webpack4打包文件结果原理解析
首先上结论,简单来说就是:
- 把解析的所有模块变成一个对象
- 通过一个微入口去按顺序进行加载
- 依次实现一个递归依赖关系
- 通过入口对应的value(方法)去执行文件
一、准备工作
1-首先准备需要打包的demo :
a.js
module.exports = "学习webpack"
Index.js
let str = require('./a.js')
console.log(str);
可以看出,代码的结果是打印 ”学习webpack”
2- 在package.json中进行以下打包指令配置
"scripts": { "build": "webpack --config webpack.config.my.js" },
准备工作做好后就可以执行 npm run build 进行打包了
二、分析文件
在dist目录(打包生成目录)中可以看到生成的bundle.js文件,原文件比较大,精简后可得到以下结果:
现在我们来分析这个文件的打包原理:
(function (modules) { var installedModules = {}; function __webpack_require__(moduleId) { if (installedModules[moduleId]) { return installedModules[moduleId].exports; } var module = (installedModules[moduleId] = { i: moduleId, l: false, exports: {} }); modules[moduleId].call( module.exports, module, module.exports, __webpack_require__ ); module.l = true; return module.exports; } return __webpack_require__((__webpack_require__.s = "./src/index.js")); })({ "./src/a.js": function (module, exports) { eval( 'module.exports = "学习webpack"\n\n//# sourceURL=webpack:///./src/a.js?' ); }, "./src/index.js": function (module, exports, __webpack_require__) { eval( 'let str = __webpack_require__(/*! ./a.js */ "./src/a.js")\r\n\r\nconsole.log(str);\r\n\n\n//# sourceURL=webpack:///./src/index.js?' ); } });
1. 看整体首先是一个匿名自执行函数,这是webpack启动函数
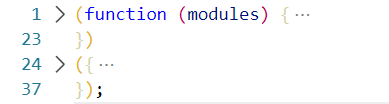
2.执行的时候会传一个对象,对象有几部分,第一部分是我们的key,第二部分是我们的value ;
key -> 当前模块的路径 : value->函数, 将此对象传入module中
({ "./src/a.js": function (module, exports) { eval( 'module.exports = "学习webpack"\n\n//# sourceURL=webpack:///./src/a.js?' ); }, "./src/index.js": function (module, exports, __webpack_require__) { eval( 'let str = __webpack_require__(/*! ./a.js */ "./src/a.js")\r\n\r\nconsole.log(str);\r\n\n\n//# sourceURL=webpack:///./src/index.js?' ); } });
3.先定义一个缓存,模块加载完了从缓存中拿 :
var installedModules = {}; /* 一个对象关系,例如 key -> "./src/index.js" value -> { i: moduleId, l: false, exports: {} } */
4. 实现一个require方法(require是不能在浏览器中运行的) :
function __webpack_require__(moduleId) { // "./src/index.js" // Check if module is in cache - 检查模块是否在缓存中 if (installedModules[moduleId]) { //如果在直接就返回了 return installedModules[moduleId].exports; } // 安装这个模块 // Create a new module (and put it into the cache) var module = (installedModules[moduleId] = { i: moduleId, l: false, exports: {} }); // Execute the module function // 从参数对象中找到那个函数并执行 modules[moduleId].call( module.exports, // this 指向 module, // 模块 module.exports, // 模块空对象 __webpack_require__ // 前面的 require 方法 ); // Flag the module as loaded module.l = true; // Return the exports of the module - 返回的结果 return module.exports; }
5. 在启动函数的结尾去调用 require 方法,
并传入 在webpack.config.js配置文件中设定的入口模块, 这里是 "./src/index.js"

6. 调用参数中入口模块对应的函数方法:
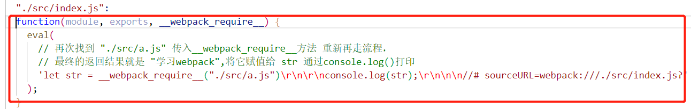
7. 可以看到该方法中存在一次递归关系,将 "./src/a.js" 再次传入require方法中找到以下函数,重走逻辑,找到以下方法:
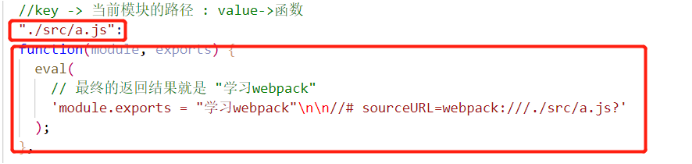
最后附上全注释版本:
//webpack打包出的文件解析 /* 把解析的所有模块变成一个对象 通过一个微入口去按顺序进行加载 依次实现一个递归依赖关系 通过入口对应的value(方法)去执行文件 */ //自执行函数 //对象当作参数传入整个 modules 里 (function(modules) { // webpackBootstrap - webpack启动函数 // The module cache - 先定义一个缓存,模块加载完了从缓存中拿 var installedModules = {}; /* 一个对象关系,例如 key -> "./src/index.js" value -> { i: moduleId, l: false, exports: {} } */ // The require function - 实现一个require方法(require是不能在浏览器中运行的) function __webpack_require__(moduleId) { // "./src/index.js" // Check if module is in cache - 检查模块是否在缓存中 if (installedModules[moduleId]) { //如果在直接就返回了 return installedModules[moduleId].exports; } // 安装这个模块 // Create a new module (and put it into the cache) var module = (installedModules[moduleId] = { i: moduleId, l: false, exports: {} }); // Execute the module function // 从参数对象中找到那个函数并执行 modules[moduleId].call( module.exports, // this 指向 module, // 模块 module.exports, // 模块空对象 __webpack_require__ // 前面的 require 方法 ); // Flag the module as loaded module.l = true; // Return the exports of the module - 返回的结果 return module.exports; } // Load entry module and return exports return __webpack_require__((__webpack_require__.s = "./src/index.js")); //传入入口模块 })({ //key -> 当前模块的路径 : value->函数 "./src/a.js": function(module, exports) { eval( // 最终的返回结果就是 "学习webpack" 'module.exports = "学习webpack"\n\n//# sourceURL=webpack:///./src/a.js?' ); }, "./src/index.js": function(module, exports, __webpack_require__) { eval( // 再次找到 "./src/a.js" 传入__webpack_require__方法 重新再走流程, // 最终的返回结果就是 "学习webpack",将它赋值给 str 通过console.log()打印 'let str = __webpack_require__("./src/a.js")\r\n\r\nconsole.log(str);\r\n\n\n//# sourceURL=webpack:///./src/index.js?' ); } });
本文作者:言叶以上
本文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/anqwjoe/p/12289880.html
版权声明:本作品采用知识共享署名-非商业性使用-禁止演绎 2.5 中国大陆许可协议进行许可。





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步