SpringMVC入门
1、SpringMVC简介
1.1、SpringMVC概述
SpringMVC与Servlet技术功能等同,是一种基于Java的实现MVC设计模型的请求驱动类型的轻量级Web框架,属于SpringFrameWork的后续产品,已经融合在Spring Web Flow中。
SpringMVC已经成为目前最主流的MVC框架之一,并且随着Spring 3.0 的发布,全面超越Struts2,成为最优秀的MVC框架。它通过一套注解,让一个简单的Java类称为处理请求的控制器,而无需实现任何接口。同时,他还支持RESTful编程风格的请求。
SpringMVC的优点:相比Servlet使用更简单,开发更便捷,灵活性强。
1.2、SpringMVC快速入门

需求:客户端发起请求,服务器端接收请求,执行逻辑并进行视图跳转。
1.2.1、开发步骤
- 使用SpringMVC技术需要先导入SpringMVC坐标与Servlet坐标;
pom.xml: ... <dependency> <groupId>javax.servlet</groupId> <artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId> <version>3.1.0</version> <scope>provided</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> <artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId> <version>5.2.10.RELEASE</version> </dependency> ... <!-- 添加Tomcat插件 --> <build> <finalName>SSM</finalName> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.apache.tomcat.maven</groupId> <artifactId>tomcat7-maven-plugin</artifactId> <version>2.1</version> <configuration> <port>80</port> <path>/</path> </configuration> </plugin> </plugins> </build> - 创建控制器Controller类和视图页面,使用注解配置Controller类中业务方法的映射地址。
@Controller //将控制器加入到容器中 @RequestMapping("/user") public class UserController { // 请求地址: http://localhost:80/user/login ,访问时会执行该方法 @RequestMapping(value="/login",method = RequestMethod.GET,params = {"username"}) public String save(){ System.out.println("Controller save running...."); return "success.jsp"; //跳转到success.jsp } // 设置当前操作的访问路径 @RequestMapping("/save") // 设置当前操作的返回值类型 @ResponseBody public String save() { System.out.println("user save ..."); return "{'module':'springmvc'}"; } } - 初始化SpringMVC环境(同Spring环境),设定SpringMVC加载对应的bean。
/** * 创建SpringMVC的配置文件,加载controller对应的bean */ @Configuration @ComponentScan("com.clp.controller") public class SpringMvcConfig { } - 初始化Servlet容器,加载SpringMVC环境,并设置SpringMVC技术处理的请求。
AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer类是SpringMVC提供的快速初始化Web3.0容器的抽象类。 AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer提供3个接口方法供用户实现: createRootApplicationContext()方法: 如果创建Servlet容器时需要加载非SpringMVC对应的bean,使用当前方法进行。使用方式同createServletApplicationContext() /** * 定义一个servlet容器启动的配置类,在里面加载spring的配置 */ public class ServletContainerInitConfig extends AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer { // 加载SpringMVC容器配置 @Override protected WebApplicationContext createServletApplicationContext() { AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext(); ctx.register(SpringMvcConfig.class); return ctx; } // 设置哪些请求归属SpringMVC处理 @Override protected String[] getServletMappings() { return new String[]{"/"}; // 所有请求归SpringMVC进行处理 } // 加载Spring容器的配置 @Override protected WebApplicationContext createRootApplicationContext() { AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext(); ctx.register(SpringConfig.class); return ctx; } } 上述的简化配置: class ServletContainersInitConfig extends AbstractAnnotationConfigDispatcherServletInitializer { @Override protected Class<?>[] getRootConfigClasses() { return new Class[]{SpringConfig.class}; } @Override protected Class<?>[] getServletConfigClasses() { return new Class[]{SpringMvcConfig.class}; } @Override protected String[] getServletMappings() { return new String[]{"/"}; } } /* 注:在web.xml中配置的方式: <!-- springMvc的前端控制器 --> <servlet> <servlet-name>DispatcherServlet</servlet-name> <servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class> <init-param> <param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name> <param-value>classpath:spring-mvc.xml</param-value> </init-param> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>DispatcherServlet</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping> */
1.2.2、流程分析
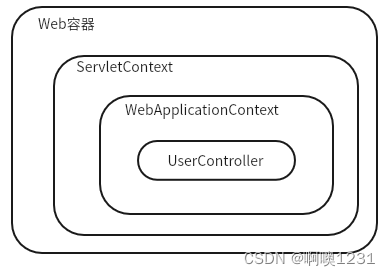
启动服务器初始化过程:
- 服务器启动,执行ServletContainerInitConfig类,初始化web容器;
- 执行createServletApplicationContext()方法,创建了WebApplicationContext对象;
- 加载SpringMvcConfig;
- 执行@ComponentScan加载对应的bean;
- 加载UserController,每个@RequestMapping的名称对应一个具体的方法;
- 执行getServletMappings方法,定义所有的请求都通过SpringMvc。

单次请求过程:
- 发送请求localhost/save;
- web容器发现所有请求都通过SpringMVC,将请求交给SpringMVC处理;
- 解析请求路径/save;
- 由/save匹配执行对应的方法save();
- 执行save();
- 检测到有@ResponseBody直接将save()方法的返回值作为响应体返回给请求方。
1.3、SpringMVC的组件解析

- 用户发送请求至前端控制器DispatcherServlet;
- DispatcherServlet搜到请求调用HandlerMapping处理器映射器;
- 处理器映射器找到具体的处理器(可以根据xml配置、注解进行查找),生成处理器对象及处理器拦截器(如果有则生成)一并返回给DIspatcherServlet;
- DispatcherServlet调用HandlerAdapter处理器适配器;
- HandlerAdapter经过适配调用具体的处理器(Controller,也叫后端控制器);
- Controller执行完成返回ModelAndView;
- HandlerAdapter将controller执行结果ModelAndView返回给DispatcherServlet;
- DispatcherServlet将ModelAndView传给ViewResolver视图解析器;
- ViewResolver解析后返回具体View;
- DispatcherServlet根据View进行渲染视图(即将模型数据填充至视图中)。DispatcherServlet响应用户。
1.4、Controller加载控制与业务bean加载控制
- SpringMVC相关bean(表现层bean);
- Spring控制的bean:① 业务bean(Service);② 功能bean(DataSource等)。
因为功能不同,如何避免Spring错误地加载到SpringMVC的bean?——加载Spring控制的bean的时候排除掉SpringMVC控制的bean。
- SpringMVC相关bean加载控制:SpringMVC加载的bean对应的包均在com.itheima.controller包内;
- Spring相关bean加载控制:① 方式1:Spring加载的bean设定扫描范围为com.itheima,排除掉controller包内的bean;② 方式2:Spring加载的bean设定扫描范围为精准范围,例如service包、dao包等;③ 方式3:不区分Spring与SpringMVC的环境,加载到同一个环境中。
- @ComponentScan注解属性: excludeFilters:排除扫描路径中加载的bean,需要指定类别(type)与具体项(classes); includeFilters:加载指定的bean,需要指定类别(type)与具体项(classes)。 @Configuration @ComponentScan(value="com.clp", excludeFilters = @ComponentScan.Filter( type = FilterType.ANNOTATION, // 按注解过滤 classes = Controller.class // 排除使用@Controller注解的类 ) ) @EnableTransactionManagement public class SpringConfig { }
2、请求
2.1、请求映射路径
@RequestMapping
作用:用于建立请求URL和处理请求方法之间的对应关系;
作用位置:
类上:请求URL的第一级访问目录,此处不写的话,就相当于应用的根目录。
方法上:请求URL的第二级访问目录,与类上的使用@RequestMapping标注的一极目录一起组成访问虚拟路径。
属性:
value:用于指定请求的URL,它和path属性的作用是一样的。
method:用于指定请求的方式。
params:用于指定限制请求参数的条件,它支持简单的表达式。要求请求参数的key和value必须和配置一模一样。
/**
* 定义Controller
*/
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("/save")
@ResponseBody
public String save() {
System.out.println("user save ...");
return "{'module':'user save'}";
}
@RequestMapping("/delete")
@ResponseBody
public String dalete() {
System.out.println("user delete ...");
return "{'module':'user delete'}";
}
}
浏览器访问:http://127.0.0.1/user/save,后端会执行save()方法2.2、获得请求头
2.2.1、@RequestHeader
使用@RequestHeader可以获得请求头信息,相当于web阶段学习的request.getHeader(name)。@RequestHeader注解的属性如下:
- value:请求头的名称。
- required:是否必须携带此请求头。

@RequestMapping(value="/quick20")
@ResponseBody //告诉SpringMVC框架,不是页面跳转,而是回写
public void save20(@RequestHeader(value="User-Agent",required = false) String user_agent) throws IOException {
System.out.println(user_agent);
}2.2.2、@CookieValue
使用@CookieValue可以获得指定Cookie的值。@CookieValue注解的属性如下:
- value:指定cookie的名称。
- required:是否必须携带此cookie。
@RequestMapping(value="/quick21")
@ResponseBody //告诉SpringMVC框架,不是页面跳转,而是回写
public void save21(@CookieValue(value="JSESSIONID") String jsessionid) throws IOException {
System.out.println(jsessionid);
}2.3、请求方式
2.3.1、Get / Post 请求传参 & Post请求中文乱码处理
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.clp.controller")
public class SpringMvcConfig {
}
/*********************************************************************************/
/**
* 定义一个servlet容器启动的配置类,在里面加载spring的配置
*/
public class ServletContainerInitConfig extends AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer {
// 加载SpringMVC容器配置
@Override
protected WebApplicationContext createServletApplicationContext() {
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
ctx.register(SpringMvcConfig.class);
return ctx;
}
// 设置哪些请求归属SpringMVC处理
@Override
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[]{"/"}; // 所有请求归SpringMVC进行处理
}
// 加载Spring容器的配置
@Override
protected WebApplicationContext createRootApplicationContext() {
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
ctx.register(SpringConfig.class);
return ctx;
}
@Override
protected Filter[] getServletFilters() {
// Post请求中文乱码处理:配置字符过滤器,为web容器添加过滤器并指定字符集,spring-web包中提供了专用的字符过滤器
CharacterEncodingFilter filter = new CharacterEncodingFilter();
filter.setEncoding("UTF-8");
return new Filter[]{filter};
}
}
/*********************************************************************************/
/**
* 定义Controller
*/
@Controller
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
@RequestMapping("/save")
@ResponseBody
public String save() {
System.out.println("user save ...");
return "{'module':'user save'}";
}
@RequestMapping("/delete")
@ResponseBody
public String dalete() {
System.out.println("user delete ...");
return "{'module':'user delete'}";
}
/**
* Get请求:url地址传参,地址参数名与形参变量名相同,定义形参即可接收参数。
* 例如:http://127.0.0.1/user/commonParam?name=zhangsan&age=18
* @param name
* @param age
* @return
*/
@RequestMapping("/commonParam")
@ResponseBody
public String commonParam(String name, int age) {
System.out.println("普通参数传递 name:" + name + ", age: " + age);
return "{'module':'common param'}";
}
}注:通过配置方式获得过滤器:
web.xml:
...
<!--配置全局过滤的filter-->
<filter>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>encoding</param-name>
<param-value>UTF-8</param-value>
</init-param>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>CharacterEncodingFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
...2.4、请求参数
服务器端要获得请求的参数,有时还需要进行数据的封装,SpringMVC可以接收如下类型的参数:
参数种类:
- 普通参数;
- POJO类型参数;
- 嵌套POJO类型参数;
- 数组类型参数;
- 集合类型参数。
2.4.1、获得普通类型参数
普通参数:url地址传参,地址参数名与形参变量名相同,定义形参即可接收参数。
Controller的业务方法的参数名称要与请求参数的name一致,参数值会自动映射匹配。当请求的参数名称与Controller的业务方法参数名称不一致时,就需要通过@RequestParam注解显式地绑定。注解@RequestParam有如下参数可以使用:
- value:请求参数名称。
- required:此在指定的请求参数是否必须包括,默认是true,提交时如果没有此参数则报错。
- dafaultValue:当没有指定请求参数时,则使用指定的默认值赋值。
/*
* 普通参数:请求参数名与形参名不同
* 例如:http://127.0.0.1/user/commonParamDifferentName?name=zhangsan&age=18
*/
@RequestMapping("/commonParamDifferentName")
@ResponseBody
// @RequestParam的作用是绑定Get请求参数与形参的对应关系
public String commonParamDifferentName(@RequestParam("name") String userName, int age) {
System.out.println("【普通参数传递】 userName:" + userName + ", age:" + age);
return "'module':'common param different name'";
}2.4.2、获得POJO类型参数(简单JavaBean)
Controller中的业务方法的POJO参数的属性名与请求参数的name一致,参数值会自动映射匹配。
public class User {
private String name;
private int age;
// getter()/setter()...
}
/*
* POJO参数
* 例如:http://127.0.0.1/user/commonParamDifferentName?name=zhangsan&age=18
* */
@RequestMapping("/pojoParam")
@ResponseBody
public String pojoParam(User user) {
System.out.println("【pojo参数传递】 user:" + user);
return "{'module':'pojo param'}";
}2.4.3、获得嵌套POJO类型参数
public class Address {
private String city;
private String province;
// getter & setter
}
public class User {
private String name;
private int age;
private Address address;
// getter & setter
}
/*
* 嵌套POJO参数
* 例如:http://127.0.0.1/user/commonParamDifferentName?name=zhangsan&age=18&address.city=beijing&address.province=beijing
* */
@RequestMapping("/pojoParam")
@ResponseBody
public String pojoParam(User user) {
System.out.println("【pojo参数传递】 user:" + user);
return "{'module':'pojo param'}";
}2.4.4、获得数组类型参数
Controller中的业务方法数组名称与请求参数的name一致,参数值会自动映射匹配。
/**
* 数组参数
* 例如:http://127.0.0.1/user/arrayParam?likes=game&likes=music&likes=travel
*/
@RequestMapping("/arrayParam")
@ResponseBody
public String arrayParam(String[] likes) {
System.out.println("【数组参数传递】 likes:" + Arrays.toString(likes));
return "{'module':'array param'}";
}2.4.5、获得集合类型参数
获得集合参数时,一定要在参数前添加@RequestParam注解。
/**
* 集合参数
* 例如:http://127.0.0.1/user/listParam?likes=game&likes=music&likes=travel
*/
@RequestMapping("listParam")
@ResponseBody
public String listParam(@RequestParam List<String> likes) {
System.out.println("【集合参数传递】 likes:" + likes);
return "{'module':'list param'}";
}2.5、请求参数——传递json数据
解析json数据需要先导入相关坐标:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.9.0</version>
</dependency>再在SpringMVC核心配置类中进行如下配置,开启自动转换json数据的支持(@EnableWebMVC注解功能强大,该注解整合了多个功能,此处仅使用其中一部分功能,即json数据进行自动类型转换):
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("com.clp.controller")
@EnableWebMvc // 开启由json数据转换成对象的功能
public class SpringMvcConfig {
}2.5.1、集合参数
/**
* 集合参数:json格式
* 例如:http://127.0.0.1/user/listParamForJson,请求体:["game", "music", "travel"]
*/
@RequestMapping("/listParamForJson")
@ResponseBody
// @RequestBody的作用是将请求体的内容映射为对应的对象
public String listParamForJson(@RequestBody List<String> likes) {
System.out.println("【list param - json 参数传递】 likes:" + likes);
return "{'module':'list param - json'}";
}2.5.2、POJO参数
/**
* 集合参数:json格式
* 例如:http://127.0.0.1/user/pojoParamForJson,请求体:{"name":"zhangsan","age":"18","address":{"province":"beijing","city":"beijing"}}
*/
@RequestMapping("/pojoParamForJson")
@ResponseBody
// @RequestBody的作用是将请求体的内容映射为对应的对象
public String pojoParamForJson(@RequestBody User user) {
System.out.println("【pojo param - json 参数传递】 likes:" + user);
return "{'module':'pojo param - json'}";
}2.5.3、集合+POJO参数
/**
* 集合参数:json格式
* 例如:http://127.0.0.1/user/listPojoParamForJson,请求体:[{"name":"zhangsan","age":"18"},{"name":"lisi","age":"20"}]
*/
@RequestMapping("listPojoParamForJson")
@ResponseBody
// @RequestBody的作用是将请求体的内容映射为对应的对象
public String listPojoParamForJson(@RequestBody List<User> userList) {
System.out.println("【list pojo param - json 参数传递】 likes:" + userList);
return "{'module':'list pojo param - json'}";
}2.6、请求参数——日期类型参数传递
日期类型数据基于系统不同格式也不尽相同。
/**
* 日期参数
* 例如:http://127.0.0.1/user/dateParam?date1=2088/08/08&date2=2088-08-18&date3=2088/08/28 8:08:08
*/
@RequestMapping("/dateParam")
@ResponseBody
// 接收形参时,根据不同的日期格式设置不同的接收方式
// @DateTimeFormat用于指定日期时间型数据格式。属性pattern:日期时间格式字符串
public String dateParam(Date date1,
@DateTimeFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd") Date date2,
@DateTimeFormat(pattern = "yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss") Date date3) {
System.out.println("【参数传递】 date1:" + date1);
System.out.println("【参数传递】 date2:" + date2);
System.out.println("【参数传递】 date3:" + date3);
return "{'module':'date param'}";
}2.6.1、类型转换器
Converter接口:
public interface Converter<S, T> {
@Nullable
T convert(S var1);
}
- 请求参数年龄数据(String -> Integer);
- 日期格式转换(String -> Date)。2.7、@RequestBody、@RequestParam、@PathVariable的区别
区别:
- @RequestParam用于接收url地址传参、表单传参【application/x-www-form-urlencoded】;
- @RequestBody用于接收json数据【application/json】;
- @PathVariable用于接收路径参数,使用{参数名称}描述路径参数。
应用:
- 后期开发中,发送请求参数超过1个时,以发送json格式数据为主,@RequestBody应用较广;
- 如果发送非json格式数据,选用@RequestParam接收请求参数;
- 采用RESTful进行开发,当参数数量较少时,例如1个,可以采用@PathVariable接收请求路径变量,通常用于传递id值。
3、响应
3.1、SpringMVC的数据响应方式
1、页面跳转
直接返回字符串
通过ModelAndView对象返回
2、回写数据
直接返回字符串
返回对象或集合3.1.1、响应页面
1、返回字符串形式
直接返回字符串“此种方式会将返回的字符串与视图解析器的前后缀拼接后跳转。

/**
* 响应页面 / 跳转页面
*/
@RequestMapping("/toJumpPage")
public String toJumpPage() {
System.out.println("跳转页面");
return "page.jsp";
}2、返回ModelAndView对象
package com.itheima.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
@Controller //将控制器加入到容器中
@RequestMapping("/user")
public class UserController {
// 请求地址: http://localhost:80/user/login ,访问时会执行该方法,要求使用GET方式请求
@RequestMapping(value="/login",method = RequestMethod.GET,params = {"username"})
public String save(){
System.out.println("Controller save running....");
return "/success"; //跳转到success.jsp( / 代表在当前web应用下寻找资源)
}
@RequestMapping(value="/quick2")
public ModelAndView save2() {
/**
* Model:模型,作用封装数据
* View:视图,作用展示数据
*/
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
//设置模型数据(放入request域)
modelAndView.addObject("username","zhangsan");
//设置视图名称
modelAndView.setViewName("success");
return modelAndView; //请求转发
}
@RequestMapping(value="/quick3")
public ModelAndView save3(ModelAndView modelAndView) {
//设置模型数据(放入request域)
modelAndView.addObject("username","zhangsan");
//设置视图名称
modelAndView.setViewName("success");
return modelAndView; //请求转发
}
@RequestMapping(value="/quick4")
public String save4(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("username","lisi");
return "success"; //请求转发
}
@RequestMapping(value="/quick5")
public String save5(HttpServletRequest request) {
request.setAttribute("username","wangwu");
return "success"; //请求转发
}
}3.1.2、响应文本数据(字符串)
Web基础阶段,客户端访问服务器端,如果想直接回写字符串作为响应体返回的话,只需要使用response.getWriter().print("hello world")即可,那么在Controller中想直接回写字符串该怎样呢?
- 方法1:通过SpringMVC框架注入的response对象,使用response.getWriter().print("hello world")回写数据,此时不需要视图跳转,业务方法返回值为void。
@RequestMapping(value="/quick6") public void save6(HttpServletResponse response) throws IOException { response.getWriter().print("hello world"); } - 方法2:将需要回写的字符串直接返回,但此时需要通过@ResponseBody注解告知SpringMVC框架,方法返回的字符串不是跳转是直接在http响应体中返回。
@RequestMapping(value="/quick7") @ResponseBody //告诉SpringMVC框架,不是页面跳转,而是回写 public String save7() throws IOException { return "hello world"; } @RequestMapping(value="/quick8") @ResponseBody //告诉SpringMVC框架,不是页面跳转,而是回写 public String save8() throws IOException { return "{'username':'zhangsan','age':'18'}"; } @RequestMapping(value="/quick9") @ResponseBody //告诉SpringMVC框架,不是页面跳转,而是回写 public String save9() throws IOException { User user = new User(); user.setUsername("zhangsan"); user.setAge(20); //使用json的转换工具,将对象转换成json格式字符串,再返回 ObjectMapper objectMapper = new ObjectMapper(); String json = objectMapper.writeValueAsString(user); return json; }
/**
* 响应文本数据
*/
@RequestMapping("/toText")
@ResponseBody
public String toText() {
System.out.println("返回纯文本数据");
return "response text";
}3.1.3、响应json数据(对象集合转json数组)
通过SpringMVC帮助我们对对象或集合进行json字符串的转换并回写,为处理器适配器配置消息转换参数,指定使用jackson进行对象或集合的转换,因此需要在spring-mvc.xml中进行如下配置:
spring-mvc.xml
...
<!--配置处理器映射器-->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter">
<property name="messageConverters">
<list>
<bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.json.MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter"></bean>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
... /**
* 响应POJO对象
*/
@RequestMapping("/toJsonPojo")
@ResponseBody // 加上该注解后返回的对象自动转为json格式字符串
public User toJsonPojo() {
System.out.println("返回json对象数据");
User user = new User();
user.setName("zhangsan");
user.setAge(18);
return user;
}
/**
* 响应POJO集合对象
*/
@RequestMapping("/toJsonList")
@ResponseBody // 加上该注解后返回的对象自动转为json格式字符串
public List<User> toJsonList() {
System.out.println("返回json集合数据");
User user1 = new User();
user1.setName("张三");
user1.setAge(18);;
User user2 = new User();
user2.setName("李四");
user2.setAge(20);;
List<User> userList = Arrays.asList(user1, user2);
return userList;
}在方法上添加@ResponseBody就可以返回json格式的字符串,但是这样配置比较麻烦,配置的代码比较多,因此,我们可以使用mvc的注解驱动代替上述配置。
spring-mvc.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:mvc="http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc http://www.springframework.org/schema/mvc/spring-mvc.xsd">
<!--Controller的组件扫描-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.itheima">
<context:include-filter type="annotation" expression="org.springframework.stereotype.Controller"/>
</context:component-scan>
<!--配置内部资源视图解析器-->
<bean id="viewResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<!-- /jsp/success.jsp -->
<property name="prefix" value="/jsp/"></property>
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp"></property>
</bean>
<!--配置处理器映射器-->
<!-- <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation.RequestMappingHandlerAdapter">-->
<!-- <property name="messageConverters">-->
<!-- <list>-->
<!-- <bean class="org.springframework.http.converter.json.MappingJackson2HttpMessageConverter"></bean>-->
<!-- </list>-->
<!-- </property>-->
<!-- </bean>-->
<!--mvc的注解驱动-->
<mvc:annotation-driven />
</beans>在SpringMVC的各个组件中,处理器映射器、处理器适配器、视图解析器称为SpringMVC的三大组件。使用<mvc:annotation-driven>自动加载RequestMappingHandlerMapping(处理映射器)和RequestMappingHandlerAdapter(处理适配器),可用在spring-mvc.xml配置文件中使用<mvc:annotation-driven>替代注解处理器和适配器的配置。同时使用<mvc:annotation-driven>默认底层就会集成jackson进行对象或集合的json格式字符串的转换。
3.2、类型转换器HttpMessageConverter
- HttpMessageConverter接口
public interface HttpMessageConverter<T> {
boolean canRead(Class<?> clazz, @Nullable MediaType mediaType);
boolean canWrite(Class<?> clazz, @Nullable MediaType mediaType);
List<MediaType> getSupportedMediaTypes();
T read(Class<? extends T> clazz, HttpInputMessage inputMessage)
throws IOException, HttpMessageNotReadableException;
void write(T t, @Nullable MediaType contentType, HttpOutputMessage outputMessage)
throws IOException, HttpMessageNotReadableException;
}4、配置对静态资源的访问放行
@Configuration
public class SpringMvcSupport extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport {
/**
* 放行 非SpringMvc的请求
* @param registry
*/
@Override
protected void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
// 当访问/pages/????的时候不要走mvc,走/pages目录下的内容
registry.addResourceHandler("/pages/**").addResourceLocations("/pages/");
// 其他静态资源
registry.addResourceHandler("/js/**").addResourceLocations("/js/");
registry.addResourceHandler("/css/**").addResourceLocations("/css/");
registry.addResourceHandler("/plugins/**").addResourceLocations("/plugins/");
}
}
@Configuration
@ComponentScan({"com.clp.controller", "com.clp.config"}) // 添加扫描
@EnableWebMvc // 开启由json数据转换成对象的功能
public class SpringMvcConfig {
}5、自定义类型转换器
SpringMVC默认已经提供了一些常用的类型转换器,例如客户端提交的字符串转换成int型进行参数设置。但是不是所有的数据类型都提供了转换器,没有提供的就需要自定义转换器,例如:日期类型的数据就需要自定义转换器。
自定义类型转换器的开发步骤:
- 定义转换器实现Converter接口;
- 在配置文件中声明转换器;
- 在<annotation-driver>中引用转换器。
import org.springframework.core.convert.converter.Converter;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class DateConverter implements Converter<String, Date> {
public Date convert(String dateStr) {
//将日期字符串转换成日期对象,然后返回
SimpleDateFormat format = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
Date date = null;
try {
date = format.parse(dateStr);
} catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return date;
}spring-mvc.xml:
...
<!--mvc的注解驱动-->
<mvc:annotation-driven conversion-service="conversionService"/>
<!--声明转换器-->
<bean id="conversionService" class="org.springframework.context.support.ConversionServiceFactoryBean">
<property name="converters">
<list>
<bean class="com.converter.DateConverter"></bean>
</list>
</property>
</bean>
... //localhost:80/user/quick18?date=2020-12-12
@RequestMapping(value="/quick18")
@ResponseBody //告诉SpringMVC框架,不是页面跳转,而是回写
public void save17(Date date) throws IOException {
System.out.println(date);
}6、获得Servlet相关API
SpringMVC支持使用原始ServletAPI对象作为控制器方法的参数进行注入,常用的参数如下:
- HttpServletRequest
- HttpServletResponse
- HttpSession

@RequestMapping(value="/quick19")
@ResponseBody //告诉SpringMVC框架,不是页面跳转,而是回写
public void save19(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, HttpSession session) throws IOException {
System.out.println(request);
System.out.println(response);
System.out.println(session);
}7、REST风格
7.1、简介
REST(Representational State Transfer,表现形式状态转换)。根据REST风格对资源进行访问称为RESTful。Restful是一种软件架构风格、设计风格,而不是标准,知识提供了一组设计原则和约束条件。主要用于客户端和服务器交互的软件,基于这个风格设计的软件可以更简洁,更有层次,更易于实现缓存机制等。
Restful风格的请求是使用"url+请求方式"表示一次请求的目的,HTTP协议里面四个表示操作方式的动词如下:
- GET:用于获取资源。
- POST:用于新建资源。
- PUT:用于更新资源。
- DELETE:用于删除资源。


上述行为是约定方式,约定不是规范,可以打破,所以称REST风格,而不是REST规范。描述模块的名称通常使用复数,也就是加s的格式描述,表示此类资源,而非单个资源,例如:users、books、accounts...
REST风格的优点:
- 隐藏资源的访问行为,无法通过地址得知对资源是何种操作;
- 书写简化。
7.2、入门案例
@Controller
public class UserController {
/*
* @RequestMapping:设置当前控制器方法请求访问路径。
* 属性:
* 1、value(默认):请求访问路径;
* 2、method:http请求动作,标准动作(GET、POST、PUT、DELETE)
*
* @PathVariable:绑定路径参数与处理器方法形参间的关系,要求路径参数名与形参名一一对应。
* */
@RequestMapping(value = "/users/{id}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public String get(@PathVariable Integer id) {
System.out.println("user get ..." + id);
return "{'module':'user get'}";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/users", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public String getAll() {
System.out.println("user getAll...");
return "{'module':'user getAll'}";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/users", method = RequestMethod.POST)
@ResponseBody
public String post(@RequestBody User user) {
System.out.println("user post ..." + user);
return "{'module':'user post'}";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/users/{id}", method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
@ResponseBody
public String delete(@PathVariable Integer id) {
System.out.println("user delete ..." + id);
return "{'module':'user delete'}";
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/users", method = RequestMethod.PUT)
@ResponseBody
public String put(@RequestBody User user) {
System.out.println("user put ..." + user);
return "{'module':'user put'}";
}
}7.3、RESTful快速开发
/*
* @RestController:设置当前控制器类为RESTful风格,等同于@Controller与@ResponseBody两个注解组合功能。
* @GetMapping & @PostMapping & @PutMapping & @DeleteMapping:
* 设置当前控制器方法请求访问路径与请求动作,每种对应一个请求动作,例如@GetMapping对应GET请求。
* */
//@Controller
//@ResponseBody
@RestController // @RestController = @Controller + @ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/books")
public class BookController {
// @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
@PostMapping // @PostMapping = @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
public String post(@RequestBody Book book) {
System.out.println("book post ..." + book);
return "{'module':'book post'}";
}
// @RequestMapping(value = "/{id}", method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
@DeleteMapping("/{id}") // @DeleteMapping("/{id}") = @RequestMapping(value = "/{id}", method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
public String delete(@PathVariable Integer id) {
System.out.println("book delete ..." + id);
return "{'module':'book delete'}";
}
// @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.PUT)
@PutMapping // @PutMapping = @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.PUT)
public String put(@RequestBody Book book) {
System.out.println("book put ..." + book);
return "{'module':'book put'}";
}
// @RequestMapping(value = "/{id}}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@GetMapping("/{id}") // @GetMapping("/{id}") = @RequestMapping(value = "/{id}}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String get(@PathVariable Integer id) {
System.out.println("book get ..." + id);
return "{'module':'book get'}";
}
// @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
@GetMapping // @GetMapping = @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
public String getAll() {
System.out.println("book getAll ...");
return "{'module':'book getAll'}";
}
}8、SSM整合
8.1、SSM整合流程
1、创建工程
2、SSM整合
- Spring
SpringConfig
- MyBatis
MyBatisConfig
JdbcConfig
jdbc.properties
- SpringMVC
ServletConfig
SpringMvcConfig
3、功能模块
- 表与实体类
- dao(接口+自动代理)
- service(接口+实现类)
业务层接口测试(整合JUnit)
- controller
表现层接口测试(PostMan)8.1.1、导入相关坐标
pom.xml:
...
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.2.10.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.2.10.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>5.2.10.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis</artifactId>
<version>3.5.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring</artifactId>
<version>1.3.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.47</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibaba</groupId>
<artifactId>druid</artifactId>
<version>1.1.16</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>3.1.0</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.9.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.4</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
...
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat7-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.1</version>
<configuration>
<port>80</port>
<path>/</path>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
...8.1.2、SSM整合
jdbc.properties:
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ssmdb
jdbc.username=root
jdbc.password=123456public class JdbcConfig {
/*
* 简单类型的依赖注入使用@Value
* */
@Value("${jdbc.driver}")
private String driver;
@Value("${jdbc.url}")
private String url;
@Value("${jdbc.username}")
private String username;
@Value("${jdbc.password}")
private String password;
// 1、定义一个方法获得要管理的对象
// 2、添加@Bean表示当前方法的返回值是一个bean
/*
* 引用类型的依赖注入:主需要为bean定义方法设置形参即可,容器会根据 类型 自动装配对象。
* */
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
DruidDataSource dataSource = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource.setDriverClassName(driver);
dataSource.setUrl(url);
dataSource.setUsername(username);
dataSource.setPassword(password);
return dataSource;
}
/**
* 创建平台事务管理器
* @param dataSource
* @return
*/
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager(DataSource dataSource) {
DataSourceTransactionManager dtm = new DataSourceTransactionManager();
dtm.setDataSource(dataSource);
return dtm;
}
}public class MyBatisConfig {
/**
* SqlSessionFactoryBean专门产生SqlSessionFactory
* @return
*/
@Bean
public SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactoryBean(DataSource dataSource) {
SqlSessionFactoryBean ssfb = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
ssfb.setDataSource(dataSource); // 设置数据源
ssfb.setTypeAliasesPackage("com.clp.domain"); // 设置实体类别名扫描包
return ssfb;
}
/**
* 扫描Dao层的映射信息
* @return
*/
@Bean
public MapperScannerConfigurer mapperScannerConfigurer() {
MapperScannerConfigurer msc = new MapperScannerConfigurer();
msc.setBasePackage("com.clp.dao");
return msc;
}
}@Configuration
@ComponentScan({"com.clp.service"})
@PropertySource("jdbc.properties")
@Import({JdbcConfig.class, MyBatisConfig.class})
@EnableTransactionManagement // 开启事务管理器
public class SpringConfig {
}@Configuration
@ComponentScan({"com.clp.controller"})
@EnableWebMvc // 开启由json数据转换成对象的功能
public class SpringMvcConfig {
}/**
* 定义一个servlet容器启动的配置类,在里面加载spring的配置(需继承AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer,这样tomcat可以探测到这个类)
*/
public class ServletConfig extends AbstractDispatcherServletInitializer {
/*
* 注:Web容器(Tomcat)启动时,会加载SpringMvcConfig和SpringConfig配置类。
* 这两个配置类产生的容器对象不是同一个对象。
* SpringMVC容器能访问Spring容器,而Spring容器不能访问SpringMVC容器。
* */
// 加载SpringMVC容器配置
@Override
protected WebApplicationContext createServletApplicationContext() {
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
ctx.register(SpringMvcConfig.class);
return ctx;
}
// 拦截请求:设置哪些请求归属SpringMVC处理
@Override
protected String[] getServletMappings() {
return new String[]{"/"}; // 所有请求归SpringMVC进行处理
}
// 加载Spring容器的配置
@Override
protected WebApplicationContext createRootApplicationContext() {
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
ctx.register(SpringConfig.class);
return ctx;
}
// 设置过滤器,处理中文乱码问题
@Override
protected Filter[] getServletFilters() {
// Post请求中文乱码处理:配置字符过滤器,为web容器添加过滤器并指定字符集,spring-web包中提供了专用的字符过滤器
CharacterEncodingFilter filter = new CharacterEncodingFilter();
filter.setEncoding("UTF-8");
return new Filter[]{filter};
}
}8.1.3、功能模块
public interface BookDao {
@Insert("insert into book values(null, #{type}, #{name}, #{description})")
void save(Book book);
@Update("update book set type=#{type}, name=#{name}, description=#{description} where id = #{id}")
void update(Book book);
@Delete("delete from book where id = #{id}")
void delete(Integer id);
@Select("select * from book where id = #{id}")
Book getById(Integer id);
@Select("select * from book")
List<Book> getAll();
}@Transactional
public interface BookService {
boolean save(Book book);
boolean update(Book book);
boolean delete(Integer id);
Book getById(Integer id);
List<Book> getAll();
}
@Service
public class BookServiceImpl implements BookService {
@Autowired
private BookDao bookDao;
@Override
public boolean save(Book book) {
bookDao.save(book);
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean update(Book book) {
bookDao.update(book);
return true;
}
@Override
public boolean delete(Integer id) {
bookDao.delete(id);
return true;
}
@Override
public Book getById(Integer id) {
return bookDao.getById(id);
}
@Override
public List<Book> getAll() {
return bookDao.getAll();
}
}@RestController // @RestController = @Controller + @ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/books")
public class BookController {
@Autowired
private BookService bookService;
// @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
@PostMapping // @PostMapping = @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
public boolean post(@RequestBody Book book) {
return bookService.save(book);
}
// @RequestMapping(value = "/{id}", method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
@DeleteMapping("/{id}") // @DeleteMapping("/{id}") = @RequestMapping(value = "/{id}", method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
public boolean delete(@PathVariable Integer id) {
return bookService.delete(id);
}
// @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.PUT)
@PutMapping // @PutMapping = @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.PUT)
public boolean put(@RequestBody Book book) {
return bookService.update(book);
}
// @RequestMapping(value = "/{id}}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@GetMapping("/{id}") // @GetMapping("/{id}") = @RequestMapping(value = "/{id}}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public Book get(@PathVariable Integer id) {
return bookService.getById(id);
}
// @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
@GetMapping // @GetMapping = @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
public List<Book> getAll() {
return bookService.getAll();
}
}8.1.4、测试
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class)
@ContextConfiguration(classes = SpringConfig.class)
public class BookServiceTest {
@Autowired
private BookService bookService;
@Test
public void testGetById() {
Book book = bookService.getById(1);
System.out.println(book);
}
@Test
public void testGetAll() {
List<Book> bookList = bookService.getAll();
System.out.println(bookList);
}
}8.2、表现层数据封装
前端接收数据格式——封装特殊消息到message(msg)属性中。
- 设置统一数据返回结果类:
public class Result {
private Object data; // 数据
private Integer code; // 编码
private String msg; // 消息
}
注意:Result类中的字段并不是固定的,可以根据需要自行增减。
提供若干个构造方法,方便操作。
- 设置统一数据返回结果编码
public class Code {
public static final Integer SAVE_OK = 20011;
public static final Integer DELETE_OK = 20021;
public static final Integer UPDATE_OK = 20031;
public static final Integer GET_OK = 20041;
public static final Integer SAVE_ERR = 20010;
public static final Integer DELETE_ERR = 20020;
public static final Integer UPDATE_ERR = 20030;
public static final Integer GET_ERR = 20040;
}
注意:Code类的常量设计也不是固定的,可以根据需要自行增减,例如将查询再进行细分为GET_OK,GET_ALL_OK,GET_PAGE_OK。
- 根据情况设定合理的Result
@RestController // @RestController = @Controller + @ResponseBody
@RequestMapping("/books")
public class BookController {
@Autowired
private BookService bookService;
// @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
@PostMapping // @PostMapping = @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
public Result post(@RequestBody Book book) {
boolean flag = bookService.save(book);
return new Result(flag ? Code.SAVE_OK : Code.SAVE_ERR, flag);
}
// @RequestMapping(value = "/{id}", method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
@DeleteMapping("/{id}") // @DeleteMapping("/{id}") = @RequestMapping(value = "/{id}", method = RequestMethod.DELETE)
public Result delete(@PathVariable Integer id) {
boolean flag = bookService.delete(id);
return new Result(flag ? Code.DELETE_OK : Code.DELETE_ERR, flag);
}
// @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.PUT)
@PutMapping // @PutMapping = @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.PUT)
public Result put(@RequestBody Book book) {
boolean flag = bookService.update(book);
return new Result(flag ? Code.UPDATE_OK : Code.UPDATE_ERR, flag);
}
// @RequestMapping(value = "/{id}}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@GetMapping("/{id}") // @GetMapping("/{id}") = @RequestMapping(value = "/{id}}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public Result get(@PathVariable Integer id) {
Book book = bookService.getById(id);
return new Result(
book != null ? Code.GET_OK : Code.GET_ERR,
book,
book != null ? "查询成功" : "查询失败"
);
}
// @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
@GetMapping // @GetMapping = @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
public Result getAll() {
List<Book> bookList = bookService.getAll();
return new Result(
bookList != null ? Code.GET_OK : Code.GET_ERR,
bookList,
bookList != null ? "查询成功" : "查询失败"
);
}
}9、异常处理
9.1、异常处理的思路
系统中异常包括两类:预期异常和运行时异常RintimeException,前者通过捕获异常从而获取异常信息,后者主要通过规范代码开发、测试等手段减少运行时异常的发生。
系统的Dao、Service、Controller出现都通过throws Exception向上抛出,最后由SpringMVC前端控制器交由异常处理器进行异常处理。如下图:

9.2、异常处理的两种方式
9.2.1、简单异常处理器SimpleMappingExceptionResolver
使用SpringMVC提供的简单异常处理器SimpleMappingExceptionResolver。
SpringMVC已经定义好了该类型转换器,在使用时可以根据项目情况进行相应异常与视图的映射配置。
spring-mvc.xml:
...
<!--配置简单映射异常处理器-->
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.handler.SimpleMappingExceptionResolver">
<property name="defaultErrorView" value="error.jsp" />
<property name="exceptionMappings">
<map>
<entry key="java.lang.ClassCastException" value="error1.jsp"/>
<entry key="com.exception.MyException" value="error2.jsp"/>
</map>
</property>
</bean>
...9.2.2、自定义异常处理器
实现Spring的异常处理接口HandleExceptionResolver自定义自己的异常处理器。
自定义异常处理步骤:
- 创建异常处理器实现HandlerExceptionResolver;
- 配置异常处理器;
- 编写异常页面;
- 测试异常跳转。
package com.exception;
public class MyException extends Exception{
}
/************************************************************************************/
package com.exception;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.HandlerExceptionResolver;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
public class MyExceptionResolver implements HandlerExceptionResolver {
@Override
/**
* 参数Exception:异常对象。
* 返回值ModelAndView:跳转的错误视图信息。
*/
public ModelAndView resolveException(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) {
ModelAndView modelAndView = new ModelAndView();
if(ex instanceof MyException) {
modelAndView.addObject("info","自定义异常");
}else if(ex instanceof ClassCastException) {
modelAndView.addObject("info","类型转换异常");
}
modelAndView.setViewName("error.jsp");
return null;
}
}spring-mvc.xml:
...
<!--自定义异常处理器-->
<bean class="com.exception.MyExceptionResolver" />
...9.3、Spring中的异常处理器
出现异常现象的常见位置与常见诱因如下:
- 框架内部抛出的异常:因使用不合规导致;
- 数据层抛出的异常:因外部服务器故障导致(例如:服务器访问超时);
- 业务层抛出的异常:因业务逻辑书写错误导致(例如:遍历业务书写操作,导致索引异常等);
- 表现层抛出的异常:因数据收集、校验等规则导致(例如:不匹配的数据类型间导致的异常);
- 工具类抛出的异常:因工具类书写不严谨不够健壮导致(例如:必要释放的连接长期未释放等)。
思考:
- 各个层级均出现异常,异常代码书写在哪一层?——所有的异常均抛出到表现层进行处理。
- 表现层处理异常,每个方法中单独书写,代码书写量巨大且意义不强,如何解决?——AOP思想。
Spring中的异常处理器可以集中、统一地处理项目中出现的异常。
// 声明这个类是异常处理器,用于AOP处理异常,需要SpringMvcConfig配置扫描该类所在的包(@ComponentScan)
@RestControllerAdvice
public class ProjectExceptionAdvice {
@ExceptionHandler(Exception.class) // 拦截异常
// 方法的返回值将会作为响应结果
public Result doException(Exception ex) {
System.out.println("获取异常");
return new Result(666, null);
}
}
BookController:
@PostMapping // @PostMapping = @RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.POST)
public Result post(@RequestBody Book book) {
boolean flag = bookService.save(book);
int i = 1 / 0; // 手动产生异常
return new Result(flag ? Code.SAVE_OK : Code.SAVE_ERR, flag);
}9.4、项目异常处理方案
- 项目异常分类
- 业务异常(BusinessException)
规范的用户行为产生的异常
不规范的用户行为操作产生的异常
- 系统异常(SystenException)
项目运行过程中可预计且无法避免的异常
- 其他异常(Exception)
编程人员未预期到的异常
- 项目异常处理方案:
- 业务异常(BusinessException)
发送对应消息传递给用户,提醒规范操作
- 系统异常(SystemException)
发送固定消息传递给用户,安抚用户
发送特定消息给运维人员,提醒用户
记录日志
- 其他异常(Exception)
发送固定消息传递给用户,安抚用户
发送特定消息给编程人员,提醒维护(纳入预期范围内)
记录日志步骤:
- 自定义项目系统级异常、业务级异常:
public class SystemException extends RuntimeException{ private Integer code; // 异常编号 public Integer getCode() { return code; } public void setCode(Integer code) { this.code = code; } public SystemException(Integer code, String message) { super(message); this.code = code; } public SystemException(Integer code, String message, Throwable cause) { super(message, cause); this.code = code; } } public class BusinessException extends RuntimeException{ private Integer code; // 异常编号 public Integer getCode() { return code; } public void setCode(Integer code) { this.code = code; } public BusinessException(Integer code, String message) { super(message); this.code = code; } public BusinessException(Integer code, String message, Throwable cause) { super(message, cause); this.code = code; } } - 自定义异常编码(持续补充):
public class Code { public static final Integer SYSTEM_ERR = 50001; public static final Integer BUSINESS_ERR = 60001; public static final Integer SYSTEM_UNKNOWN_ERR = 59999; } - 触发(模拟)自定义异常:
@Service public class BookServiceImpl implements BookService { @Autowired private BookDao bookDao; @Override public boolean save(Book book) { if (true) { throw new BusinessException(Code.BUSINESS_ERR, "请不要使用你的技术挑战我的耐心!"); } // 将可能出现的异常进行包装,转换成自定义异常 try { int i = 1 / 0; } catch (Exception e) { throw new SystemException(Code.SYSTEM_ERR, "服务器访问超时,请重试!", e); } bookDao.save(book); return true; } } - 拦截并处理异常;
// 声明这个类是异常处理器,用于AOP处理异常,需要SpringMvcConfig配置扫描该类所在的包(@ComponentScan) @RestControllerAdvice public class ProjectExceptionAdvice { // 处理系统异常 @ExceptionHandler(SystemException.class) public Result doSystemException(SystemException ex) { // 记录日志 // 发送消息给运维 // 发送邮件给开发人员 return new Result(ex.getCode(), null, ex.getMessage()); } // 处理业务异常 @ExceptionHandler(BusinessException.class) public Result doBusinessException(BusinessException ex) { return new Result(ex.getCode(), null, ex.getMessage()); } // 处理其他异常 @ExceptionHandler(Exception.class) // 拦截异常 // 方法的返回值作为出现异常的方法的返回值 public Result doException(Exception ex) { return new Result(Code.SYSTEM_UNKNOWN_ERR, null, "系统繁忙,请稍后再试!"); } }
10、拦截器
10.1、拦截器的概念
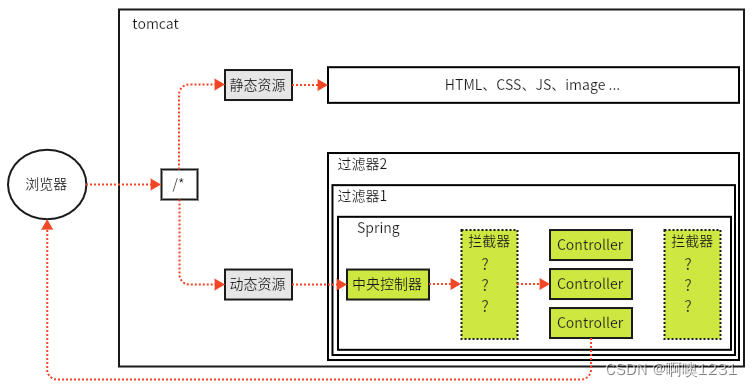
拦截器(Interceptor)是一种动态拦截方法调用的机制,在SpringMVC中动态拦截控制器方法的执行。SpringMVC的拦截器类似于Servlet开发中的过滤器Filter,用于对处理器进行预处理和后处理。
拦截器的作用:
- 在指定的方法调用前后执行预先设定的代码;
- 阻止原始方法的执行。
将拦截器按一定的顺序联结成一条链,这条链称为拦截器链(Interceptor Chain)。在访问被拦截的方法或字段时,拦截器链中的拦截器就会按其之前定义的顺序被调用。拦截器也是AOP思想的具体体现。
10.2、拦截器和过滤器的区别
| 区别 | 过滤器(Filter) | 拦截器(Interceptor) |
|---|---|---|
| 使用范围 | 是servlet规范中的一部分,任何Java Web工程都可以使用。 | 是SpringMVC框架自己的,只有使用了SpringMVC框架的工程才能用。 |
| 拦截范围 | 在url-pattern中配置了/*之后,可以对所有要访问的资源拦截。 | 仅针对SpringMVC的访问进行增强。在<mvc:mapping path="" />中配置了/**之后,也可以对所有资源进行拦截,但是可以通过<mvc:exclude-mapping path="" />标签排除不需要拦截的资源。 |
10.3、拦截器入门案例
自定义拦截器很简单,只有如下三步:
- 创建拦截器类实现HandlerInterceptor接口;
/** * 拦截器(interceptor)包在controller包下,因为已经配置了扫描controller包,所以不用再配置interceptor包了 */ @Component public class ProjectInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor{ // 被拦截的原始操作之前运行的方法 @Override public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception { System.out.println("preHandle"); return true; // return false 会终止原始操作的执行。因此下面两个方法不会再执行 } // 被拦截的原始操作之后运行的方法 @Override public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception { System.out.println("postHandle"); return; } // 被拦截的原始操作之后并且在postHandle()方法后执行的方法 @Override public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception { System.out.println("afterCompletion"); return; } } - 配置拦截器;
@Configuration public class SpringMvcSupport extends WebMvcConfigurationSupport { @Autowired private ProjectInterceptor projectInterceptor; /** * 配置拦截器,并设定拦截的访问路径,路径可以通过可变参数设置多个 */ @Override protected void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) { // addPathPatterns()方法的参数表示拦截的url字符串匹配则进行拦截 registry.addInterceptor(projectInterceptor).addPathPatterns("/books", "/books/*"); } } @Configuration @ComponentScan({"com.clp.controller", "com.clp.config"}) // 添加扫描 @EnableWebMvc // 开启由json数据转换成对象的功能 public class SpringMvcConfig { } /* - xml配置方式: spring-mvc.xml: ... <!--配置拦截器--> <mvc:interceptors> <mvc:interceptor> <!--对哪些资源执行拦截操作(此处代表对所有)--> <mvc:mapping path="/**" /> <!--配置哪些资源排除拦截操作--> <mvc:exclude-mapping path="/user/login"/> <bean class="com.interceptor.MyInterceptor1" /> </mvc:interceptor> </mvc:interceptors> ... */ - 上述配置的简化版(注意:侵入式较强): @Configuration @ComponentScan({"com.clp.controller"}) @EnableWebMvc // 开启由json数据转换成对象的功能 public class SpringMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer { @Autowired private ProjectInterceptor projectInterceptor; /** * 配置拦截器 */ @Override public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) { // addPathPatterns()方法的参数表示拦截的url字符串匹配则进行拦截 registry.addInterceptor(projectInterceptor).addPathPatterns("/books", "/books/*"); } } - 测试拦截器的拦截效果。
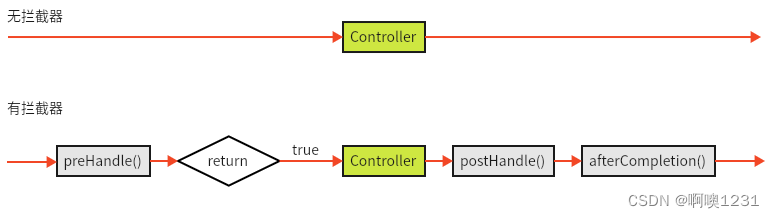
10.4、拦截器HandlerInterceptor接口方法说明
| 方法名 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| preHandle() | 方法将在请求处理之前进行调用,该方法的返回值是布尔值boolean类型的,当它返回为false时,表示请求结束,后续的Interceptor和Controller都不会再执行;当返回值为true时就会继续调用下一个Interceptor的preHandle方法。 |
| postHandle() | 该方法是在当前请求进行处理之后被调用,前提是preHandle方法的返回值为true时才能被调用,且它会在DispatcherServlet进行视图返回渲染之前被调用,所以我们可以在这个方法中对Controller处理之后的ModelAndView对象进行操作。 |
| afterCompletion() | 该方法将在整个请求结束之后,也就是在DispatcherServlet渲染了对应的视图之后执行,前提是preHandle方法的返回值为true时才能被调用。 |
10.5、拦截器执行流程
10.6、拦截器参数
- 前置处理
@Component
public class ProjectInterceptor implements HandlerInterceptor{
// 被拦截的原始操作之前运行的方法
@Override
public boolean preHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler) throws Exception {
HandlerMethod hm = (HandlerMethod) handler;
String contentType = request.getHeader("Content-Type");
System.out.println("preHandle" + contentType);
return true; // return false 会终止原始操作的执行。因此下面两个方法不会再执行
}
}
- 参数
request:请求对象
response:响应对象
handler:被调用的处理器对象,本质上是一个方法对象,对反射技术中的Method对象进行了再包装
- 返回值
若返回值为false:被拦截的处理器将不执行- 后置处理
// 被拦截的原始操作之后运行的方法
@Override
public void postHandle(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, ModelAndView modelAndView) throws Exception {
System.out.println("postHandle");
return;
}
- 参数:
modelAndView:如果处理器执行完成具有返回结果,可以读取到对应数据与页面信息,并进行调整。- 完成后处理
// 被拦截的原始操作之后并且在postHandle()方法后执行的方法
@Override
public void afterCompletion(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response, Object handler, Exception ex) throws Exception {
System.out.println("afterCompletion");
return;
}
- 参数:
ex:如果处理器执行过程中出现异常对象,可以针对异常情况进行单独处理。10.7、多拦截器执行顺序
10.7.1、拦截器链配置方式
@Configuration
@ComponentScan({"com.clp.controller"})
@EnableWebMvc // 开启由json数据转换成对象的功能
public class SpringMvcConfig implements WebMvcConfigurer {
@Autowired
private ProjectInterceptor projectInterceptor;
@Autowired
private ProjectInterceptor2 projectInterceptor2;
/**
* 配置拦截器
*/
@Override
public void addInterceptors(InterceptorRegistry registry) {
// addPathPatterns()方法的参数表示拦截的url字符串匹配则进行拦截
// 拦截器链的执行顺序与添加顺序有关
registry.addInterceptor(projectInterceptor).addPathPatterns("/books", "/books/*");
registry.addInterceptor(projectInterceptor2).addPathPatterns("/books", "/books/*");
}
}10.7.2、拦截器链的运行顺序
- 当配置多个拦截器时,形成拦截器链。
- 拦截器链的运行顺序参照拦截器添加顺序为准。
- 当拦截器中出现对原始处理器的拦截,后面的拦截器均终止运行。
- 当拦截器运行中断,仅运行配置在前面的拦截器的afterCompletion操作。
11、文件上传
11.1、文件上传三要素
- 表单项type="file"
- 表单的提交方式是post
- 表单的enctype属性是多部份表单形式,及enctype="multipart/form-data"
form.jsp:
...
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/quick22" method="post"
enctype="multipart/form-data">
名称:<input type="text" name="username"><br />
文件:<input type="file" name="uploadFile"><br />
<input type="submit" value="提交"><br />
</form>
...11.2、文件上传原理
当form表单修改为多部分表单时,request.getParameter()将失效;
enctype="application/x-www-form-urlencoded"时,form表单的正文内容格式是:key=value&key=value...;
当form表单的enctype取值为multipart/form-data时,请求正文内容就变成多部分形式:

11.3、单文件上传步骤
- 导入fileupload和io坐标;
- 配置文件上传解析器;
- 编写文件上传代码。
pom.xml:
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-fileupload</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-fileupload</artifactId>
<version>1.3.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-io</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-io</artifactId>
<version>2.3</version>
</dependency>spring-mvc.xml:
...
<bean id="multipartResolver" class="org.springframework.web.multipart.commons.CommonsMultipartResolver">
<!--上传文件总大小-->
<property name="maxUploadSize" value="5242800" />
<!--上传单个文件的大小-->
<property name="maxUploadSizePerFile" value="5242800" />
<!--上传文件的编码类型-->
<property name="defaultEncoding" value="UTF-8" />
</bean>
... @RequestMapping(value="/quick22")
@ResponseBody //告诉SpringMVC框架,不是页面跳转,而是回写
public void save22(String username, MultipartFile uploadFile) throws IOException {
System.out.println(username);
//获得文件名称
String originalFilename = uploadFile.getOriginalFilename();
//保存文件
uploadFile.transferTo(new File("D:\\upload\\"+originalFilename));
}11.4、多文件上传实现
多文件上传,只需要将页面修改为多个文件上传项,将方法参数MultipartFile类型修改为MultipartFile[]即可。
...
<form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/quick22" method="post"
enctype="multipart/form-data">
名称:<input type="text" name="username1"><br />
文件:<input type="file" name="uploadFile1"><br />
名称:<input type="text" name="username2"><br />
文件:<input type="file" name="uploadFile2"><br />
<input type="submit" value="提交"><br />
</form>
... @RequestMapping(value="/quick22")
@ResponseBody //告诉SpringMVC框架,不是页面跳转,而是回写
public void save22(String username1,String username2, MultipartFile uploadFile1, MultipartFile uploadFile2) throws IOException {
System.out.println(username);
//获得文件名称
String originalFilename1 = uploadFile1.getOriginalFilename();
//保存文件
uploadFile1.transferTo(new File("D:\\upload\\"+originalFilename1));
//获得文件名称
String originalFilename2 = uploadFile1.getOriginalFilename();
//保存文件
uploadFile2.transferTo(new File("D:\\upload\\"+originalFilename2));
} <form action="${pageContext.request.contextPath}/quick23" method="post"
enctype="multipart/form-data">
名称:<input type="text" name="username"><br />
文件1:<input type="file" name="uploadFiles"><br />
文件2:<input type="file" name="uploadFiles"><br />
文件3:<input type="file" name="uploadFiles"><br />
<input type="submit" value="提交"><br />
</form> @RequestMapping(value="/quick23")
@ResponseBody //告诉SpringMVC框架,不是页面跳转,而是回写
public void save23(String username, MultipartFile[] uploadFiles) throws IOException {
System.out.println(username);
for(MultipartFile multipartFile : uploadFiles) {
//获得文件名称
String originalFilename = multipartFile.getOriginalFilename();
//保存文件
multipartFile.transferTo(new File("D:\\upload\\"+originalFilename));
}
}
