Leetcode Binary Tree Preorder Traversal
Given a binary tree, return the preorder traversal of its nodes' values.
For example:
Given binary tree {1,#,2,3},
1
\
2
/
3
return [1,2,3].
Note: Recursive solution is trivial, could you do it iteratively?
解题思路:
简单来说,preorder: root - left subtree - right subtree
Depth-first
There are three types of depth-first traversal: pre-order,[1] in-order,[1] and post-order.[1] For a binary tree, they are defined as display operations recursively at each node, starting with the root node, whose algorithm is as follows:[2] [3]
Pre-order
- Display the data part of root element (or current element)
- Traverse the left subtree by recursively calling the pre-order function.
- Traverse the right subtree by recursively calling the pre-order function.
In-order (symmetric)
- Traverse the left subtree by recursively calling the in-order function
- Display the data part of root element (or current element)
- Traverse the right subtree by recursively calling the in-order function
Post-order
- Traverse the left subtree by recursively calling the post-order function.
- Traverse the right subtree by recursively calling the post-order function.
- Display the data part of root element (or current element).
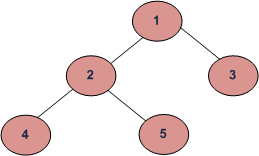 Preorder traversal for the given figure is 1 2 4 5 3.
Preorder traversal for the given figure is 1 2 4 5 3.
两种方法:1)recursive 2) iterative, 用stack
Java code:
1. recursive
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ public class Solution { public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<Integer>(); if(root != null){ result.add(root.val); result.addAll(preorderTraversal(root.left)); result.addAll(preorderTraversal(root.right)); } return result; } }
2. iterative
public class Solution { public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new LinkedList<Integer>(); Stack<TreeNode> s = new Stack<TreeNode>(); if(root == null){ return result; } s.push(root); while(!s.isEmpty()){ TreeNode node = s.pop(); result.add(node.val); if(node.right != null){ s.push(node.right); } if(node.left != null){ s.push(node.left); } } return result; } }
20160602:
recursion:
/** * Definition for a binary tree node. * public class TreeNode { * int val; * TreeNode left; * TreeNode right; * TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } * } */ public class Solution { public List<Integer> preorderTraversal(TreeNode root) { List<Integer> result = new ArrayList<Integer>(); preorderTraversal(root, result); return result; } private void preorderTraversal(TreeNode root, List<Integer> list) { if(root == null) { return; } list.add(root.val); preorderTraversal(root.left, list); preorderTraversal(root.right, list); } }
Reference:
1. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tree_traversal
2. http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/618/
3. https://leetcode.com/discuss/64936/preorder-traversal-java-solution-both-iteration-recursion



