论文阅读 | MobileNetV2: Inverted Residuals and Linear Bottlenecks
论文阅读 | MobileNetV2: Inverted Residuals and Linear Bottlenecks
Motivation
- MobileNet V2 是对MobileNetV1的一个改进.
- MobileNet V2 主要提出两方面的改进:
- Linear Bottlenecks:在维度较小的 1x1 卷积之后不再采用ReLU操作,避免对特征的破坏。
- Inverted Residuals:与传统resnet结构中先对bottlenecks降维再复原不同,这里先用一个expand layer进行升维,然后再depthwise concolution最后再1x1降维复原。
Depthwise Separable Convolutions
MobileNet V2 依然使用 Depthwise Separable Convolutions 结构,这里不再详细阐述。
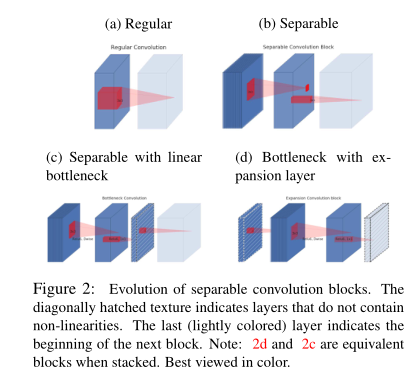
Linear Bottlenecks
对于ReLU函数,文章中有两个结论:
- If the manifold of interest remains non-zero vol-ume after ReLUtransformation, it corresponds toa linear transformation.
- ReLU is capable of preserving complete information about the input manifold, but only if the input manifold lies in a low-dimensional subspace of the input space.
这两个观点为我们优化现有的神经结构提供了一个经验提示:假设感兴趣的流形是低维的,我们可以通过在卷积块中插入线性瓶颈层来捕捉这一点。实验证据表明,使用线性层是至关重要的,因为它可以防止非线性破坏过多的信息。
对于一个输入图像,首先通过一个随机矩阵T将数据转换为n维,然后对这n维数据进行ReLU操作,最后再使用T的逆矩阵转换回来,实验发现当n很小的时候,后面接ReLU非线性变换的话会导致很多信息的丢失。
为了减少信息丢失,就有了文中的linear bottleneck,意思就是bottleneck的最后输出不接非线性激活层,只做linear操作,即维度缩减的那一层不加ReLU.
Inverted Residuals
MobileNet 主要的创新就是使用DepthWise Convolution layer层来降低计算量,但是它提取得到的特征受限于输入的通道数,若是采用以往的residual block,先“压缩”,再卷积提特征,那么DWConv layer可提取得特征就太少了,因此一开始不“压缩”,一开始先“扩张”,本文实验“扩张”倍数为6。 MobileNetV2为 “扩张”→“卷积提特征”→ “压缩”,因此称为Inverted residuals.
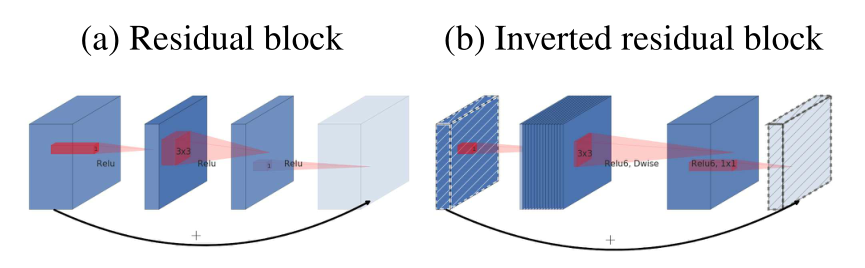
ResNet 与 MobileNet V2 的不同之处为:ResNet是先压缩后扩张,而MobileNet V2 是先扩张后压缩。
MobileNetV2相比MobileNetV1主要多了两点:
- depth-wise convolution之前多了一个1*1的卷积扩张层,提升通道数量,获得更多特征
- 最后不采用ReLU,防止ReLU操作丢失低维特征
参考
1.MobileNetV2: Inverted Residuals and Linear Bottlenecks
2.https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/37851650
3.https://blog.csdn.net/u011995719/article/details/79135818
4.https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/33075914



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号