TensorFlow HOWTO 2.3 支持向量分类(高斯核)
遇到非线性可分的数据集时,我们需要使用核方法,但为了使用核方法,我们需要返回到拉格朗日对偶的推导过程,不能简单地使用 Hinge 损失。
操作步骤
导入所需的包。
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import matplotlib as mpl
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import sklearn.datasets as ds
import sklearn.model_selection as ms
为了展示非线性可分的数据集,我们需要把它创建出来。依旧把标签变成 1 和 -1,原标签为 0 的样本标签为 1。
circles = ds.make_circles(n_samples=500, factor=0.5, noise=0.1)
x_ = circles[0]
y_ = (circles[1] == 0).astype(int)
y_[y_ == 0] = -1
y_ = np.expand_dims(y_ , 1)
x_train_, x_test_, y_train_, y_test_ = \
ms.train_test_split(x_, y_, train_size=0.7, test_size=0.3
定义超参数。
| 变量 | 含义 |
|---|---|
n_batch | 样本批量大小 |
n_input | 样本特征数 |
n_epoch | 迭代数 |
lr | 学习率 |
gamma | 高斯核系数 |
n_batch = len(x_train_)
n_input = 2
n_epoch = 2000
lr = 0.05
gamma = 10
搭建模型。首先定义占位符(数据)和变量(模型参数)。
由于模型参数a和样本x是对应的,不像之前的w, b那样和类别对应,所以需要传入批量大小。并且在预测时,也需要训练集,所以在计算图中,要把训练集和测试集分开。
| 变量 | 含义 |
|---|---|
x_train | 输入,训练集的特征 |
y_train | 训练集的真实标签 |
a | 模型参数 |
x_train = tf.placeholder(tf.float64, [n_batch, n_input])
y_train = tf.placeholder(tf.float64, [n_batch, 1])
a = tf.Variable(np.random.rand(n_batch, 1))
定义高斯核。由于高斯核函数是个相对独立,又反复调用的东西,把它写成函数抽象出来。
它的定义是这样的:
exp
(
−
γ
∥
x
−
y
∥
2
)
\exp(- \gamma \|x - y\|^2)
exp(−γ∥x−y∥2),x和y是两个向量。
但在这里,我们要为两个矩阵的每一行计算这个函数,用了一些小技巧。(待补充)
def rbf_kernel(x, y, gamma):
x_3d_i = tf.expand_dims(x, 1)
y_3d_j = tf.expand_dims(y, 0)
kernel = tf.reduce_sum((x_3d_i - y_3d_j) ** 2, 2)
kernel = tf.exp(- gamma * kernel)
return kernel
kernel = rbf_kernel(x_train, x_train, gamma)
定义损失。我们使用的损失为:
1 n ( ∑ i , j a i a j y ( i ) y ( j ) K ( x ( i ) , x ( j ) ) − ∑ i a i ) \frac{1}{n} \big(\sum_{i,j}a_i a_j y^{(i)}y^{(j)}K(x^{(i)},x^{(j)}) - \sum_i a_i \big) n1(∑i,jaiajy(i)y(j)K(x(i),x(j))−∑iai)
这个公式的来历请见扩展阅读的第一个链接。
| 变量 | 含义 |
|---|---|
loss | 损失 |
op | 优化操作 |
a_cross = a * tf.transpose(a)
y_cross = y_train * tf.transpose(y_train)
loss = tf.reduce_sum(a_cross * y_cross * kernel)
loss -= tf.reduce_sum(a)
loss /= n_batch
op = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(lr).minimize(loss)
定义度量指标。我们在测试集上计算它,为此,我们在计算图中定义测试集。
| 变量 | 含义 |
|---|---|
x_test | 测试集的特征 |
y_test | 测试集的真实标签 |
y_hat | 标签的预测值 |
x_test = tf.placeholder(tf.float64, [None, n_input])
y_test = tf.placeholder(tf.float64, [None, 1])
kernel_pred = rbf_kernel(x_train, x_test, gamma)
y_hat = tf.transpose(kernel_pred) @ (y_train * a)
y_hat = tf.sign(y_hat - tf.reduce_mean(y_hat))
acc = tf.reduce_mean(tf.to_double(tf.equal(y_hat, y_test)))
使用训练集训练模型。
losses = []
accs = []
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
for e in range(n_epoch):
_, loss_ = sess.run([op, loss], feed_dict={x_train: x_train_, y_train: y_train_})
losses.append(loss_)
使用训练集和测试集计算准确率。
acc_ = sess.run(acc, feed_dict={x_train: x_train_, y_train: y_train_, x_test: x_test_, y_test: y_test_})
accs.append(acc_)
每一百步打印损失和度量值。
if e % 100 == 0:
print(f'epoch: {e}, loss: {loss_}, acc: {acc_}')
得到决策边界:
x_plt = x_[:, 0]
y_plt = x_[:, 1]
c_plt = y_.ravel()
x_min = x_plt.min() - 1
x_max = x_plt.max() + 1
y_min = y_plt.min() - 1
y_max = y_plt.max() + 1
x_rng = np.arange(x_min, x_max, 0.05)
y_rng = np.arange(y_min, y_max, 0.05)
x_rng, y_rng = np.meshgrid(x_rng, y_rng)
model_input = np.asarray([x_rng.ravel(), y_rng.ravel()]).T
model_output = sess.run(y_hat, feed_dict={x_train: x_train_, y_train: y_train_, x_test: model_input}).astype(int)
c_rng = model_output.reshape(x_rng.shape)
输出:
epoch: 0, loss: 3.71520431509184, acc: 0.9666666666666667
epoch: 100, loss: -0.0727806862453766, acc: 0.9733333333333334
epoch: 200, loss: -0.1344057865226747, acc: 0.9666666666666667
epoch: 300, loss: -0.19954100171678735, acc: 0.9666666666666667
epoch: 400, loss: -0.26744944765154044, acc: 0.9666666666666667
epoch: 500, loss: -0.3376130527328746, acc: 0.9666666666666667
epoch: 600, loss: -0.40968204759135396, acc: 0.9666666666666667
epoch: 700, loss: -0.48337264821214987, acc: 0.9666666666666667
epoch: 800, loss: -0.5584322960888252, acc: 0.9666666666666667
epoch: 900, loss: -0.634641530183908, acc: 0.9666666666666667
epoch: 1000, loss: -0.7118203254530981, acc: 0.9666666666666667
epoch: 1100, loss: -0.7898283716352298, acc: 0.9666666666666667
epoch: 1200, loss: -0.8685602440121085, acc: 0.9666666666666667
epoch: 1300, loss: -0.9479390005125, acc: 0.9666666666666667
epoch: 1400, loss: -1.02791046598349, acc: 0.9666666666666667
epoch: 1500, loss: -1.1084388930145652, acc: 0.9666666666666667
epoch: 1600, loss: -1.1895038125649773, acc: 0.9666666666666667
epoch: 1700, loss: -1.2710975807209766, acc: 0.9666666666666667
epoch: 1800, loss: -1.3532232661574393, acc: 0.9666666666666667
epoch: 1900, loss: -1.4358926633795104, acc: 0.9733333333333334
绘制整个数据集以及决策边界。
plt.figure()
cmap = mpl.colors.ListedColormap(['r', 'b'])
plt.scatter(x_plt, y_plt, c=c_plt, cmap=cmap)
plt.contourf(x_rng, y_rng, c_rng, alpha=0.2, linewidth=5, cmap=cmap)
plt.title('Data and Model')
plt.xlabel('x')
plt.ylabel('y')
plt.show()
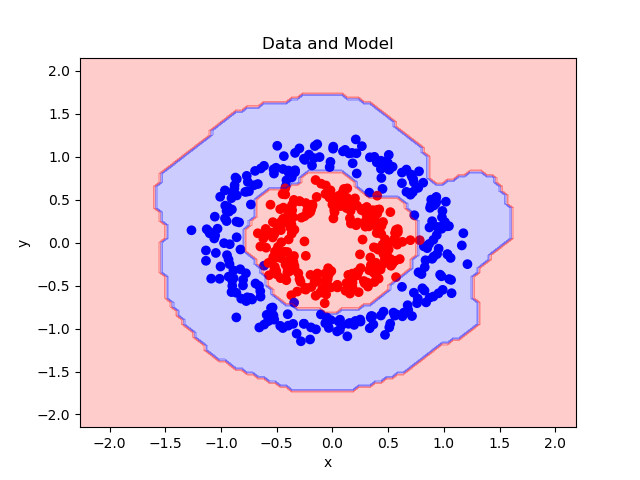
绘制训练集上的损失。
plt.figure()
plt.plot(losses)
plt.title('Loss on Training Set')
plt.xlabel('#epoch')
plt.ylabel('SVM Loss')
plt.show()
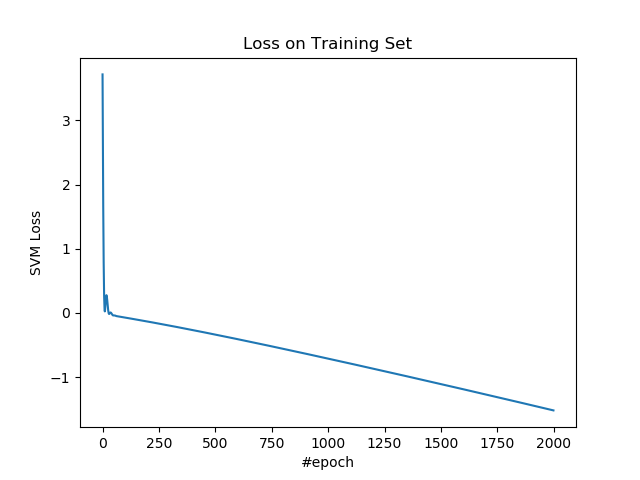
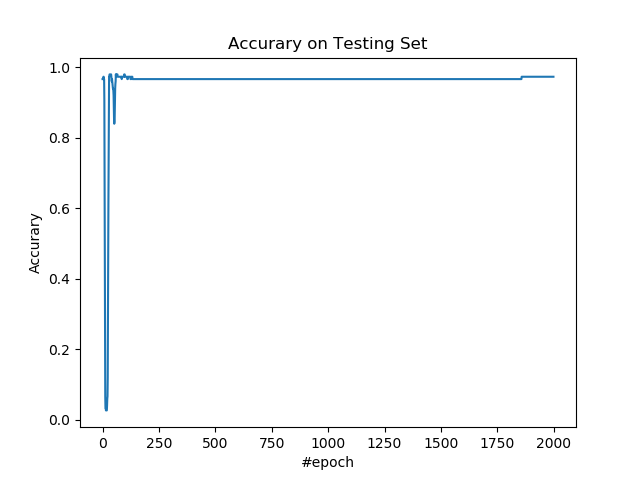
绘制测试集上的准确率。
plt.figure()
plt.plot(accs)
plt.title('Accurary on Testing Set')
plt.xlabel('#epoch')
plt.ylabel('Accurary')
plt.show()
扩展阅读




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号