Linux系统时间的设定以及自带的timesync时间同步
1.三个阶段的系统时间设定
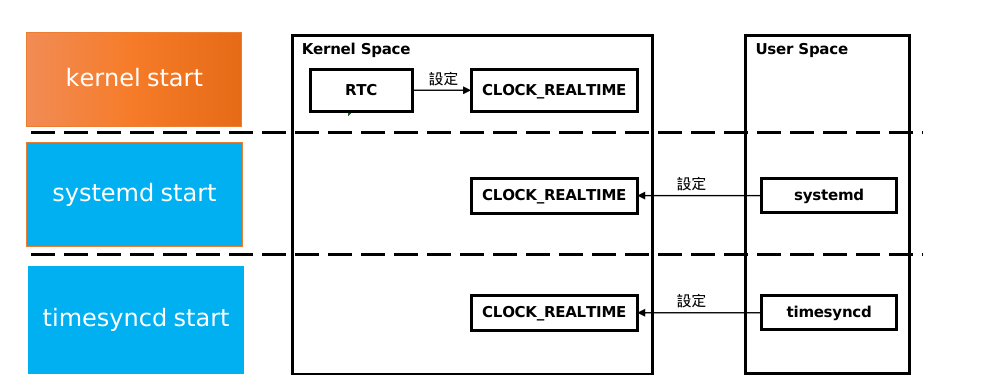

1.1 内核启动阶段
这里是在menuconfig文件配置RTC设定系统时间选项。
CONFIG_RTC_HCTOSYS_DEVICE="rtc1",或者直接在deconfig中添加选项。
没选就不会设置,我猜默认1970-XX-XXX。(因为很久以前看的,没有笔记习惯,所以具体逻辑忘记了)
1.2 systemd启动
int clock_apply_epoch(ClockChangeDirection *ret_attempted_change) { struct stat st; struct timespec ts; usec_t epoch_usec, now_usec; /* NB: we update *ret_attempted_change in *all* cases, both * on success and failure, to indicate what we intended to do! */ assert(ret_attempted_change); if (stat(EPOCH_FILE, &st) < 0) { if (errno != ENOENT) log_warning_errno(errno, "Cannot stat " EPOCH_FILE ": %m"); epoch_usec = (usec_t) TIME_EPOCH * USEC_PER_SEC; } else epoch_usec = timespec_load(&st.st_mtim); now_usec = now(CLOCK_REALTIME); if (now_usec < epoch_usec) *ret_attempted_change = CLOCK_CHANGE_FORWARD; else if (now_usec > usec_add(epoch_usec, CLOCK_VALID_RANGE_USEC_MAX)) *ret_attempted_change = CLOCK_CHANGE_BACKWARD; else { *ret_attempted_change = CLOCK_CHANGE_NOOP; return 0; } if (clock_settime(CLOCK_REALTIME, timespec_store(&ts, epoch_usec)) < 0) return -errno; return 1; }
systemd版本应该是250。
默认的情况下,在编译systemd的时候会记录一个编译时间。
没有特别设置而且是git下来的情况应该是git log中的最近的一次提交记录。
如果不是git 的,使用的是NEW文件的修改时间。
参照:meson.build(systemd的Build文件)
上面记录的时间 > RTC的时间 就会重新设置系统时间。
上面记录的时间 < RTC的时间 保持不变(具体还会判断一下可以超过太多也是不行的)。
参照:src/shared/clock-util.c(int clock_apply_epoch(ClockChangeDirection *ret_attempted_change))
1.3 timesyncd启动
static int load_clock_timestamp(uid_t uid, gid_t gid) { _cleanup_close_ int fd = -1; usec_t min = TIME_EPOCH * USEC_PER_SEC; usec_t ct; int r; /* Let's try to make sure that the clock is always * monotonically increasing, by saving the clock whenever we * have a new NTP time, or when we shut down, and restoring it * when we start again. This is particularly helpful on * systems lacking a battery backed RTC. We also will adjust * the time to at least the build time of systemd. */ fd = open(CLOCK_FILE, O_RDWR|O_CLOEXEC, 0644); if (fd >= 0) { struct stat st; usec_t stamp; /* check if the recorded time is later than the compiled-in one */ r = fstat(fd, &st); if (r >= 0) { stamp = timespec_load(&st.st_mtim); if (stamp > min) min = stamp; } if (geteuid() == 0) { /* Try to fix the access mode, so that we can still touch the file after dropping privileges */ r = fchmod_and_chown(fd, 0644, uid, gid); if (r < 0) log_warning_errno(r, "Failed to chmod or chown %s, ignoring: %m", CLOCK_FILE); } } else { r = mkdir_safe_label(STATE_DIR, 0755, uid, gid, MKDIR_FOLLOW_SYMLINK | MKDIR_WARN_MODE); if (r < 0) { log_debug_errno(r, "Failed to create state directory, ignoring: %m"); goto settime; } /* create stamp file with the compiled-in date */ r = touch_file(CLOCK_FILE, false, min, uid, gid, 0644); if (r < 0) log_debug_errno(r, "Failed to create %s, ignoring: %m", CLOCK_FILE); } settime: ct = now(CLOCK_REALTIME); if (ct < min) { struct timespec ts; char date[FORMAT_TIMESTAMP_MAX]; log_info("System clock time unset or jumped backwards, restoring from recorded timestamp: %s", format_timestamp(date, sizeof(date), min)); if (clock_settime(CLOCK_REALTIME, timespec_store(&ts, min)) < 0) log_error_errno(errno, "Failed to restore system clock, ignoring: %m"); } return 0; }
这里需要启用ntp服务。
timedatectl set-ntp true
没启用ntp时,是不会设置系统时间的。
设置系统时间的逻辑和systemd相同,也是通过比较决定是否设定。
1.4默认的ntp服务器
默认的ntp服务器是google的,国内访问不了,注意改成国内的。
/etc/systemd/timesysncd.conf
ntp.aliyun.com


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号