Linux中ext2文件系统的结构
1、ext2产生的历史
最早的Linux内核是从MINIX系统过渡发展而来的。Linux最早的文件系统就是MINIX文件系统。MINIX文件系统几乎到处都是bug,采用的是16bit偏移量,最大容量为64M,文件名最长为14字符。
Linux内核0.96版本,包含了虚拟文件系统(vitual file system, VFS),VFS中提供了基础的API用于简化扩展新的文件系统——扩展的文件系统(extended file system, ext)基于VFS API。
1992年Linux发布的0.96内核版本拥有了Linux真正意义上的文件系统——扩展的文件系统(The Extended Filesystem, ext),ext采用虚拟文件系统(virtual file system, VFS)即基础的API接口简化扩展的文件系统添加于内核。ext使得单个文件的最大数据容量可达2G,文件名的最大长度扩展到了255个字符。但是ext中不支持文件访问atime,文件内容修改mtime,文件属性修改iNode中的ctime相互独立的时间戳。
为了解决文件的时间戳问题,1993年Linux 0.99版本内核推出,Linux推出了两种新的文件系统:xiafs和ext2(The Second Extended Filesystem).ext2的许多设计理念与Berkeley Fast File System相同,具有扩展的理念,在磁盘数据结构中预留了扩展空间,给将来的新版文件系统的留下了扩展空间。
之后,ext2成了VFS API中许多新扩展的测试平台。例如VFS内含的POSIX访问控制协议草案和扩展属性协议最先内嵌于ext2,归功于ext2的易扩展和易于理解的中断机制。到了Linux的2.6.17内核版本,ext2中的文件最大可达2TB。目前,ext2在闪盘和固态硬盘领域其影响仍由于日志文件系统(ext3/ext4)。因为ext2没有ext3那样额外的日志写操作。因为频繁的写操作,会降低磁盘的使用寿命,相反固态硬盘的寿命因此得以延长。闪盘因为在挂载的时候没有访问时间戳atime,寿命也得意延长。
翻译自维基百科:https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ext2
2、ext2文件系统的结构
在磁盘中,ext2文件系统的结构可以用以下图来描述:
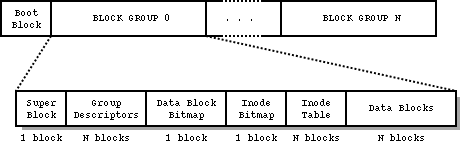
注意:以上是一个磁盘分区,第一个block,是系统启动扇区(boot sector),其余的分区空间都给了ext2文件系统,ext2将该磁盘分区分成了若干个块组(block group 0-N)。
以下是ext2数据结构(ext2_fs.h):

1 /* 2 * linux/include/linux/ext2_fs.h 3 * 4 * Copyright (C) 1992, 1993, 1994, 1995 5 * Remy Card (card@masi.ibp.fr) 6 * Laboratoire MASI - Institut Blaise Pascal 7 * Universite Pierre et Marie Curie (Paris VI) 8 * 9 * from 10 * 11 * linux/include/linux/minix_fs.h 12 * 13 * Copyright (C) 1991, 1992 Linus Torvalds 14 */ 15 16 #ifndef _LINUX_EXT2_FS_H 17 #define _LINUX_EXT2_FS_H 18 19 #include <linux/types.h> 20 21 /* 22 * The second extended filesystem constants/structures 23 */ 24 25 /* 26 * Define EXT2FS_DEBUG to produce debug messages 27 */ 28 #undef EXT2FS_DEBUG 29 30 /* 31 * Define EXT2_PREALLOCATE to preallocate data blocks for expanding files 32 */ 33 #define EXT2_PREALLOCATE 34 #define EXT2_DEFAULT_PREALLOC_BLOCKS 8 35 36 /* 37 * The second extended file system version 38 */ 39 #define EXT2FS_DATE "95/08/09" 40 #define EXT2FS_VERSION "0.5b" 41 42 /* 43 * Debug code 44 */ 45 #ifdef EXT2FS_DEBUG 46 # define ext2_debug(f, a...) { \ 47 printk ("EXT2-fs DEBUG (%s, %d): %s:", \ 48 __FILE__, __LINE__, __FUNCTION__); \ 49 printk (f, ## a); \ 50 } 51 #else 52 # define ext2_debug(f, a...) /**/ 53 #endif 54 55 /* 56 * Special inode numbers 57 */ 58 #define EXT2_BAD_INO 1 /* Bad blocks inode */ 59 #define EXT2_ROOT_INO 2 /* Root inode */ 60 #define EXT2_ACL_IDX_INO 3 /* ACL inode */ 61 #define EXT2_ACL_DATA_INO 4 /* ACL inode */ 62 #define EXT2_BOOT_LOADER_INO 5 /* Boot loader inode */ 63 #define EXT2_UNDEL_DIR_INO 6 /* Undelete directory inode */ 64 65 /* First non-reserved inode for old ext2 filesystems */ 66 #define EXT2_GOOD_OLD_FIRST_INO 11 67 68 /* 69 * The second extended file system magic number 70 */ 71 #define EXT2_SUPER_MAGIC 0xEF53 72 73 /* 74 * Maximal count of links to a file 75 */ 76 #define EXT2_LINK_MAX 32000 77 78 /* 79 * Macro-instructions used to manage several block sizes 80 */ 81 #define EXT2_MIN_BLOCK_SIZE 1024 82 #define EXT2_MAX_BLOCK_SIZE 4096 83 #define EXT2_MIN_BLOCK_LOG_SIZE 10 84 #ifdef __KERNEL__ 85 # define EXT2_BLOCK_SIZE(s) ((s)->s_blocksize) 86 #else 87 # define EXT2_BLOCK_SIZE(s) (EXT2_MIN_BLOCK_SIZE << (s)->s_log_block_size) 88 #endif 89 #define EXT2_ACLE_PER_BLOCK(s) (EXT2_BLOCK_SIZE(s) / sizeof (struct ext2_acl_entry)) 90 #define EXT2_ADDR_PER_BLOCK(s) (EXT2_BLOCK_SIZE(s) / sizeof (__u32)) 91 #ifdef __KERNEL__ 92 # define EXT2_BLOCK_SIZE_BITS(s) ((s)->s_blocksize_bits) 93 #else 94 # define EXT2_BLOCK_SIZE_BITS(s) ((s)->s_log_block_size + 10) 95 #endif 96 #ifdef __KERNEL__ 97 #define EXT2_ADDR_PER_BLOCK_BITS(s) ((s)->u.ext2_sb.s_addr_per_block_bits) 98 #define EXT2_INODE_SIZE(s) ((s)->u.ext2_sb.s_inode_size) 99 #define EXT2_FIRST_INO(s) ((s)->u.ext2_sb.s_first_ino) 100 #else 101 #define EXT2_INODE_SIZE(s) (((s)->s_rev_level == EXT2_GOOD_OLD_REV) ? \ 102 EXT2_GOOD_OLD_INODE_SIZE : \ 103 (s)->s_inode_size) 104 #define EXT2_FIRST_INO(s) (((s)->s_rev_level == EXT2_GOOD_OLD_REV) ? \ 105 EXT2_GOOD_OLD_FIRST_INO : \ 106 (s)->s_first_ino) 107 #endif 108 109 /* 110 * Macro-instructions used to manage fragments 111 */ 112 #define EXT2_MIN_FRAG_SIZE 1024 113 #define EXT2_MAX_FRAG_SIZE 4096 114 #define EXT2_MIN_FRAG_LOG_SIZE 10 115 #ifdef __KERNEL__ 116 # define EXT2_FRAG_SIZE(s) ((s)->u.ext2_sb.s_frag_size) 117 # define EXT2_FRAGS_PER_BLOCK(s) ((s)->u.ext2_sb.s_frags_per_block) 118 #else 119 # define EXT2_FRAG_SIZE(s) (EXT2_MIN_FRAG_SIZE << (s)->s_log_frag_size) 120 # define EXT2_FRAGS_PER_BLOCK(s) (EXT2_BLOCK_SIZE(s) / EXT2_FRAG_SIZE(s)) 121 #endif 122 123 /* 124 * ACL structures 125 */ 126 struct ext2_acl_header /* Header of Access Control Lists */ 127 { 128 __u32 aclh_size; 129 __u32 aclh_file_count; 130 __u32 aclh_acle_count; 131 __u32 aclh_first_acle; 132 }; 133 134 struct ext2_acl_entry /* Access Control List Entry */ 135 { 136 __u32 acle_size; 137 __u16 acle_perms; /* Access permissions */ 138 __u16 acle_type; /* Type of entry */ 139 __u16 acle_tag; /* User or group identity */ 140 __u16 acle_pad1; 141 __u32 acle_next; /* Pointer on next entry for the */ 142 /* same inode or on next free entry */ 143 }; 144 145 /* 146 * Structure of a blocks group descriptor 147 */ 148 struct ext2_group_desc 149 { 150 __u32 bg_block_bitmap; /* Blocks bitmap block */ 151 __u32 bg_inode_bitmap; /* Inodes bitmap block */ 152 __u32 bg_inode_table; /* Inodes table block */ 153 __u16 bg_free_blocks_count; /* Free blocks count */ 154 __u16 bg_free_inodes_count; /* Free inodes count */ 155 __u16 bg_used_dirs_count; /* Directories count */ 156 __u16 bg_pad; 157 __u32 bg_reserved[3]; 158 }; 159 160 /* 161 * Macro-instructions used to manage group descriptors 162 */ 163 #ifdef __KERNEL__ 164 # define EXT2_BLOCKS_PER_GROUP(s) ((s)->u.ext2_sb.s_blocks_per_group) 165 # define EXT2_DESC_PER_BLOCK(s) ((s)->u.ext2_sb.s_desc_per_block) 166 # define EXT2_INODES_PER_GROUP(s) ((s)->u.ext2_sb.s_inodes_per_group) 167 # define EXT2_DESC_PER_BLOCK_BITS(s) ((s)->u.ext2_sb.s_desc_per_block_bits) 168 #else 169 # define EXT2_BLOCKS_PER_GROUP(s) ((s)->s_blocks_per_group) 170 # define EXT2_DESC_PER_BLOCK(s) (EXT2_BLOCK_SIZE(s) / sizeof (struct ext2_group_desc)) 171 # define EXT2_INODES_PER_GROUP(s) ((s)->s_inodes_per_group) 172 #endif 173 174 /* 175 * Constants relative to the data blocks 176 */ 177 #define EXT2_NDIR_BLOCKS 12 178 #define EXT2_IND_BLOCK EXT2_NDIR_BLOCKS 179 #define EXT2_DIND_BLOCK (EXT2_IND_BLOCK + 1) 180 #define EXT2_TIND_BLOCK (EXT2_DIND_BLOCK + 1) 181 #define EXT2_N_BLOCKS (EXT2_TIND_BLOCK + 1) 182 183 /* 184 * Inode flags 185 */ 186 #define EXT2_SECRM_FL 0x00000001 /* Secure deletion */ 187 #define EXT2_UNRM_FL 0x00000002 /* Undelete */ 188 #define EXT2_COMPR_FL 0x00000004 /* Compress file */ 189 #define EXT2_SYNC_FL 0x00000008 /* Synchronous updates */ 190 #define EXT2_IMMUTABLE_FL 0x00000010 /* Immutable file */ 191 #define EXT2_APPEND_FL 0x00000020 /* writes to file may only append */ 192 #define EXT2_NODUMP_FL 0x00000040 /* do not dump file */ 193 #define EXT2_NOATIME_FL 0x00000080 /* do not update atime */ 194 /* Reserved for compression usage... */ 195 #define EXT2_DIRTY_FL 0x00000100 196 #define EXT2_COMPRBLK_FL 0x00000200 /* One or more compressed clusters */ 197 #define EXT2_NOCOMP_FL 0x00000400 /* Don't compress */ 198 #define EXT2_ECOMPR_FL 0x00000800 /* Compression error */ 199 /* End compression flags --- maybe not all used */ 200 #define EXT2_BTREE_FL 0x00001000 /* btree format dir */ 201 #define EXT2_RESERVED_FL 0x80000000 /* reserved for ext2 lib */ 202 203 #define EXT2_FL_USER_VISIBLE 0x00001FFF /* User visible flags */ 204 #define EXT2_FL_USER_MODIFIABLE 0x000000FF /* User modifiable flags */ 205 206 /* 207 * ioctl commands 208 */ 209 #define EXT2_IOC_GETFLAGS _IOR('f', 1, long) 210 #define EXT2_IOC_SETFLAGS _IOW('f', 2, long) 211 #define EXT2_IOC_GETVERSION _IOR('v', 1, long) 212 #define EXT2_IOC_SETVERSION _IOW('v', 2, long) 213 214 /* 215 * Structure of an inode on the disk 216 */ 217 struct ext2_inode { 218 __u16 i_mode; /* File mode */ 219 __u16 i_uid; /* Low 16 bits of Owner Uid */ 220 __u32 i_size; /* Size in bytes */ 221 __u32 i_atime; /* Access time */ 222 __u32 i_ctime; /* Creation time */ 223 __u32 i_mtime; /* Modification time */ 224 __u32 i_dtime; /* Deletion Time */ 225 __u16 i_gid; /* Low 16 bits of Group Id */ 226 __u16 i_links_count; /* Links count */ 227 __u32 i_blocks; /* Blocks count */ 228 __u32 i_flags; /* File flags */ 229 union { 230 struct { 231 __u32 l_i_reserved1; 232 } linux1; 233 struct { 234 __u32 h_i_translator; 235 } hurd1; 236 struct { 237 __u32 m_i_reserved1; 238 } masix1; 239 } osd1; /* OS dependent 1 */ 240 __u32 i_block[EXT2_N_BLOCKS];/* Pointers to blocks */ 241 __u32 i_generation; /* File version (for NFS) */ 242 __u32 i_file_acl; /* File ACL */ 243 __u32 i_dir_acl; /* Directory ACL */ 244 __u32 i_faddr; /* Fragment address */ 245 union { 246 struct { 247 __u8 l_i_frag; /* Fragment number */ 248 __u8 l_i_fsize; /* Fragment size */ 249 __u16 i_pad1; 250 __u16 l_i_uid_high; /* these 2 fields */ 251 __u16 l_i_gid_high; /* were reserved2[0] */ 252 __u32 l_i_reserved2; 253 } linux2; 254 struct { 255 __u8 h_i_frag; /* Fragment number */ 256 __u8 h_i_fsize; /* Fragment size */ 257 __u16 h_i_mode_high; 258 __u16 h_i_uid_high; 259 __u16 h_i_gid_high; 260 __u32 h_i_author; 261 } hurd2; 262 struct { 263 __u8 m_i_frag; /* Fragment number */ 264 __u8 m_i_fsize; /* Fragment size */ 265 __u16 m_pad1; 266 __u32 m_i_reserved2[2]; 267 } masix2; 268 } osd2; /* OS dependent 2 */ 269 }; 270 271 #define i_size_high i_dir_acl 272 273 #if defined(__KERNEL__) || defined(__linux__) 274 #define i_reserved1 osd1.linux1.l_i_reserved1 275 #define i_frag osd2.linux2.l_i_frag 276 #define i_fsize osd2.linux2.l_i_fsize 277 #define i_uid_low i_uid 278 #define i_gid_low i_gid 279 #define i_uid_high osd2.linux2.l_i_uid_high 280 #define i_gid_high osd2.linux2.l_i_gid_high 281 #define i_reserved2 osd2.linux2.l_i_reserved2 282 #endif 283 284 #ifdef __hurd__ 285 #define i_translator osd1.hurd1.h_i_translator 286 #define i_frag osd2.hurd2.h_i_frag; 287 #define i_fsize osd2.hurd2.h_i_fsize; 288 #define i_uid_high osd2.hurd2.h_i_uid_high 289 #define i_gid_high osd2.hurd2.h_i_gid_high 290 #define i_author osd2.hurd2.h_i_author 291 #endif 292 293 #ifdef __masix__ 294 #define i_reserved1 osd1.masix1.m_i_reserved1 295 #define i_frag osd2.masix2.m_i_frag 296 #define i_fsize osd2.masix2.m_i_fsize 297 #define i_reserved2 osd2.masix2.m_i_reserved2 298 #endif 299 300 /* 301 * File system states 302 */ 303 #define EXT2_VALID_FS 0x0001 /* Unmounted cleanly */ 304 #define EXT2_ERROR_FS 0x0002 /* Errors detected */ 305 306 /* 307 * Mount flags 308 */ 309 #define EXT2_MOUNT_CHECK 0x0001 /* Do mount-time checks */ 310 #define EXT2_MOUNT_GRPID 0x0004 /* Create files with directory's group */ 311 #define EXT2_MOUNT_DEBUG 0x0008 /* Some debugging messages */ 312 #define EXT2_MOUNT_ERRORS_CONT 0x0010 /* Continue on errors */ 313 #define EXT2_MOUNT_ERRORS_RO 0x0020 /* Remount fs ro on errors */ 314 #define EXT2_MOUNT_ERRORS_PANIC 0x0040 /* Panic on errors */ 315 #define EXT2_MOUNT_MINIX_DF 0x0080 /* Mimics the Minix statfs */ 316 #define EXT2_MOUNT_NO_UID32 0x0200 /* Disable 32-bit UIDs */ 317 318 #define clear_opt(o, opt) o &= ~EXT2_MOUNT_##opt 319 #define set_opt(o, opt) o |= EXT2_MOUNT_##opt 320 #define test_opt(sb, opt) ((sb)->u.ext2_sb.s_mount_opt & \ 321 EXT2_MOUNT_##opt) 322 /* 323 * Maximal mount counts between two filesystem checks 324 */ 325 #define EXT2_DFL_MAX_MNT_COUNT 20 /* Allow 20 mounts */ 326 #define EXT2_DFL_CHECKINTERVAL 0 /* Don't use interval check */ 327 328 /* 329 * Behaviour when detecting errors 330 */ 331 #define EXT2_ERRORS_CONTINUE 1 /* Continue execution */ 332 #define EXT2_ERRORS_RO 2 /* Remount fs read-only */ 333 #define EXT2_ERRORS_PANIC 3 /* Panic */ 334 #define EXT2_ERRORS_DEFAULT EXT2_ERRORS_CONTINUE 335 336 /* 337 * Structure of the super block 338 */ 339 struct ext2_super_block { 340 __u32 s_inodes_count; /* Inodes count */ 341 __u32 s_blocks_count; /* Blocks count */ 342 __u32 s_r_blocks_count; /* Reserved blocks count */ 343 __u32 s_free_blocks_count; /* Free blocks count */ 344 __u32 s_free_inodes_count; /* Free inodes count */ 345 __u32 s_first_data_block; /* First Data Block */ 346 __u32 s_log_block_size; /* Block size */ 347 __s32 s_log_frag_size; /* Fragment size */ 348 __u32 s_blocks_per_group; /* # Blocks per group */ 349 __u32 s_frags_per_group; /* # Fragments per group */ 350 __u32 s_inodes_per_group; /* # Inodes per group */ 351 __u32 s_mtime; /* Mount time */ 352 __u32 s_wtime; /* Write time */ 353 __u16 s_mnt_count; /* Mount count */ 354 __s16 s_max_mnt_count; /* Maximal mount count */ 355 __u16 s_magic; /* Magic signature */ 356 __u16 s_state; /* File system state */ 357 __u16 s_errors; /* Behaviour when detecting errors */ 358 __u16 s_minor_rev_level; /* minor revision level */ 359 __u32 s_lastcheck; /* time of last check */ 360 __u32 s_checkinterval; /* max. time between checks */ 361 __u32 s_creator_os; /* OS */ 362 __u32 s_rev_level; /* Revision level */ 363 __u16 s_def_resuid; /* Default uid for reserved blocks */ 364 __u16 s_def_resgid; /* Default gid for reserved blocks */ 365 /* 366 * These fields are for EXT2_DYNAMIC_REV superblocks only. 367 * 368 * Note: the difference between the compatible feature set and 369 * the incompatible feature set is that if there is a bit set 370 * in the incompatible feature set that the kernel doesn't 371 * know about, it should refuse to mount the filesystem. 372 * 373 * e2fsck's requirements are more strict; if it doesn't know 374 * about a feature in either the compatible or incompatible 375 * feature set, it must abort and not try to meddle with 376 * things it doesn't understand... 377 */ 378 __u32 s_first_ino; /* First non-reserved inode */ 379 __u16 s_inode_size; /* size of inode structure */ 380 __u16 s_block_group_nr; /* block group # of this superblock */ 381 __u32 s_feature_compat; /* compatible feature set */ 382 __u32 s_feature_incompat; /* incompatible feature set */ 383 __u32 s_feature_ro_compat; /* readonly-compatible feature set */ 384 __u8 s_uuid[16]; /* 128-bit uuid for volume */ 385 char s_volume_name[16]; /* volume name */ 386 char s_last_mounted[64]; /* directory where last mounted */ 387 __u32 s_algorithm_usage_bitmap; /* For compression */ 388 /* 389 * Performance hints. Directory preallocation should only 390 * happen if the EXT2_COMPAT_PREALLOC flag is on. 391 */ 392 __u8 s_prealloc_blocks; /* Nr of blocks to try to preallocate*/ 393 __u8 s_prealloc_dir_blocks; /* Nr to preallocate for dirs */ 394 __u16 s_padding1; 395 __u32 s_reserved[204]; /* Padding to the end of the block */ 396 }; 397 398 #ifdef __KERNEL__ 399 #define EXT2_SB(sb) (&((sb)->u.ext2_sb)) 400 #else 401 /* Assume that user mode programs are passing in an ext2fs superblock, not 402 * a kernel struct super_block. This will allow us to call the feature-test 403 * macros from user land. */ 404 #define EXT2_SB(sb) (sb) 405 #endif 406 407 /* 408 * Codes for operating systems 409 */ 410 #define EXT2_OS_LINUX 0 411 #define EXT2_OS_HURD 1 412 #define EXT2_OS_MASIX 2 413 #define EXT2_OS_FREEBSD 3 414 #define EXT2_OS_LITES 4 415 416 /* 417 * Revision levels 418 */ 419 #define EXT2_GOOD_OLD_REV 0 /* The good old (original) format */ 420 #define EXT2_DYNAMIC_REV 1 /* V2 format w/ dynamic inode sizes */ 421 422 #define EXT2_CURRENT_REV EXT2_GOOD_OLD_REV 423 #define EXT2_MAX_SUPP_REV EXT2_DYNAMIC_REV 424 425 #define EXT2_GOOD_OLD_INODE_SIZE 128 426 427 /* 428 * Feature set definitions 429 */ 430 431 #define EXT2_HAS_COMPAT_FEATURE(sb,mask) \ 432 ( EXT2_SB(sb)->s_es->s_feature_compat & cpu_to_le32(mask) ) 433 #define EXT2_HAS_RO_COMPAT_FEATURE(sb,mask) \ 434 ( EXT2_SB(sb)->s_es->s_feature_ro_compat & cpu_to_le32(mask) ) 435 #define EXT2_HAS_INCOMPAT_FEATURE(sb,mask) \ 436 ( EXT2_SB(sb)->s_es->s_feature_incompat & cpu_to_le32(mask) ) 437 #define EXT2_SET_COMPAT_FEATURE(sb,mask) \ 438 EXT2_SB(sb)->s_es->s_feature_compat |= cpu_to_le32(mask) 439 #define EXT2_SET_RO_COMPAT_FEATURE(sb,mask) \ 440 EXT2_SB(sb)->s_es->s_feature_ro_compat |= cpu_to_le32(mask) 441 #define EXT2_SET_INCOMPAT_FEATURE(sb,mask) \ 442 EXT2_SB(sb)->s_es->s_feature_incompat |= cpu_to_le32(mask) 443 #define EXT2_CLEAR_COMPAT_FEATURE(sb,mask) \ 444 EXT2_SB(sb)->s_es->s_feature_compat &= ~cpu_to_le32(mask) 445 #define EXT2_CLEAR_RO_COMPAT_FEATURE(sb,mask) \ 446 EXT2_SB(sb)->s_es->s_feature_ro_compat &= ~cpu_to_le32(mask) 447 #define EXT2_CLEAR_INCOMPAT_FEATURE(sb,mask) \ 448 EXT2_SB(sb)->s_es->s_feature_incompat &= ~cpu_to_le32(mask) 449 450 #define EXT2_FEATURE_COMPAT_DIR_PREALLOC 0x0001 451 #define EXT2_FEATURE_COMPAT_IMAGIC_INODES 0x0002 452 #define EXT3_FEATURE_COMPAT_HAS_JOURNAL 0x0004 453 #define EXT2_FEATURE_COMPAT_EXT_ATTR 0x0008 454 #define EXT2_FEATURE_COMPAT_RESIZE_INO 0x0010 455 #define EXT2_FEATURE_COMPAT_DIR_INDEX 0x0020 456 #define EXT2_FEATURE_COMPAT_ANY 0xffffffff 457 458 #define EXT2_FEATURE_RO_COMPAT_SPARSE_SUPER 0x0001 459 #define EXT2_FEATURE_RO_COMPAT_LARGE_FILE 0x0002 460 #define EXT2_FEATURE_RO_COMPAT_BTREE_DIR 0x0004 461 #define EXT2_FEATURE_RO_COMPAT_ANY 0xffffffff 462 463 #define EXT2_FEATURE_INCOMPAT_COMPRESSION 0x0001 464 #define EXT2_FEATURE_INCOMPAT_FILETYPE 0x0002 465 #define EXT3_FEATURE_INCOMPAT_RECOVER 0x0004 466 #define EXT3_FEATURE_INCOMPAT_JOURNAL_DEV 0x0008 467 #define EXT2_FEATURE_INCOMPAT_ANY 0xffffffff 468 469 #define EXT2_FEATURE_COMPAT_SUPP 0 470 #define EXT2_FEATURE_INCOMPAT_SUPP EXT2_FEATURE_INCOMPAT_FILETYPE 471 #define EXT2_FEATURE_RO_COMPAT_SUPP (EXT2_FEATURE_RO_COMPAT_SPARSE_SUPER| \ 472 EXT2_FEATURE_RO_COMPAT_LARGE_FILE| \ 473 EXT2_FEATURE_RO_COMPAT_BTREE_DIR) 474 #define EXT2_FEATURE_RO_COMPAT_UNSUPPORTED ~EXT2_FEATURE_RO_COMPAT_SUPP 475 #define EXT2_FEATURE_INCOMPAT_UNSUPPORTED ~EXT2_FEATURE_INCOMPAT_SUPP 476 477 /* 478 * Default values for user and/or group using reserved blocks 479 */ 480 #define EXT2_DEF_RESUID 0 481 #define EXT2_DEF_RESGID 0 482 483 /* 484 * Structure of a directory entry 485 */ 486 #define EXT2_NAME_LEN 255 487 488 struct ext2_dir_entry { 489 __u32 inode; /* Inode number */ 490 __u16 rec_len; /* Directory entry length */ 491 __u16 name_len; /* Name length */ 492 char name[EXT2_NAME_LEN]; /* File name */ 493 }; 494 495 /* 496 * The new version of the directory entry. Since EXT2 structures are 497 * stored in intel byte order, and the name_len field could never be 498 * bigger than 255 chars, it's safe to reclaim the extra byte for the 499 * file_type field. 500 */ 501 struct ext2_dir_entry_2 { 502 __u32 inode; /* Inode number */ 503 __u16 rec_len; /* Directory entry length */ 504 __u8 name_len; /* Name length */ 505 __u8 file_type; 506 char name[EXT2_NAME_LEN]; /* File name */ 507 }; 508 509 /* 510 * Ext2 directory file types. Only the low 3 bits are used. The 511 * other bits are reserved for now. 512 */ 513 enum { 514 EXT2_FT_UNKNOWN, 515 EXT2_FT_REG_FILE, 516 EXT2_FT_DIR, 517 EXT2_FT_CHRDEV, 518 EXT2_FT_BLKDEV, 519 EXT2_FT_FIFO, 520 EXT2_FT_SOCK, 521 EXT2_FT_SYMLINK, 522 EXT2_FT_MAX 523 }; 524 525 /* 526 * EXT2_DIR_PAD defines the directory entries boundaries 527 * 528 * NOTE: It must be a multiple of 4 529 */ 530 #define EXT2_DIR_PAD 4 531 #define EXT2_DIR_ROUND (EXT2_DIR_PAD - 1) 532 #define EXT2_DIR_REC_LEN(name_len) (((name_len) + 8 + EXT2_DIR_ROUND) & \ 533 ~EXT2_DIR_ROUND) 534 535 #ifdef __KERNEL__ 536 /* 537 * Function prototypes 538 */ 539 540 /* 541 * Ok, these declarations are also in <linux/kernel.h> but none of the 542 * ext2 source programs needs to include it so they are duplicated here. 543 */ 544 # define NORET_TYPE /**/ 545 # define ATTRIB_NORET __attribute__((noreturn)) 546 # define NORET_AND noreturn, 547 548 /* balloc.c */ 549 extern int ext2_bg_has_super(struct super_block *sb, int group); 550 extern unsigned long ext2_bg_num_gdb(struct super_block *sb, int group); 551 extern int ext2_new_block (struct inode *, unsigned long, 552 __u32 *, __u32 *, int *); 553 extern void ext2_free_blocks (struct inode *, unsigned long, 554 unsigned long); 555 extern unsigned long ext2_count_free_blocks (struct super_block *); 556 extern void ext2_check_blocks_bitmap (struct super_block *); 557 extern struct ext2_group_desc * ext2_get_group_desc(struct super_block * sb, 558 unsigned int block_group, 559 struct buffer_head ** bh); 560 561 /* dir.c */ 562 extern int ext2_add_link (struct dentry *, struct inode *); 563 extern ino_t ext2_inode_by_name(struct inode *, struct dentry *); 564 extern int ext2_make_empty(struct inode *, struct inode *); 565 extern struct ext2_dir_entry_2 * ext2_find_entry (struct inode *,struct dentry *, struct page **); 566 extern int ext2_delete_entry (struct ext2_dir_entry_2 *, struct page *); 567 extern int ext2_empty_dir (struct inode *); 568 extern struct ext2_dir_entry_2 * ext2_dotdot (struct inode *, struct page **); 569 extern void ext2_set_link(struct inode *, struct ext2_dir_entry_2 *, struct page *, struct inode *); 570 571 /* fsync.c */ 572 extern int ext2_sync_file (struct file *, struct dentry *, int); 573 extern int ext2_fsync_inode (struct inode *, int); 574 575 /* ialloc.c */ 576 extern struct inode * ext2_new_inode (const struct inode *, int); 577 extern void ext2_free_inode (struct inode *); 578 extern unsigned long ext2_count_free_inodes (struct super_block *); 579 extern void ext2_check_inodes_bitmap (struct super_block *); 580 extern unsigned long ext2_count_free (struct buffer_head *, unsigned); 581 582 /* inode.c */ 583 extern void ext2_read_inode (struct inode *); 584 extern void ext2_write_inode (struct inode *, int); 585 extern void ext2_put_inode (struct inode *); 586 extern void ext2_delete_inode (struct inode *); 587 extern int ext2_sync_inode (struct inode *); 588 extern void ext2_discard_prealloc (struct inode *); 589 extern void ext2_truncate (struct inode *); 590 591 /* ioctl.c */ 592 extern int ext2_ioctl (struct inode *, struct file *, unsigned int, 593 unsigned long); 594 595 /* super.c */ 596 extern void ext2_error (struct super_block *, const char *, const char *, ...) 597 __attribute__ ((format (printf, 3, 4))); 598 extern NORET_TYPE void ext2_panic (struct super_block *, const char *, 599 const char *, ...) 600 __attribute__ ((NORET_AND format (printf, 3, 4))); 601 extern void ext2_warning (struct super_block *, const char *, const char *, ...) 602 __attribute__ ((format (printf, 3, 4))); 603 extern void ext2_update_dynamic_rev (struct super_block *sb); 604 extern void ext2_put_super (struct super_block *); 605 extern void ext2_write_super (struct super_block *); 606 extern int ext2_remount (struct super_block *, int *, char *); 607 extern struct super_block * ext2_read_super (struct super_block *,void *,int); 608 extern int ext2_statfs (struct super_block *, struct statfs *); 609 610 /* 611 * Inodes and files operations 612 */ 613 614 /* dir.c */ 615 extern struct file_operations ext2_dir_operations; 616 617 /* file.c */ 618 extern struct inode_operations ext2_file_inode_operations; 619 extern struct file_operations ext2_file_operations; 620 621 /* inode.c */ 622 extern struct address_space_operations ext2_aops; 623 624 /* namei.c */ 625 extern struct inode_operations ext2_dir_inode_operations; 626 627 /* symlink.c */ 628 extern struct inode_operations ext2_fast_symlink_inode_operations; 629 630 #endif /* __KERNEL__ */ 631 632 #endif /* _LINUX_EXT2_FS_H */
2.1 超级块(Super Blook)
超级块的数据结构如下:

336 /* 337 * Structure of the super block 338 */ 339 struct ext2_super_block { 340 __u32 s_inodes_count; /* Inodes count */ 341 __u32 s_blocks_count; /* Blocks count */ 342 __u32 s_r_blocks_count; /* Reserved blocks count */ 343 __u32 s_free_blocks_count; /* Free blocks count */ 344 __u32 s_free_inodes_count; /* Free inodes count */ 345 __u32 s_first_data_block; /* First Data Block */ 346 __u32 s_log_block_size; /* Block size */ 347 __s32 s_log_frag_size; /* Fragment size */ 348 __u32 s_blocks_per_group; /* # Blocks per group */ 349 __u32 s_frags_per_group; /* # Fragments per group */ 350 __u32 s_inodes_per_group; /* # Inodes per group */ 351 __u32 s_mtime; /* Mount time */ 352 __u32 s_wtime; /* Write time */ 353 __u16 s_mnt_count; /* Mount count */ 354 __s16 s_max_mnt_count; /* Maximal mount count */ 355 __u16 s_magic; /* Magic signature */ 356 __u16 s_state; /* File system state */ 357 __u16 s_errors; /* Behaviour when detecting errors */ 358 __u16 s_minor_rev_level; /* minor revision level */ 359 __u32 s_lastcheck; /* time of last check */ 360 __u32 s_checkinterval; /* max. time between checks */ 361 __u32 s_creator_os; /* OS */ 362 __u32 s_rev_level; /* Revision level */ 363 __u16 s_def_resuid; /* Default uid for reserved blocks */ 364 __u16 s_def_resgid; /* Default gid for reserved blocks */ 365 /* 366 * These fields are for EXT2_DYNAMIC_REV superblocks only. 367 * 368 * Note: the difference between the compatible feature set and 369 * the incompatible feature set is that if there is a bit set 370 * in the incompatible feature set that the kernel doesn't 371 * know about, it should refuse to mount the filesystem. 372 * 373 * e2fsck's requirements are more strict; if it doesn't know 374 * about a feature in either the compatible or incompatible 375 * feature set, it must abort and not try to meddle with 376 * things it doesn't understand... 377 */ 378 __u32 s_first_ino; /* First non-reserved inode */ 379 __u16 s_inode_size; /* size of inode structure */ 380 __u16 s_block_group_nr; /* block group # of this superblock */ 381 __u32 s_feature_compat; /* compatible feature set */ 382 __u32 s_feature_incompat; /* incompatible feature set */ 383 __u32 s_feature_ro_compat; /* readonly-compatible feature set */ 384 __u8 s_uuid[16]; /* 128-bit uuid for volume */ 385 char s_volume_name[16]; /* volume name */ 386 char s_last_mounted[64]; /* directory where last mounted */ 387 __u32 s_algorithm_usage_bitmap; /* For compression */ 388 /* 389 * Performance hints. Directory preallocation should only 390 * happen if the EXT2_COMPAT_PREALLOC flag is on. 391 */ 392 __u8 s_prealloc_blocks; /* Nr of blocks to try to preallocate*/ 393 __u8 s_prealloc_dir_blocks; /* Nr to preallocate for dirs */ 394 __u16 s_padding1; 395 __u32 s_reserved[204]; /* Padding to the end of the block */ 396 };
主要的几项描述有:s_inodes_count / s_blocks_count(该分区inode/block总数),s_free_inodes_count / s_free_blocks_count(该分区空闲inode/block数),s_first_data_block(数据块中的起始块位置),s_log_block_size(块大小),s_blocks_per_group(每个块组的块数),s_magic(魔数)
struct ext2_super_block {
__u32 s_inodes_count; /* Inodes count */
__u32 s_blocks_count; /* Blocks count */
...
__u32 s_free_blocks_count; /* Free blocks count */
__u32 s_free_inodes_count; /* Free inodes count */
__u32 s_first_data_block; /* First Data Block */
__u32 s_log_block_size; /* Block size */
...
__u32 s_blocks_per_group; /* # Blocks per group */
...
__u16 s_magic; /* Magic signature */ # ext2的魔数为0xEF53
...
说明:每个块组中都有一份超级块的拷贝。当文件系统挂载时,通常只有块组0中的超级块(主备份)会被读取,其他的块组中的超级块只是作为备份,以防文件系统的崩溃。
2.2 组描述符表(Group Descriptors Table,GDT)
超级块之后就是组描述符表,是由该分区所有的块的组描述符(Group Descriptor)组成的,每个块组描述符记录了本块组的inode/block bitmap和inode table等。块组描述符数据结构如下所示:
struct ext2_group_desc
{
__u32 bg_block_bitmap; /* Blocks bitmap block */
__u32 bg_inode_bitmap; /* Inodes bitmap block */
__u32 bg_inode_table; /* Inodes table block */
__u16 bg_free_blocks_count; /* Free blocks count */
__u16 bg_free_inodes_count; /* Free inodes count */
__u16 bg_used_dirs_count; /* Directories count */
__u16 bg_pad;
__u32 bg_reserved[3];
};
说明:与超级类似,组描述符表也存在各块组中紧接着超级块,其目的与超级块一样,作为备份,防止文件系统的崩溃。
2.3 块位图和inode位图(block/inode bitmap)
位图(bitmap)是位(bit)的序列,每一个位代表该位图所在块组中的一个特定的数据块(block bitmap)或inode table中一个特定的inode(inode bitmap)。当bit为0时,表示对应的block/inode空闲;为1时,表示已被占用。
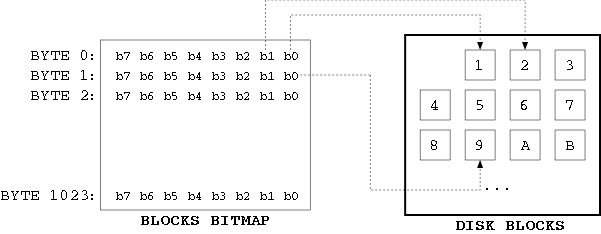
位图始终索引其所在的块组,并且block位图和inode位图均为1block大小,从而限制了该块组的大小。例如一般的block大小为1024bytes,因此一个块组总共有1024*8个block。
2.4 inode表(inode table)
inode表由一系列连续的block块组成,每个块中都预定义了一定数量的inode。inode表的起始块位置(块号)存储在组描述符的bg_inode_table字段中。
系统对inode表中的inode进行编号,从1开始,inode的数据结构被定义在ext2_fs.h文件的struct ext2_inode函数中:

214 /* 215 * Structure of an inode on the disk 216 */ 217 struct ext2_inode { 218 __u16 i_mode; /* File mode */ 219 __u16 i_uid; /* Low 16 bits of Owner Uid */ 220 __u32 i_size; /* Size in bytes */ 221 __u32 i_atime; /* Access time */ 222 __u32 i_ctime; /* Creation time */ 223 __u32 i_mtime; /* Modification time */ 224 __u32 i_dtime; /* Deletion Time */ 225 __u16 i_gid; /* Low 16 bits of Group Id */ 226 __u16 i_links_count; /* Links count */ 227 __u32 i_blocks; /* Blocks count */ 228 __u32 i_flags; /* File flags */ 229 union { 230 struct { 231 __u32 l_i_reserved1; 232 } linux1; 233 struct { 234 __u32 h_i_translator; 235 } hurd1; 236 struct { 237 __u32 m_i_reserved1; 238 } masix1; 239 } osd1; /* OS dependent 1 */ 240 __u32 i_block[EXT2_N_BLOCKS];/* Pointers to blocks */ 241 __u32 i_generation; /* File version (for NFS) */ 242 __u32 i_file_acl; /* File ACL */ 243 __u32 i_dir_acl; /* Directory ACL */ 244 __u32 i_faddr; /* Fragment address */ 245 union { 246 struct { 247 __u8 l_i_frag; /* Fragment number */ 248 __u8 l_i_fsize; /* Fragment size */ 249 __u16 i_pad1; 250 __u16 l_i_uid_high; /* these 2 fields */ 251 __u16 l_i_gid_high; /* were reserved2[0] */ 252 __u32 l_i_reserved2; 253 } linux2; 254 struct { 255 __u8 h_i_frag; /* Fragment number */ 256 __u8 h_i_fsize; /* Fragment size */ 257 __u16 h_i_mode_high; 258 __u16 h_i_uid_high; 259 __u16 h_i_gid_high; 260 __u32 h_i_author; 261 } hurd2; 262 struct { 263 __u8 m_i_frag; /* Fragment number */ 264 __u8 m_i_fsize; /* Fragment size */ 265 __u16 m_pad1; 266 __u32 m_i_reserved2[2]; 267 } masix2; 268 } osd2; /* OS dependent 2 */ 269 };
以下是inode数据结构中比较重要的字段:
struct ext2_inode {
__u16 i_mode; /* File type and access rights */
__u16 i_uid; /* Low 16 bits of Owner Uid */
__u32 i_size; /* Size in bytes */
__u32 i_atime; /* Access time */
__u32 i_ctime; /* Creation time */
__u32 i_mtime; /* Modification time */
__u32 i_dtime; /* Deletion Time */
__u16 i_gid; /* Low 16 bits of Group Id */
__u16 i_links_count; /* Links count */
__u32 i_blocks; /* Blocks count */
__u32 i_flags; /* File flags */
...
__u32 i_block[EXT2_N_BLOCKS]; /* Pointers to blocks */
...
};
i_mode字段中包含了文件的类型和文件的访问权限,被定义在宏文件macro (sys/stat.h)中。
| Sign | Type | Macro |
| - | Regular file | S_ISREG(m) |
| d | Directory | S_ISDIR(m) |
| c | Character Device | S_ISCHR(m) |
| b | Block Device | S_ISBLK(m) |
| f | Fifo | S_ISIFO(m) |
| s | Socket | S_ISSOCK(m) |
| l | Symbolic Link | S_ISLNK(m) |
| Domain | Read | Write | Exec | All |
| User | S_IRUSR | S_IWUSR | S_IXUSR | S_IRWXU |
| Group | S_IRGRP | S_IWGRP | S_IXGRP | S_IRWXG |
| All | S_IROTH | S_IWOTH | S_IXOTH | S_IRWXO |
i_blocks是该inode指向的文件已使用的block数量;指向数据块的指针存储于字段i_block[EXT2_N_BLOCKS]的数组结构中。
变量EXT2_N_BLOCKS定义在ext2_fs.h的第177行中:
174 /*
175 * Constants relative to the data blocks
176 */
177 #define EXT2_NDIR_BLOCKS 12
178 #define EXT2_IND_BLOCK EXT2_NDIR_BLOCKS
179 #define EXT2_DIND_BLOCK (EXT2_IND_BLOCK + 1)
180 #define EXT2_TIND_BLOCK (EXT2_DIND_BLOCK + 1)
181 #define EXT2_N_BLOCKS (EXT2_TIND_BLOCK + 1)
在i_block[]数组中有15个指针,它们所代表的含义如下:
-
i_block[0..11]point directly to the first 12 data blocks of the file. # 序列号0-11的12个元素(指针)指向文件开头的12个数据块 -
i_block[12]points to a single indirect block # 第13号元素指向单索引间接块 -
i_block[13]points to a double indirect block # 第14号元素指向双索引间接块 -
i_block[14]points to a triple indirect block # 第15号元素指向三索引间接块
由此我们可以计算出ext2文件系统单个文件的最大容量(假设block大小为1K),数组i_block[]的长度为32bit/8=4byte:
- 直接索引:12 指针
- 单间接索引:1024/4=256个直接索引,256 指针
- 双间接索引:1024/4=256个单间接索引,256*256 指针
- 三间接索引:1024/4=256个双间接索引,256*256*256 指针
因此可得到12K+256K+64M+16G,即大致为16G。如果block的大小为4K,则文件最大可为4T。(注意:真正决定文件大小的是底层的寄存器,寄存器的位数决定了其寻址的能力)
2.5 inode表中的inode指向的目录文件
inode指向的目录文件需加以注意,我们可以通过测试S_ISDIR(mode) macro来加以识别:
if (S_ISDIR(inode.i_mode)) ...
假设inode指向的块是目录实体/home,目录中的内容包含了一系列的文件名和指向inode表中的对应的,如下图:

目录文件的数据结构如下:
struct ext2_dir_entry_2 {
__u32 inode; /* Inode number */
__u16 rec_len; /* Directory entry length */
__u8 name_len; /* Name length */
__u8 file_type;
char name[EXT2_NAME_LEN]; /* File name */
};
字段file_type总共有0-7可能的值,分别代表: 
目录内容中的各项(实体)的大小是非固定的,大小取决于文件名称的长度。文件名称最大长度为EXT2_NAME_LEN的值,一般为255;文件名称的实际长度存放于字段name_len;rec_len存储的是本目录实体的大小,该字段自然也就决定了下一目录实体的位置了。
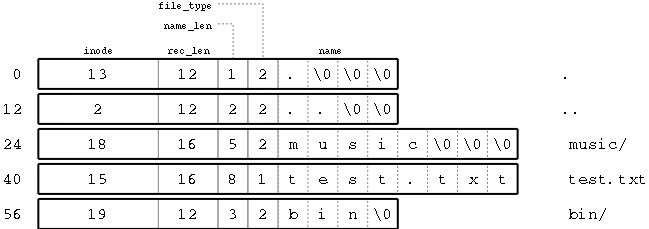 Example of EXT2 directory
Example of EXT2 directory
注意:目录中的inode号,指向的是inode表中的inode,指向data block的是i_block[EXT2_N_BLOCKS]的数组中的指针。
2.6 文件操作(创建、查找、修改、删除)的本质
http://cs.smith.edu/~nhowe/Teaching/csc262/oldlabs/ext2.html
https://www.cnblogs.com/f-ck-need-u/p/7016077.html
待完善...




