软件测试第二周作业 wordcount
Github地址
https://github.com/Anry-Hu/commit1
PSP2.1表格
|
PSP2.1 |
PSP阶段 |
预估耗时 (分钟) |
实际耗时 (分钟) |
|
Planning |
计划 |
||
|
· Estimate |
· 估计这个任务需要多少时间 |
480 | 640 |
|
Development |
开发 |
||
|
· Analysis |
· 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) |
30 | 30 |
|
· Design Spec |
· 生成设计文档 |
- | - |
|
· Design Review |
· 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) |
- | - |
|
· Coding Standard |
· 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) |
- | - |
|
· Design |
· 具体设计 |
30 | 40 |
|
· Coding |
· 具体编码 |
300 | 420 |
|
· Code Review |
· 代码复审 |
30 | 30 |
|
· Test |
· 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) |
60 | 90 |
|
Reporting |
报告 |
||
|
· Test Report |
· 测试报告 |
- | - |
|
· Size Measurement |
· 计算工作量 |
- | - |
|
· Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan |
· 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 |
30 | 30 |
|
合计 |
480 | 640 |
解题思路
编码语言为C++,使用的是VS2017。
总的解题思路:
先将题目分为几个模块:基本功能、扩展功能、文件功能。然后一步步解决。先从基本功能入手,完成之后,再去套用文件,最后加上附加功能和高级功能。
程序实现过程
分函数实现:
通过从文件中读取数据,每读一次就进行一次判断,然后完成相应功能。
字符函数:
这个比较容易,读多少字符就计算多少。
单词函数:
按照最新样例中的需求,我规定的单词划分准则是这样:按照标识符来划分,但是有一定差别,比如一个标识符是从字母开始,遇到(,),,, ,\t,\n就会停止,这里面的内容就为一个标识符。其它符号比如#等与字母一起出现算作一个标识符,单独出现不算一个单词。计算单词数量的方法与原理类似,当遇到字母时,便开始计数,然后停止,以此类推,将文件全部读完,单词数便得到。需要注意的是判断字母停止时,必须加上对文件结尾的判断,不然会陷入死循环。
行数:
这个比较容易,出现一个\n数量就加一,需要注意的是初始行数为1。
代码行/空行/注释行:
首先理解其含义,空行:一行出现的字符少于等于一,通通视为空行,空行与代码行是对立的,并且显然不是注释行,因为注释行的出现必然带两个字符。
其次,了解注释行:有//和/**/出现的地方,都算注释行,但是有时代码会与注释同时出现,如何计算呢?情况分为三种:注释后有代码,比如*/codeline,算作代码行;注释前有代码,比如codeline//,如果代码行只有一个字符,那么整行算作注释行,因为一般是}//如此,所以算注释行易于接受,但是如果代码行的字符大于一,则这一行既算作注释行也算作代码行,因为一般是int c=1;//noteline,很多人写代码喜欢加注释,所以同时算作比较合理;最后一种情况是出错,出错的话算作代码行,比如codeline*/,前面缺少/*。有了注释行的定义,我们便可以计算,//可以直接算,/**/也可以直接算,出现一次\n就加一,然后判断这行的情况,通过一些数据来保存状态,判断可不可取,并且有个int数据专门计算既算注释行又算代码行的行数。
最后,是计算代码行,通过总行数-空行-代码行+既算代码行又算注释行的行,便可以得到答案。
计算停用词表的单词数:
因为已经实现了单词函数,所以这个比较容易实现,先从stoplist.txt里面读取停用词表的词,然后在单词数计算时,进行比较,如果单词和和停用词表的单词一样,那么不进行计算。在这里,停用词表已经给定了,用户不需要输入stoplist.txt,直接使用-e便可。
-s功能的实现:
一开始理解错了-s的功能,把它弄成了递归调用文件,比如说输入指令为-c XX.txt YY.txt,那么只有XX.txt得到调用,如果改为输入-c -s XX.txt YY.txt,那么两个文件都可以得到调用。后面才发现弄错了,这是调用文件夹下的所有合格的文件。这是一个深刻的教训,因为基本上弄好了,不太好改了,所以我这边稍微改了一下功能,通过*.txt来读取所有txt文件,所以,如果你输入 -c *.txt,那么这个文件夹下的所有后缀名为txt的文件都可以得到调用。直接输入*.txt指的是默认文件夹,可以直接将路径写出来。
-o功能的实现:
通过C++的文件输出流,获取文件夹名,然后直接输出便可。
高级功能的实现:
通过io.h里面的函数,将文件夹调用出来,然后进行选择,获取所选文件的名字,然后就可以操作了。
一个小图形界面的实现:
利用MFC做了一个小型图形界面,通过-z功能可以调用,原理是用MFC做成一个exe程序,然后在此程序里用-z来调用这个exe程序,需要用到windows.h的函数。MFC的代码不进行展示了,因为原理类似。
程序实现指令:
通过输入 -c -w -l -a -e -o -x -z 来实现不同的功能。实现方法为:每个功能用一个state来保存状态,然后检测输入指令,如果得到确认,相应的状态也会改变,最后,根据状态来实现功能。如何获取输入的文件名呢?进行判断,如果不是功能指令,就是文件名,然后保存便可。
下面通过代码来进行分析:
#include<iostream> #include<fstream> #include<string> #include<windows.h> #include<commdlg.h> #include<stdio.h> #include<io.h> #include<Windows.h> using namespace std; int num, char_num, word_num, line_num, code_line, blank_line, comment_line, id_num; //储存相应的数目 bool start; //一个开始状态,一些情况需要使用 char token[20], rwtab[10][20]; //token是临时字符组,rwtab来保存停用词表里面的词 bool isLetter(char c) { //判断是否为字母 if ((c >= 'a'&&c <= 'z') || (c >= 'A'&&c <= 'Z')) { return true; } else return false; } bool isDigit(char c) { //判断是否为数字 if (c >= '0'&&c <= '9') { return true; } else return false; } void test_c(char *str) { //字符函数 char c; char_num = 0; //初始化字符的数量 ifstream infile(str); //打开文件 if (!infile) { //检测文件是否打开 cout << "error" << endl; } while ((c = infile.get()) != EOF) { //从文件中读取数据 char_num++; //每读取一个字符就加一 } cout << str << "," << "字符数 = " << char_num << endl; infile.close(); //关闭文件 } void test_w(char *str) { //单词函数 char c; word_num = 0; ifstream infile(str); if (!infile) { cout << "error" << endl; } c = infile.get(); while (c != EOF) { while (c == ' ' || c == '\n' || c == '\t') { //如果是这三个符号就跳过 c = infile.get(); } if (isLetter(c)) { //检测为单词时的处理情况 do { c = infile.get(); //到下面的状态时单词截止 } while (c != '\n'&&c != '\t'&&c != ' '&&c != ';'&&c != ','&&c != '('&&c != ')'&&c != EOF); //标识符 word_num++; //单词数加一 continue; } c = infile.get(); } cout << str << "," << "单词数 = " << word_num << endl; infile.close(); } void test_l(char *str) { //行数函数 char c; line_num = 1; ifstream infile(str); if (!infile) { cout << "error" << endl; } while ((c = infile.get()) != EOF) { if (c == '\n') { line_num++; //出现换行变加一 } } cout << str << "," << "行数 = " << line_num << endl; infile.close(); } void test_ll(char *str) { //行数函数的拷贝函数 char c; line_num = 1; ifstream infile(str); if (!infile) { cout << "error" << endl; } while ((c = infile.get()) != EOF) { if (c == '\n') { line_num++; //这里少了输出 } } infile.close(); } void test_a(char *str) { //代码行/空行/注释行的计算 test_ll(str); //总行数计算 num = 0; code_line = 1; comment_line = 0; //初始化 char c; int sum = 0, sum1 = 0; ifstream infile(str); ifstream infile2(str); if (!infile || !infile2) { cout << "error" << endl; } while ((c = infile.get()) != EOF) { //计算空行 if (c != '\t'&&c != ' ') { num++; } if (c == '\n') { num--; if (num <= 1) { //字符少于等于一便为空行 blank_line++; } num = 0; } } while ((c = infile2.get()) != EOF) { //计算注释行 if (c != '\t'&&c != ' '&&c != '/'&&c != '*') { sum1++; } if (c == '\n') { sum1 = 0; } if (c == '/') { c = infile2.get(); if (c == '/') { comment_line++; if (sum1 > 1) { //本人的划分原则里,有种情况是某行既是注释行也是代码行,这里通过sum1来进行区分,详细的行数划分原则上面已写 sum++; } } else if (c == '*') { comment_line++; if (sum1 > 1) { sum++; } while ((c = infile2.get()) != EOF) { if (c == '\n') { comment_line++; continue; } else if (c == '*') { c = infile2.get(); if (c == '/') { c = infile2.get(); if (c == EOF) { break; } if (c != '\n') { comment_line--; //因为*/codeline是属于代码行,所以出现这种情况时,需要去掉 break; } else { break; } } else { cout << "注释符出错" << endl; } } } } } } code_line = line_num - comment_line - blank_line + sum; //计算代码行的公式 cout << str << "," << "代码行/空行/注释行 = " << code_line << "/" << blank_line << "/" << comment_line << endl; infile.close(); infile2.close(); } void test_e(char *str) { //停用词表的使用,与单词函数大同小异 char c; int m, n, sum; id_num = 0; ifstream infile(str); ifstream infile2("stoplist.txt"); //遍历停用词表 if (!infile || !infile2) { cout << "error" << endl; } m = n = sum = 0; c = infile2.get(); while (c != EOF) { //获取停用词表里面的单词 if (isLetter(c)) { do { rwtab[sum][n++] = c; c = infile2.get(); } while (isLetter(c)); rwtab[sum][n] = '\0'; sum++; n = 0; continue; } c = infile2.get(); } c = infile.get(); while (c != EOF) { for (m = 0; m < 20; m++) { token[m] = '\0'; //临时单词 } m = 0; while (c == ' ' || c == '\n' || c == '\t') { c = infile.get(); } if (isLetter(c)) { do { token[m++] = c; c = infile.get(); } while (isLetter(c) || isDigit(c)); //标识符 token[m] = '\0'; for (n = 0; n < sum; n++) { if (strcmp(token, rwtab[n]) == 0) { //进行比较,如果属于停用词表,则不进行计算 id_num--; break; } } id_num++; continue; } c = infile.get(); } cout << str << "," << "标识符 = " << id_num << endl; infile.close(); infile2.close(); } void test_o(char *str) { //-o输出功能 ofstream outfile(str,ios::app); outfile << "字符数 = " << char_num << endl; outfile << "单词数 = " << word_num << endl; outfile << "行数 = " << line_num << endl; outfile << "代码行/空行/注释行 = " << code_line << "/" << blank_line << "/" << comment_line << endl; outfile << "标识符 = " << id_num << endl; outfile.close(); } void demo() { //测试脚本的实现 ifstream infile("demo.txt"); ifstream infile2("demo.txt"); int numofsum = 1; char ch; char name[10][1000]; //储存文件名 bool s1, s2, s3, s4, s5, s6, s7, s8, s9; //保存每个功能的状态 int sum, num, i; while((ch = infile2.get()) != EOF) { //通过换行符获取指令的数量 if (ch == '\n') { numofsum++; } } for (int j = 0; j < numofsum; j++) { cout << endl << "第" << j + 1 << "条指令:" << endl; s1 = s2 = s3 = s4 = s5 = s6 = s7 = s8 = s9 = false; //初始化 num = sum = 0; while ((ch = infile.get()) != EOF) { //对输入进行检测,并且通过回车结束输入 if (ch == ' ' || ch == '\t') { continue; } else if (ch == '-') { ch = infile.get(); if (ch == 'c') { s1 = true; } else if (ch == 'w') { s2 = true; } else if (ch == 'l') { s3 = true; } else if (ch == 'a') { s4 = true; } else if (ch == 'e') { s5 = true; } else if (ch == 's') { s6 = true; } else if (ch == 'o') { s7 = true; } else if (ch == 'x') { s8 = true; } else if (ch == 'z') { //调用exe程序,调用成功通过语言提示,不直接调用 cout << "调用exe成功!" << endl; break; } } else if (ch == '\n') { break; } else { if (ch == '*') { s9 = true; } name[sum][num++] = ch; while (1) { ch = infile.get(); if (ch == ' ' || ch == '\t' || ch == '\n' || ch == EOF) { break; } else { name[sum][num++] = ch; } } name[sum][num] = '\0'; sum++; num = 0; if (ch == '\n') { break; } } } if (s9 == true) { //*.***功能的使用,遍历所有后缀名为***的文件 const char *to_search = name[0]; //欲查找的文件,支持通配符 start = false; if (sum > 1) { start = true; strcpy(name[9], name[sum - 1]); } long handle; //用于查找的句柄 struct _finddata_t fileinfo; //文件信息的结构体 handle = _findfirst(to_search, &fileinfo); //第一次查找 if (-1 == handle) { return; } sum = 0; strcpy(name[sum++], fileinfo.name); //找到的文件名进行赋值 while (!_findnext(handle, &fileinfo)) //循环查找其他符合的文件,直到找不到其它的为止 { strcpy(name[sum++], fileinfo.name); } if (start == true) { strcpy(name[sum++], name[9]); } _findclose(handle); //关闭句柄 } if (s8 == false) { //进行判断,并且决定调用哪个功能 if (s6 == false && s1 == true && s9 == false) { //如果没有-s,默认只使用第一个文件 test_c(name[0]); } if (s6 == false && s2 == true && s9 == false) { test_w(name[0]); } if (s6 == false && s3 == true && s9 == false) { test_l(name[0]); } if (s6 == false && s4 == true && s9 == false) { test_a(name[0]); } if (s6 == false && s5 == true && s9 == false) { test_e(name[0]); } if (s6 == true || s9 == true) { //有-s,则递归调用文件 if (s7 == false) { for (i = 0; i < sum; i++) { if (s1 == true) { test_c(name[i]); } if (s2 == true) { test_w(name[i]); } if (s3 == true) { test_l(name[i]); } if (s4 == true) { test_a(name[i]); } if (s5 == true) { test_e(name[i]); } } } else if (s7 == true) { for (i = 0; i < sum - 1; i++) { if (s1 == true) { test_c(name[i]); } if (s2 == true) { test_w(name[i]); } if (s3 == true) { test_l(name[i]); } if (s4 == true) { test_a(name[i]); } if (s5 == true) { test_e(name[i]); } cout << "-o功能使用成功" << endl; ofstream outfile(name[sum - 1], ios::app); outfile << name[i] << ":" << endl; outfile.close(); test_o(name[sum - 1]); } } } if (s7 == true && s6 == false) { ofstream outfile(name[sum - 1], ios::app); outfile << name[0] << ":" << endl; outfile.close(); test_o(name[sum - 1]); } } else { //最开始是对-x的判断,因为如果有-x,那么就是自己来选择文件,所以这个功能的判断需要放第一,下面就是调用打开文件程序的代码 cout << "-x功能使用成功" << endl; OPENFILENAME ofn; // 公共对话框结构。 TCHAR szFile[MAX_PATH]; // 保存获取文件名称的缓冲区。 // 初始化选择文件对话框。 ZeroMemory(&ofn, sizeof(OPENFILENAME)); ofn.lStructSize = sizeof(OPENFILENAME); ofn.hwndOwner = NULL; ofn.lpstrFile = szFile; ofn.lpstrFile[0] = '\0'; ofn.nMaxFile = sizeof(szFile); ofn.lpstrFilter = "All(*.*)\0*.*\0Text(*.txt)\0*.TXT\0\0"; ofn.nFilterIndex = 1; ofn.lpstrFileTitle = NULL; ofn.nMaxFileTitle = 0; ofn.lpstrInitialDir = NULL; ofn.Flags = OFN_PATHMUSTEXIST | OFN_FILEMUSTEXIST; //ofn.lpTemplateName = MAKEINTRESOURCE(ID_TEMP_DIALOG); // 显示打开选择文件对话框。 if (GetOpenFileName(&ofn)) { //显示选择的文件。 cout << "成功打开文件:" << szFile << endl; } if (s1 == true) { test_c(szFile); } if (s2 == true) { test_w(szFile); } if (s3 == true) { test_l(szFile); } if (s4 == true) { test_a(szFile); } if (s5 == true) { test_e(szFile); } if (s7 == true) { cout << "-o功能使用成功" << endl; ofstream outfile(name[0]); outfile << szFile << ":" << endl; outfile.close(); test_o(name[0]); } } } infile.close(); infile2.close(); } void main() { char ch; char name[10][1000]; //储存文件名 bool s1, s2, s3, s4, s5, s6, s7, s8, s9, s10; //保存每个功能的状态 s1 = s2 = s3 = s4 = s5 = s6 = s7 = s8 = s9 = s10 = false; //初始化 int sum = 0, i; num = 0; while (1) { //对输入进行检测,并且通过回车结束输入 ch = getchar(); if (ch == ' ' || ch == '\t') { continue; } else if (ch == '-') { ch = getchar(); if (ch == 'c') { s1 = true; } else if (ch == 'w') { s2 = true; } else if (ch == 'l') { s3 = true; } else if (ch == 'a') { s4 = true; } else if (ch == 'e') { s5 = true; } else if (ch == 's') { s6 = true; } else if (ch == 'o') { s7 = true; } else if (ch == 'x') { s8 = true; } else if (ch == 'z') { //调用exe程序 WinExec("MFCtesting.exe", SW_SHOWNORMAL); return; } else if (ch == 'd') { s10 = true; } } else if (ch == '\n') { break; } else { if (ch == '*') { s9 = true; } name[sum][num++] = ch; while (1) { ch = getchar(); if (ch == ' ' || ch == '\t' || ch == '\n') { break; } else { name[sum][num++] = ch; } } name[sum][num] = '\0'; sum++; num = 0; } } if (s10 == true) { demo(); system("pause"); return; } if (s9 == true) { //*.***功能的使用,遍历所有后缀名为***的文件 const char *to_search = name[0]; //欲查找的文件,支持通配符 start = false; if (sum > 1) { start = true; strcpy(name[9], name[sum - 1]); } long handle; //用于查找的句柄 struct _finddata_t fileinfo; //文件信息的结构体 handle = _findfirst(to_search, &fileinfo); //第一次查找 if (-1 == handle) { return; } sum = 0; strcpy(name[sum++], fileinfo.name); //找到的文件名进行赋值 while (!_findnext(handle, &fileinfo)) //循环查找其他符合的文件,直到找不到其它的为止 { strcpy(name[sum++], fileinfo.name); } if (start == true) { strcpy(name[sum++], name[9]); } _findclose(handle); //关闭句柄 } if (s8 == false) { //进行判断,并且决定调用哪个功能 if (s6 == false && s1 == true && s9 == false) { //如果没有-s,默认只使用第一个文件 test_c(name[0]); } if (s6 == false && s2 == true && s9 == false) { test_w(name[0]); } if (s6 == false && s3 == true && s9 == false) { test_l(name[0]); } if (s6 == false && s4 == true && s9 == false) { test_a(name[0]); } if (s6 == false && s5 == true && s9 == false) { test_e(name[0]); } if (s6 == true || s9 == true) { //有-s,则递归调用文件 if (s7 == false) { for (i = 0; i < sum; i++) { if (s1 == true) { test_c(name[i]); } if (s2 == true) { test_w(name[i]); } if (s3 == true) { test_l(name[i]); } if (s4 == true) { test_a(name[i]); } if (s5 == true) { test_e(name[i]); } } } else if (s7 == true) { for (i = 0; i < sum - 1; i++) { if (s1 == true) { test_c(name[i]); } if (s2 == true) { test_w(name[i]); } if (s3 == true) { test_l(name[i]); } if (s4 == true) { test_a(name[i]); } if (s5 == true) { test_e(name[i]); } ofstream outfile(name[sum - 1],ios::app); outfile << name[i] << ":" << endl; outfile.close(); test_o(name[sum - 1]); } } } if (s7 == true && s6 == false) { ofstream outfile(name[sum - 1],ios::app); outfile << name[0] << ":" << endl; outfile.close(); test_o(name[sum - 1]); } } else { //最开始是对-x的判断,因为如果有-x,那么就是自己来选择文件,所以这个功能的判断需要放第一,下面就是调用打开文件程序的代码 OPENFILENAME ofn; // 公共对话框结构。 TCHAR szFile[MAX_PATH]; // 保存获取文件名称的缓冲区。 // 初始化选择文件对话框。 ZeroMemory(&ofn, sizeof(OPENFILENAME)); ofn.lStructSize = sizeof(OPENFILENAME); ofn.hwndOwner = NULL; ofn.lpstrFile = szFile; ofn.lpstrFile[0] = '\0'; ofn.nMaxFile = sizeof(szFile); ofn.lpstrFilter = "All(*.*)\0*.*\0Text(*.txt)\0*.TXT\0\0"; ofn.nFilterIndex = 1; ofn.lpstrFileTitle = NULL; ofn.nMaxFileTitle = 0; ofn.lpstrInitialDir = NULL; ofn.Flags = OFN_PATHMUSTEXIST | OFN_FILEMUSTEXIST; //ofn.lpTemplateName = MAKEINTRESOURCE(ID_TEMP_DIALOG); // 显示打开选择文件对话框。 if (GetOpenFileName(&ofn)) { //显示选择的文件。 cout << "成功打开文件:" << szFile << endl; } if (s1 == true) { test_c(szFile); } if (s2 == true) { test_w(szFile); } if (s3 == true) { test_l(szFile); } if (s4 == true) { test_a(szFile); } if (s5 == true) { test_e(szFile); } if (s7 == true) { ofstream outfile(name[0]); outfile << szFile << ":" << endl; outfile.close(); test_o(name[0]); } } system("pause"); }
测试脚本
思路:因为脚本要求我们自己想,并且不能借助工具和框架,所以我的想法是:将设计好的指令储存在一个文件里,然后读取指令,同时执行,将结果显示在屏幕上,这样,可以同时检查问题。
如何实现?直接通过一个函数来实现,通过输入指令-d,来调用这个函数,函数的代码在上面。
测试设计过程
测试用的.c和.txt文件,我会放入git里面。
-c char.c

-w -l charwithspace.c

-c -w -l char.c charwithspace.c

-c -w -l -s char.c charwithspace.c
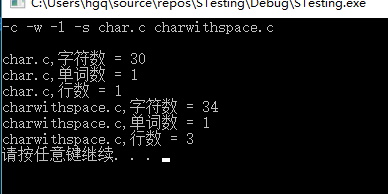
-c char.c -o outfile.txt


-c -w -l -e -a char.c -o outfile.txt
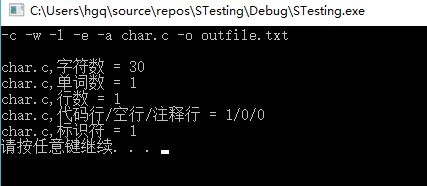

-a atest.c
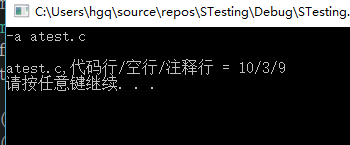
-w wordtest.c
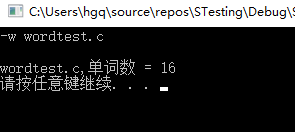
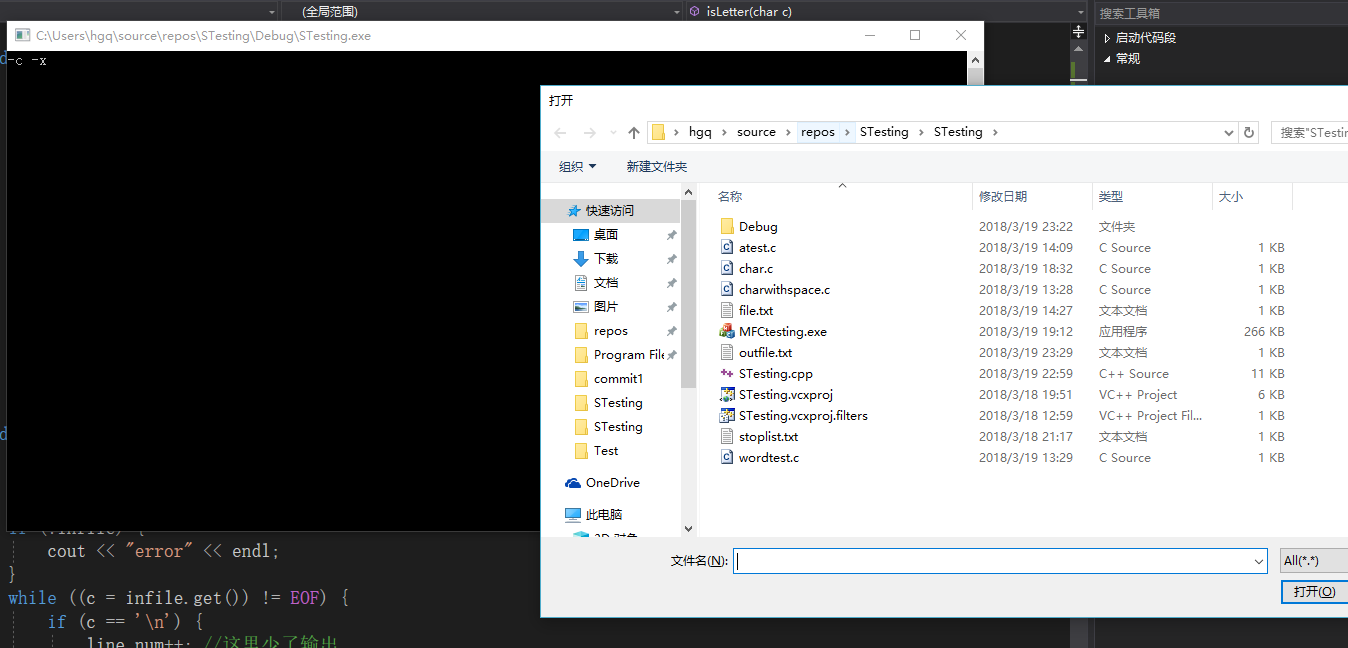
-c -x
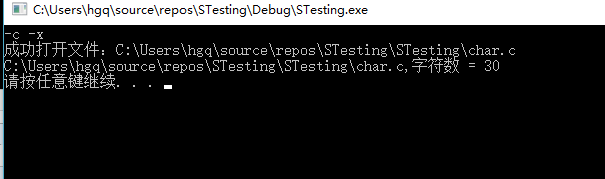
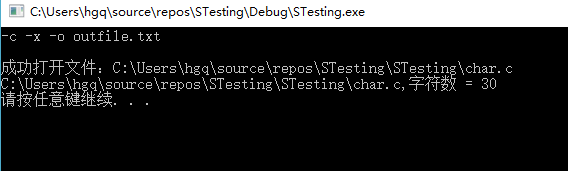
-c -x -o outfile.txt


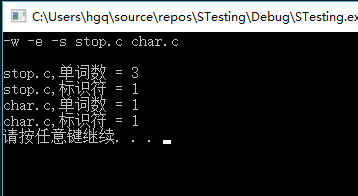
-w -e -s stop.c char.c
-c -w -l -a -e *.c -o outfile.txt

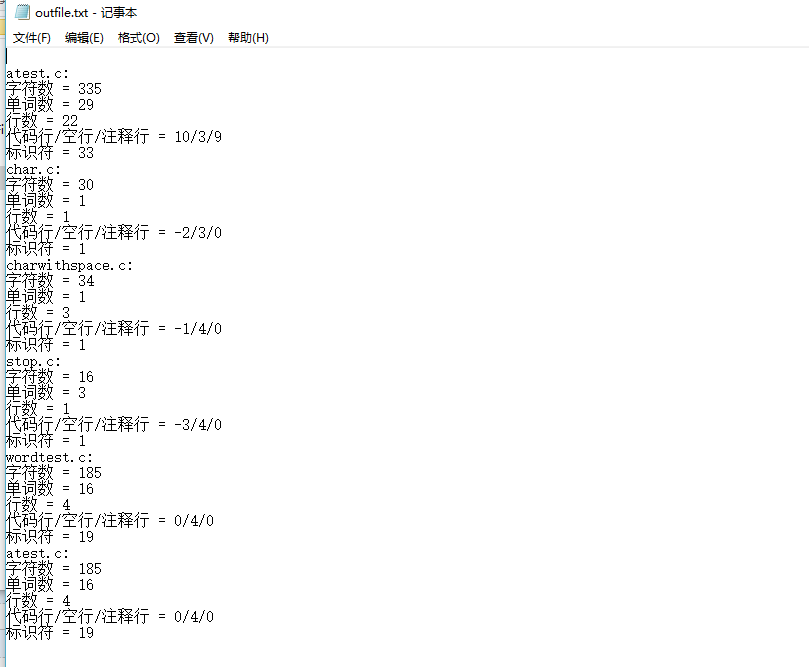
-z(调用exe程序):
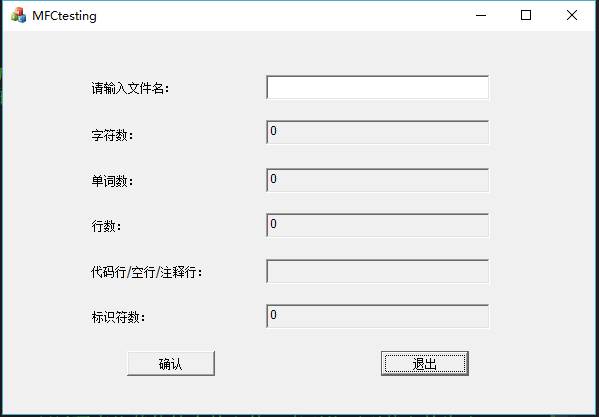
可以用来查找:

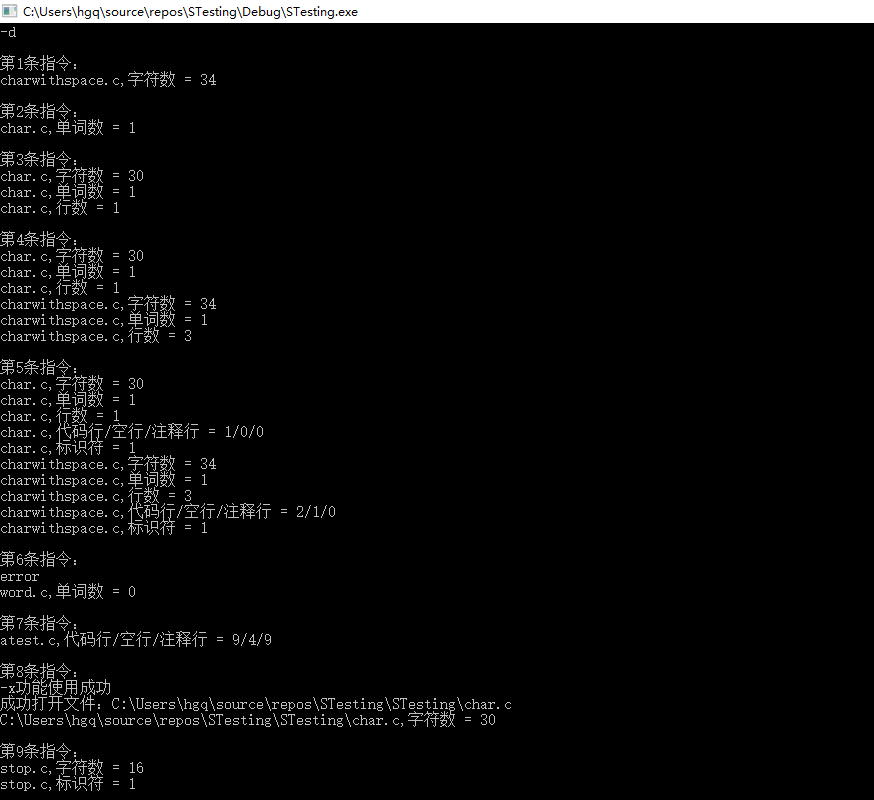
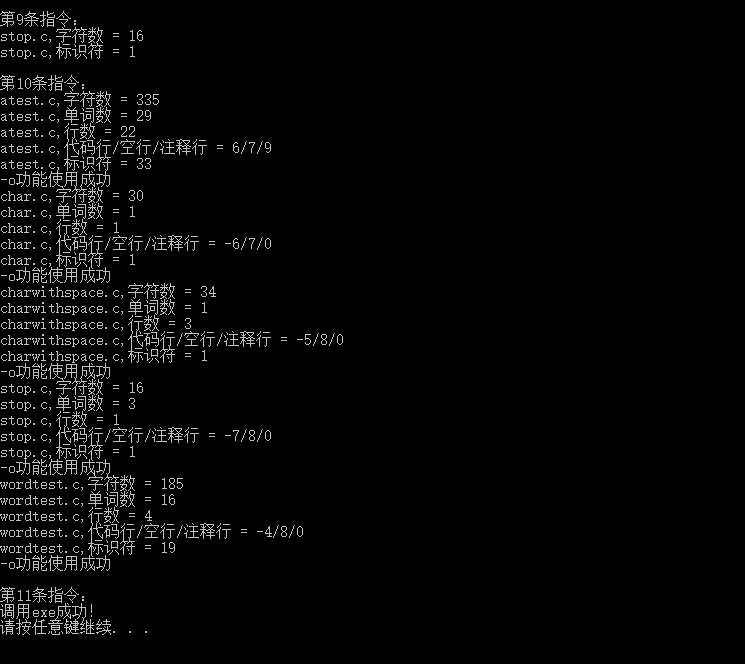
-d(进行测试脚本的测试):
首先展示储存指令的文件:

执行后:
参考文献链接
http://blog.csdn.net/ddffr/article/details/52895457
https://www.cnblogs.com/collectionne/p/6815924.html
https://www.2cto.com/kf/201508/431677.html




