k8s核心的一些资源和概念
Kubernetes Components
https://kubernetes.io/docs/concepts/overview/components/
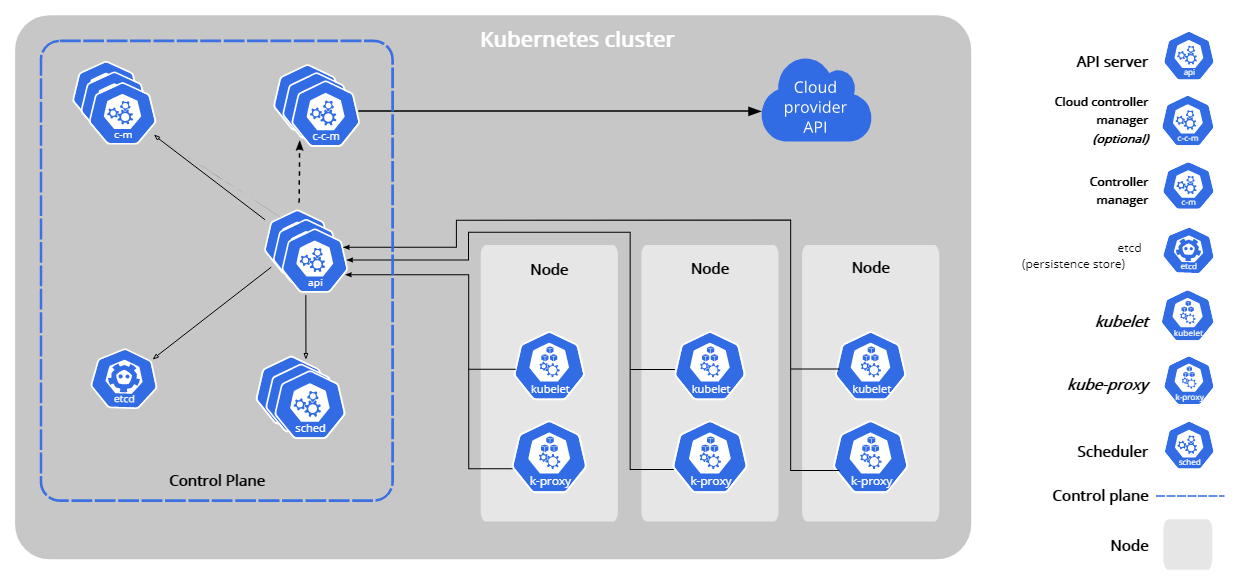
Control Plane Components |
||
kube-apiserver |
Kubernetes API 服务器验证并配置 API 对象的数据, 这些对象包括 pods、services、replicationcontrollers 等。 API 服务器为 REST 操作提供服务,并为集群的共享状态提供前端, 所有其他组件都通过该前端进行交互。 |
|
etcd |
||
kube-scheduler |
The Kubernetes scheduler is a control plane process which assigns Pods to Nodes. The scheduler determines which Nodes are valid placements for each Pod in the scheduling queue according to constraints and available resources. The scheduler then ranks each valid Node and binds the Pod to a suitable Node. Multiple different schedulers may be used within a cluster; kube-scheduler is the reference implementation. See scheduling for more information about scheduling and the kube-scheduler component. |
|
kube-controller-manager |
The Kubernetes controller manager is a daemon that embeds the core control loops shipped with Kubernetes. In applications of robotics and automation, a control loop is a non-terminating loop that regulates the state of the system. In Kubernetes, a controller is a control loop that watches the shared state of the cluster through the apiserver and makes changes attempting to move the current state towards the desired state. Examples of controllers that ship with Kubernetes today are the replication controller, endpoints controller, namespace controller, and serviceaccounts controller. |
|
cloud-controller-manager |
||
Node Components |
NodesKubernetes runs your workload by placing containers into Pods to run on Nodes. A node may be a virtual or physical machine, Typically you have several nodes in a cluster; in a learning or resource-limited environment, you might have only one node. The components on a node include the kubelet, a container runtime, and the kube-proxy |
|
kubelet |
The kubelet is the primary "node agent" that runs on each node. It can register the node with the apiserver using one of: the hostname; a flag to override the hostname; or specific logic for a cloud provider. |
|
kube-proxy |
||
Container runtime |
||
Addons |
||
DNS |
||
Web UI (Dashboard) |
||
Container Resource Monitoring |
||
Cluster-level Logging |
Kubernetes API
Kubernetes API |
||
workload-resources |
工作负载资源 |
工作负载是在 Kubernetes 上运行的应用程序。
无论你的负载是单一组件还是由多个一同工作的组件构成,在 Kubernetes 中你 可以在一组 Pods 中运行它。 //我们可以简单认为工作负载资源就是组件的集合,包括单一组件也称为工作负载资源 |
Service Resources |
Service 资源 |
service是运行在一组 Pods 上的应用程序公开为网络服务的抽象方法。
使用 Kubernetes,你无需修改应用程序即可使用不熟悉的服务发现机制。 Kubernetes Service 定义了这样一种抽象:逻辑上的一组 Pod,一种可以访问它们的策略 —— 通常称为微服务。 |
Config and Storage Resources |
配置和存储资源 |
卷 持久卷 投射卷 临时卷 存储类 动态卷供应 卷快照 卷快照类 CSI 卷克隆 存储容量 卷健康监测 特定于节点的卷数限制 |
Authentication Resources |
身份认证资源 |
|
Authorization Resources |
鉴权资源 |
|
Policy Resources |
策略资源 |
|
Extend Resources |
扩展资源 |
|
Extend Resources |
集群资源 |
|
Common Definitions |
公共定义 |
|
Common Parameters |
常用参数 |
工作负载资源(controllers)
| controllers | ||
|
|
一个 Deployment 为 Pod 和 ReplicaSet 提供声明式的更新能力,负责描述 Deployment 中的 目标状态, 而 Deployment 控制器(Controller) 以受控速率更改实际状态, 使其变为期望状态。你可以定义 Deployment 以创建新的 ReplicaSet, 或删除现有 Deployment, 并通过新的 Deployment 收养其资源。 |
|
|
|
ReplicaSet 的目的是维护一组在任何时候都处于运行状态的 Pod 副本的稳定集合。 因此,它通常用来保证给定数量的、完全相同的 Pod 的可用性 | |
|
|
StatefulSet 是用来管理有状态应用的工作负载 API 对象,StatefulSet 用来管理某 Pod 集合的部署和扩缩, 并为这些 Pod 提供持久存储和持久标识符。 | |
|
|
DaemonSet 确保全部(或者某些)节点上运行一个 Pod 的副本。 当有节点加入集群时, 也会为他们新增一个 Pod 。 当有节点从集群移除时,这些 Pod 也会被回收。删除 DaemonSet 将会删除它创建的所有 Pod。 |
|
|
|
Job 会创建一个或者多个 Pods,并将继续重试 Pods 的执行,直到指定数量的 Pods 成功终止。 随着 Pods 成功结束,Job 跟踪记录成功完成的 Pods 个数。 当数量达到指定的成功个数阈值时,任务(即 Job)结束。 删除 Job 的操作会清除所创建的全部 Pods。 挂起 Job 的操作会删除 Job 的所有活跃 Pod,直到 Job 被再次恢复执行。 |
|
|
|
TTL-after-finished 控制器 提供了一种 TTL 机制来限制已完成执行的资源对象的生命周期。 TTL 控制器目前只处理 Job | |
|
|
一个 CronJob 对象就像 crontab (cron table) 文件中的一行。 它用 Cron 格式进行编写, 并周期性地在给定的调度时间执行 Job。 | |
|
|
ReplicationController 确保在任何时候都有特定数量的 Pod 副本处于运行状态。 换句话说,ReplicationController 确保一个 Pod 或一组同类的 Pod 总是可用的 | |
组件工具
特性门控 |
||
kubelet |
The kubelet is the primary "node agent" that runs on each node. It can register the node with the apiserver using one of: The kubelet works in terms of a PodSpec. A PodSpec is a YAML or JSON object that describes a pod. Other than from a PodSpec from the apiserver, there are three ways that a container manifest can be provided to the Kubelet.
|
|
kube-apiserver |
Kubernetes API server(kube-apiserver)验证并配置 API object的数据, 这些objects包括 pods、services、replicationcontrollers 等。 API server(kube-apiserver)为 REST 操作提供服务,并为集群的共享状态提供前端, 所有其他组件都通过该前端进行交互。 |
|
kube-controller-manager |
kube-controller-manager是一个守护进程,内嵌随 Kubernetes 一起发布的核心控制回路。 在机器人和自动化的应用中,控制回路是一个永不休止的循环,用于调节系统状态。在 Kubernetes 中,每个控制器(controller,参看controllers)是一个控制回路,通过 API 服务器(kube-apiserver)监视集群的共享状态, 并尝试进行更改以将当前状态转为期望状态。 目前,Kubernetes 自带的控制器例子包括 replication controller、endpoints controller、namespace controller和serviceaccounts controller等。 |
|
kube-proxy |
Kubernetes 网络代理在每个节点上运行。网络代理反映了每个节点上 Kubernetes API 中定义的服务, 并且可以执行简单的 TCP、UDP 和 SCTP 流转发,或者在一组后端进行 循环 TCP、UDP 和 SCTP 转发。 当前可通过 Docker-links-compatible 环境变量找到服务集群 IP 和端口, 这些环境变量指定了服务代理打开的端口。 有一个可选的插件,可以为这些集群 IP 提供集群 DNS。 用户必须使用 apiserver API 创建服务才能配置代理。 |
|
kube-scheduler |
kube-scheduler是一个控制面进程,负责将 Pods 指派到节点上。 调度器基于约束和可用资源为调度队列中每个 Pod 确定其可合法放置的节点。调度器之后对所有合法的节点进行排序,将 Pod 绑定到一个合适的节点。 在同一个集群中可以使用多个不同的调度器; kube-scheduler 是其参考实现。 参阅调度 以获得关于调度和 kube-scheduler 组件的更多信息。 |
|
Kubelet 认证/鉴权 |
||
TLS 启动引导 |
||
Cluster Administration(集群管理)
| 证书 | To learn how to generate certificates for your cluster, see Certificates. | |
| 管理资源 | You've deployed your application and exposed it via a service. Now what? Kubernetes provides a number of tools to help you manage your application deployment, including scaling and updating. Among the features that we will discuss in more depth are configuration files and labels. |
|
| 集群网络系统 | Networking is a central part of Kubernetes, but it can be challenging to understand exactly how it is expected to work. There are 4 distinct networking problems to address: |
|
| Kubernetes 系统组件指标 |
|
|
| 日志架构 |
Logging Architecture Application logs can help you understand what is happening inside your application. |
|
| 系统日志 |
System LogsSystem component logs record events happening in cluster, which can be very useful for debugging. |
|
| 追踪 Kubernetes 系统组件 |
Metrics For Kubernetes System ComponentsSystem component metrics can give a better look into what is happening inside them. |
|
| Kubernetes 中的代理 | There are several different proxies you may encounter when using Kubernetes: 1. kubectl proxy 2.apiserver proxy: 3.kube proxy: 4.A Proxy/Load-balancer in front of apiserver(s): 5.Cloud Load Balancers on external services: Kubernetes users will typically not need to worry about anything other than the first two types. The cluster admin will typically ensure that the latter types are setup correctly |
|
| API 优先级和公平性 |
API Priority and FairnessControlling the behavior of the Kubernetes API server in an overload situation is a key task for cluster administrators.The kube-apiserver has some controls available (i.e. the --max-requests-inflight and --max-mutating-requests-inflight command-line flags) to limit the amount of outstanding work that will be accepted, preventing a flood of inbound requests from overloading and potentially crashing the API server, but these flags are not enough to ensure that the most important requests get through in a period of high traffic. |
|
| 安装扩展(Addons) |
Installing AddonsAdd-ons extend the functionality of Kubernetes. |
Kubernetes 网络解决四方面的问题:
- 一个 Pod 中的容器之间通过本地回路(loopback)通信。
- 集群网络在不同 pod 之间提供通信。
- Service 资源允许你 对外暴露 Pods 中运行的应用程序, 以支持来自于集群外部的访问。
- 可以使用 Services 来发布仅供集群内部使用的服务。




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(六):基于图像分类模型对图像进行分类