重新整理 .net core 实践篇—————配置系统之间谍[八](文件监控)
前言
前文提及到了当我们的配置文件修改了,那么从 configurationRoot 在此读取会读取到新的数据,本文进行扩展,并从源码方面简单介绍一下,下面内容和前面几节息息相关。
正文
先看一下,如果文件修改,那么是否有一个回调函数,可以回调呢?
答案是有的:
IChangeToken IConfiguration.GetReloadToken()
这里演示一下:
IConfigurationBuilder builder = new ConfigurationBuilder();
builder.AddJsonFile(System.AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory + "/appsettings.json",optional:false,reloadOnChange: true);
var configurationRoot = builder.Build();
Console.WriteLine(configurationRoot["key1"]);
Console.WriteLine(configurationRoot["key2"]);
IChangeToken token = configurationRoot.GetReloadToken();
token.RegisterChangeCallback(state =>
{
Console.WriteLine(configurationRoot["key1"]);
Console.WriteLine(configurationRoot["key2"]);
},configurationRoot);
Console.ReadKey();
一开始的值是:
{
"key1": "value1",
"key2": "value2"
}
然后我进行了修改:
{
"key1": "value1_change",
"key2": "value2_change"
}
结果如下:
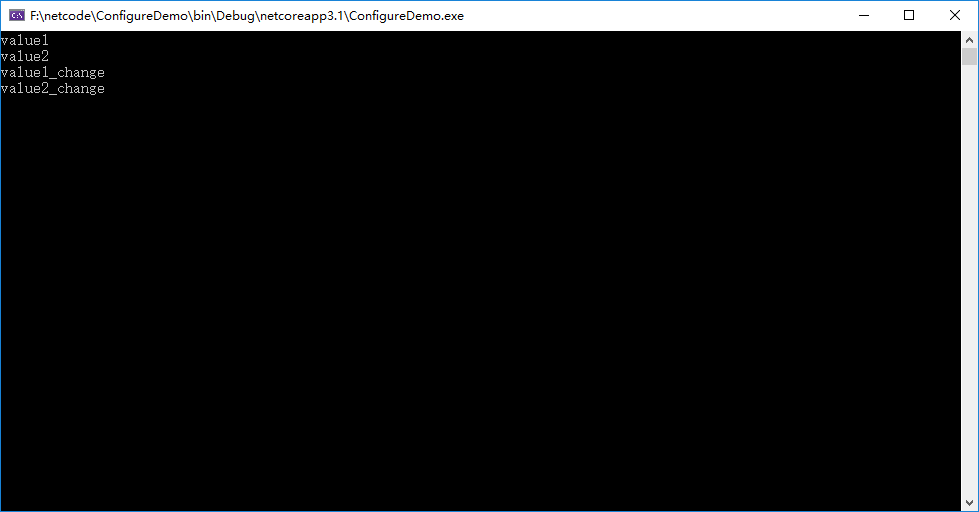
源码解读一下为什么这么做,因为在我们写代码中,这种监听场景比较常见,这里就以此为例。
如果下文如果感到有点不适,请先看一下这个:https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-cn/aspnet/core/fundamentals/change-tokens?view=aspnetcore-3.1
private readonly IList<IDisposable> _changeTokenRegistrations;
private ConfigurationReloadToken _changeToken = new ConfigurationReloadToken();
public ConfigurationRoot(IList<IConfigurationProvider> providers)
{
if (providers == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(providers));
}
_providers = providers;
_changeTokenRegistrations = new List<IDisposable>(providers.Count);
foreach (IConfigurationProvider p in providers)
{
p.Load();
_changeTokenRegistrations.Add(ChangeToken.OnChange(() => p.GetReloadToken(), () => RaiseChanged()));
}
}
private void RaiseChanged()
{
ConfigurationReloadToken previousToken = Interlocked.Exchange(ref _changeToken, new ConfigurationReloadToken());
previousToken.OnReload();
}
在ConfigurationRoot实例化的时候就为每一个provider 注册了监听事件,同时定义了回调事件。
然后看一下GetReloadToken:
/// <summary>
/// Returns a <see cref="IChangeToken"/> that can be used to observe when this configuration is reloaded.
/// </summary>
/// <returns>The <see cref="IChangeToken"/>.</returns>
public IChangeToken GetReloadToken() => _changeToken;
这里返回了ConfigurationReloadToken,也就是获取到监听对象,故而我们能够被回调。
https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-cn/aspnet/core/fundamentals/change-tokens?view=aspnetcore-3.1 中解释的比较详细故而不过多赘述。
那么就来看下json配置文件的Provider,看下其为啥能够这么监听。
public class JsonConfigurationProvider : FileConfigurationProvider
{
/// <summary>
/// Initializes a new instance with the specified source.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="source">The source settings.</param>
public JsonConfigurationProvider(JsonConfigurationSource source) : base(source) { }
/// <summary>
/// Loads the JSON data from a stream.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="stream">The stream to read.</param>
public override void Load(Stream stream)
{
try
{
Data = JsonConfigurationFileParser.Parse(stream);
}
catch (JsonException e)
{
throw new FormatException(SR.Error_JSONParseError, e);
}
}
}
上面的操作_changeTokenRegistrations.Add(ChangeToken.OnChange(() => p.GetReloadToken(), () => RaiseChanged())); 就能解释的通了,原理是利用文件系统的GetReloadToken()令牌,
只是在FileConfigurationProvider 上封装了一层转换。
简单看下:FileConfigurationProvider,下面值保留了Load部分。
public abstract class FileConfigurationProvider : ConfigurationProvider, IDisposable
{
private void Load(bool reload)
{
IFileInfo file = Source.FileProvider?.GetFileInfo(Source.Path);
if (file == null || !file.Exists)
{
if (Source.Optional || reload) // Always optional on reload
{
Data = new Dictionary<string, string>(StringComparer.OrdinalIgnoreCase);
}
else
{
var error = new StringBuilder($"The configuration file '{Source.Path}' was not found and is not optional.");
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(file?.PhysicalPath))
{
error.Append($" The physical path is '{file.PhysicalPath}'.");
}
HandleException(ExceptionDispatchInfo.Capture(new FileNotFoundException(error.ToString())));
}
}
else
{
// Always create new Data on reload to drop old keys
if (reload)
{
Data = new Dictionary<string, string>(StringComparer.OrdinalIgnoreCase);
}
static Stream OpenRead(IFileInfo fileInfo)
{
if (fileInfo.PhysicalPath != null)
{
// The default physical file info assumes asynchronous IO which results in unnecessary overhead
// especally since the configuration system is synchronous. This uses the same settings
// and disables async IO.
return new FileStream(
fileInfo.PhysicalPath,
FileMode.Open,
FileAccess.Read,
FileShare.ReadWrite,
bufferSize: 1,
FileOptions.SequentialScan);
}
return fileInfo.CreateReadStream();
}
using Stream stream = OpenRead(file);
try
{
Load(stream);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
HandleException(ExceptionDispatchInfo.Capture(e));
}
}
// REVIEW: Should we raise this in the base as well / instead?
OnReload();
}
/// <summary>
/// Loads the contents of the file at <see cref="Path"/>.
/// </summary>
/// <exception cref="FileNotFoundException">If Optional is <c>false</c> on the source and a
/// file does not exist at specified Path.</exception>
public override void Load()
{
Load(reload: false);
}
}
看下上面的load,上面的load就是读取文件,然后交由JsonConfigurationProvider 的load调用 Data = JsonConfigurationFileParser.Parse(stream);转换为字典。
这就是为上文中的ConfigurationRoot 要调用一下load了。
上文的ConfigurationRoot 调用Load 部分。
foreach (IConfigurationProvider p in providers)
{
p.Load();
_changeTokenRegistrations.Add(ChangeToken.OnChange(() => p.GetReloadToken(), () => RaiseChanged()));
}
这就回到了对前面系列中的内存字典操作了,而FileConfigurationProvider 又继承ConfigurationProvider。
ConfigurationProvider 代码如下,主要是实现IConfigurationProvider接口,很多不同的文件配置都会用到这个,比如说ini文件、xml文件等等都会先转换为字典,然后继承ConfigurationProvider:
public abstract class ConfigurationProvider : IConfigurationProvider
{
private ConfigurationReloadToken _reloadToken = new ConfigurationReloadToken();
/// <summary>
/// Initializes a new <see cref="IConfigurationProvider"/>
/// </summary>
protected ConfigurationProvider()
{
Data = new Dictionary<string, string>(StringComparer.OrdinalIgnoreCase);
}
/// <summary>
/// The configuration key value pairs for this provider.
/// </summary>
protected IDictionary<string, string> Data { get; set; }
/// <summary>
/// Attempts to find a value with the given key, returns true if one is found, false otherwise.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="key">The key to lookup.</param>
/// <param name="value">The value found at key if one is found.</param>
/// <returns>True if key has a value, false otherwise.</returns>
public virtual bool TryGet(string key, out string value)
=> Data.TryGetValue(key, out value);
/// <summary>
/// Sets a value for a given key.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="key">The configuration key to set.</param>
/// <param name="value">The value to set.</param>
public virtual void Set(string key, string value)
=> Data[key] = value;
/// <summary>
/// Loads (or reloads) the data for this provider.
/// </summary>
public virtual void Load()
{ }
/// <summary>
/// Returns the list of keys that this provider has.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="earlierKeys">The earlier keys that other providers contain.</param>
/// <param name="parentPath">The path for the parent IConfiguration.</param>
/// <returns>The list of keys for this provider.</returns>
public virtual IEnumerable<string> GetChildKeys(
IEnumerable<string> earlierKeys,
string parentPath)
{
string prefix = parentPath == null ? string.Empty : parentPath + ConfigurationPath.KeyDelimiter;
return Data
.Where(kv => kv.Key.StartsWith(prefix, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase))
.Select(kv => Segment(kv.Key, prefix.Length))
.Concat(earlierKeys)
.OrderBy(k => k, ConfigurationKeyComparer.Instance);
}
private static string Segment(string key, int prefixLength)
{
int indexOf = key.IndexOf(ConfigurationPath.KeyDelimiter, prefixLength, StringComparison.OrdinalIgnoreCase);
return indexOf < 0 ? key.Substring(prefixLength) : key.Substring(prefixLength, indexOf - prefixLength);
}
/// <summary>
/// Returns a <see cref="IChangeToken"/> that can be used to listen when this provider is reloaded.
/// </summary>
/// <returns>The <see cref="IChangeToken"/>.</returns>
public IChangeToken GetReloadToken()
{
return _reloadToken;
}
/// <summary>
/// Triggers the reload change token and creates a new one.
/// </summary>
protected void OnReload()
{
ConfigurationReloadToken previousToken = Interlocked.Exchange(ref _reloadToken, new ConfigurationReloadToken());
previousToken.OnReload();
}
/// <summary>
/// Generates a string representing this provider name and relevant details.
/// </summary>
/// <returns> The configuration name. </returns>
public override string ToString() => $"{GetType().Name}";
}
上述就是这个框架实现文件配置和文件监控的大致原理了。
这里再梳理一遍,使用JsonConfigurationFileParser.Parse 将steam流转换成字典,利用ChangeToken 对文件进行监听,如果有修改从加载即可。
好了,看完原理后,我们发现是ChangeToken的监听机制。那么问题来了,如果你看过上述ChangeToken的链接,你会发现RegisterChangeCallback只会调用一次。
原理很简单,因为这是令牌机制的,令牌过期了,那么这个RegisterChangeCallback自然调用一次,因为过期只有一次。
我们可以无限套娃方式:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
IConfigurationBuilder builder = new ConfigurationBuilder();
// builder.AddJsonFile(System.AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory + "/appsettings.dev.json", optional: false, reloadOnChange: true);
builder.AddJsonFile(System.AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory + "/appsettings.json",optional:false,reloadOnChange: true);
var configurationRoot = builder.Build();
Console.WriteLine(configurationRoot["key1"]);
Console.WriteLine(configurationRoot["key2"]);
Register(configurationRoot);
Console.ReadKey();
}
public static void Register(IConfigurationRoot configurationRoot)
{
IChangeToken token = configurationRoot.GetReloadToken();
token.RegisterChangeCallback(state =>
{
Console.WriteLine(configurationRoot["key1"]);
Console.WriteLine(configurationRoot["key2"]);
Register(configurationRoot);
}, configurationRoot);
}
也可以这么做,利用ChangeToken 本身的方法:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
IConfigurationBuilder builder = new ConfigurationBuilder();
// builder.AddJsonFile(System.AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory + "/appsettings.dev.json", optional: false, reloadOnChange: true);
builder.AddJsonFile(System.AppDomain.CurrentDomain.BaseDirectory + "/appsettings.json",optional:false,reloadOnChange: true);
var configurationRoot = builder.Build();
Console.WriteLine(configurationRoot["key1"]);
Console.WriteLine(configurationRoot["key2"]);
ChangeToken.OnChange(configurationRoot.GetReloadToken, () =>
{
Console.WriteLine(configurationRoot["key1"]);
Console.WriteLine(configurationRoot["key2"]);
});
Console.ReadKey();
}
这里OnChange的原理也是套娃,我把关键代码贴一下。
public static class ChangeToken
{
/// <summary>
/// Registers the <paramref name="changeTokenConsumer"/> action to be called whenever the token produced changes.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="changeTokenProducer">Produces the change token.</param>
/// <param name="changeTokenConsumer">Action called when the token changes.</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static IDisposable OnChange(Func<IChangeToken> changeTokenProducer, Action changeTokenConsumer)
{
if (changeTokenProducer == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(changeTokenProducer));
}
if (changeTokenConsumer == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException(nameof(changeTokenConsumer));
}
return new ChangeTokenRegistration<Action>(changeTokenProducer, callback => callback(), changeTokenConsumer);
}
private class ChangeTokenRegistration<TState> : IDisposable
{
private void OnChangeTokenFired()
{
// The order here is important. We need to take the token and then apply our changes BEFORE
// registering. This prevents us from possible having two change updates to process concurrently.
//
// If the token changes after we take the token, then we'll process the update immediately upon
// registering the callback.
IChangeToken token = _changeTokenProducer();
try
{
_changeTokenConsumer(_state);
}
finally
{
// We always want to ensure the callback is registered
RegisterChangeTokenCallback(token);
}
}
private void RegisterChangeTokenCallback(IChangeToken token)
{
IDisposable registraton = token.RegisterChangeCallback(s => ((ChangeTokenRegistration<TState>)s).OnChangeTokenFired(), this);
SetDisposable(registraton);
}
}
}
同样是套娃工程,SetDisposable是关键,比我们自己写要好,回收机制利用到位,有兴趣可以看下。
结
以上只是个人整理,如有错误,望请指出,谢谢。
下一节配置系统之变色龙(环境配置)。


