ public enum AnyEnum implements d { RED { public int getValue() { return 1; } public String getDescription() { return "我是红色"; } }, BLUE { public int getValue() { return 2; } public String getDescription() { return "我是蓝色"; } }, GREEN { public int getValue() { return 3; } public String getDescription() { return "我是绿色"; } }; public static void main(String[] args) { for (AnyEnum c : AnyEnum.values()) { System.out.println("枚举成员:" + c + " 值:" + c.getValue() + " 描述:" + c.getDescription()); } } }
执行结果:
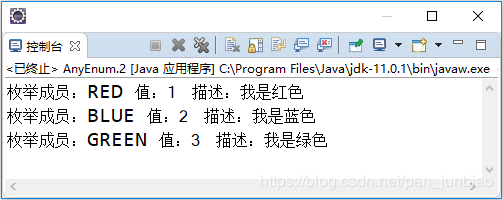
3、使用枚举类型的优势
枚举类型声明提供了一种用户友好的变量定义方法,枚举了某种数据类型所有可能出现的值。总结枚举类型,它具有以下特点:
(1)类型安全。
(2)紧凑有效的数据定义。
(3)可以和程序其他部分完美交互。
(4)运行效率高。
---------------------
作者:pan_junbiao
来源:CSDN
原文:https://blog.csdn.net/pan_junbiao/article/details/85257445
版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,转载请附上博文链接!


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号