[学习笔记] 遗传算法入门
遗传算法入门
算法原理
原理很简单,就是模仿自然界适者生存的原理,不断的淘汰不符合条件的个体,通过杂交产生新个体,变异得到新个体等。
算法的代码其实通过例子超级好理解。
例子
我也是通过网络上的博客初步了解遗传算法的,所以当我看懂了之后,就直接自己写来实现了。
这个例子是这样一个题目:
求解
\[xsin(10\pi x)+2
\]
在[-1,2]内的最大值。
写起来别提有多简单!
首先第一步:
初始化种群,我的代码中种群我随机在-1到2之间取了100个数。
第二步:
就是去选择个体,这里大家都用的轮赌法,而且是重复采样的那种,我试过不重复采样,因为种群数量比较少,所以到后面其实会有bug,导致没办法迭代。
第三步:
杂交得到后代,这里我本来是写的随机杂交,并且杂交一定代数,后来发现这样写后果太严重了,不仅适应度不是朝着想要的方向变化,而且种群数量几乎呈指数级别增长。所以想了想,我们既然要适应度朝着提高的方向发展,那么我们就可以把适应度最高的几个拿来杂交,而且我的杂交方法和别的资料也不太一样,我是按照生物里面学的每个位置取父方或母方一位数据来杂交的。最终跑出来了结果。
还有就是encode和decode也和网上写的不太一样,我没去单独考虑编码限制,而是在杂交生成新物种的时候对新物种的值进行判定,满足在-1到2之间则保存,否则丢掉重新杂交。
可视化
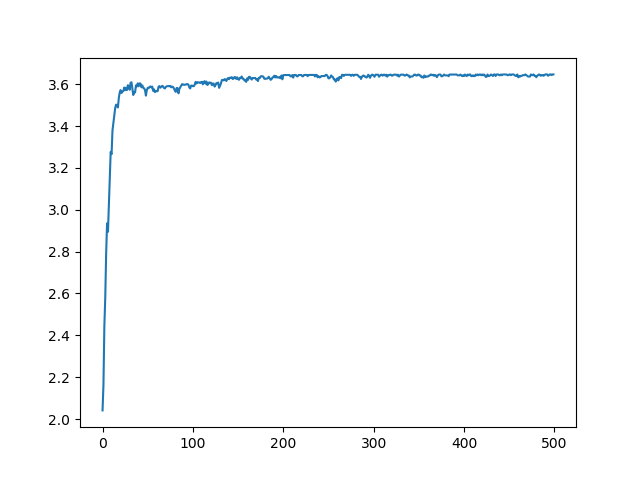
代码
'''
@Descripttion: This is Aoru Xue's demo, which is only for reference.
@version:
@Author: Aoru Xue
@Date: 2019-11-26 15:24:03
@LastEditors: Aoru Xue
@LastEditTime: 2019-11-26 20:04:21
'''
import numpy as np
import random
import math
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
# 遗传算法demo
"""[遗传算法流程]
1. 初始化
2. 选择 ->>
3. 交叉->> 生成子代
4. 变异
"""
"""[问题]
解决:f(x) = xsin(10πx) + 2 在[-1,2]内的最大值,精度取0.01。
"""
class GA():
def __init__(self,ini_num = 100,mutation_ratio = 0.01):
self.x = np.array([random.randint(0,300)/100-1. for _ in range(ini_num)])
self.mutation_ratio = mutation_ratio
def choose(self):
# 选择之后的新个体
new_x = []
# 首先求出转盘概率
probablity = []
# 站在上帝视角去评判x的值的适应度如何
fitness = self.get_fitness()
# 转化为0-1之间的值
fitness = fitness / (np.sum(fitness) )
# 转化为累计值
for idx,fit in enumerate(fitness):
probablity.append(np.sum(fitness[:idx+1,]))
# 适者生存的选择过程,选择的概率为其fitness的概率
for _ in range(int(len(self.x))): # 我这里写的是重复采样
p = random.random()
for i in range(len(self.x)):
if i ==0:
if p < probablity[0]:
#if self.x[0] in new_x:
# break
new_x.append(self.x[0])
break
elif p >= probablity[i-1] and p < probablity[i]: # 不是第一个个体的化就满足这个条件
#if self.x[i] in new_x:
# break
new_x.append(self.x[i])
break
self.x = np.array(new_x)
def get_fitness(self):
return self.x * np.sin(10 * self.x * np.pi) + 2
@staticmethod
def encode(x):
x = math.floor((x+1)*100+0.5)
return bin(x)
@staticmethod
def decode(x):
return eval(x)/100 -1
def get_sons(self,idx1,idx2):
father = list(self.encode(self.x[idx1]))[3:]
mother = list(self.encode(self.x[idx2]))[3:]
# 长度规整
if len(mother) > len(father):
for _ in range(len(mother) - len(father)):
father.insert(0,'0')
elif len(father) > len(mother):
for _ in range(len(father) - len(mother)):
mother.insert(0,'0')
sons = []
while True:
son = []
for i in range(len(father)):
p = random.random()
if p < self.mutation_ratio:
son.append(random.choice(['0','1']))
else:
son.append(random.choice([mother[i],father[i]]))
s = self.decode("0b" + "".join(son))
if len(son) and s>=-1 and s <= 2:
sons.append(s)
break
return sons
def update(self):
fitness = self.get_fitness()
max_2 = np.argsort(fitness)[-2:]
num = len(self.x)
#for _ in range(int(len(self.x) * 0.5)):
i = max_2[0]
j = max_2[1]
sons = self.get_sons(i,j)
self.x = np.concatenate([self.x,sons])
def avg_fitness(self):
return np.mean(self.get_fitness())
if __name__ == "__main__":
ga = GA()
iterations = 500
xs = []
ys = []
for _ in range(iterations):
# 适者生存
ga.choose()
# 繁衍下一代
ga.update()
xs.append(_)
ys.append(ga.avg_fitness())
plt.plot(xs,ys)
plt.show()


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号