【学习总结】SQL的学习-3-数据查询
参考链接
目录
=======================================================
带关键字查询
带关键字WHERE的查询
-
指定限制条件
-
语法:
SELECT <字段名表>FROM <表或视图名>WHERE <查询条件>
带关键字IN的查询
-
where后的查询条件中,用IN设置指定的数值,并且可以指定多个数值。
-
语法:
-
单个字段:
select * from table_name where field_name in ('xx','xxx');- IN 关键字之后的项目必须用逗号隔开,并且放在括号中;返回field_name为xx和xxx的数据。
-
多个字段:
select * from table_name where (field_name1,field_name2) in ((xx,'abc'),(xxx,'abcde'));- IN指定多个字段时,多个字段放在小括号里,多个字段对应的指定数值也放在小括号的对应位置。
-
-
示例:
-
单个字段-单个指定值:
select * from houses where purchasing_year in ('1997'); -
单个字段-多个指定值:
select * from houses where purchasing_year in ('1997','1998','1999'); -
多个字段-多个指定值:
select id from table where (num,name) in ((num1,'name1'),(num2,'name2'))
-
-
注意:
- 参数要加引号,单双均可;
- 参数太多的话影响效率。
带关键字BETWEEN-AND的范围查询
-
where后的查询条件中,用between-and指定数值的范围,闭区间;
-
语法:
select * from table_name where field_name between 'xyz' and 'abcde';- 返回field_name中数据在xyz和abcde之间的数据,包含两个端点的值。
-
示例:
select * from houses where purchasing_year between '1996' and '1998';- 结果:取出符合1996-1998的数值,包含两个端点。
带关键字LIKE的字符匹配查询
-
where后的查询条件中,用like指定像是某某字符,部分字符匹配;
- 带%:模糊匹配,即前面字符匹配时,后面字符任意;%可以放在字符的前后等任意位置。
- 不带%:精确匹配,即需要全部匹配指定字符,不多不少。
-
语法:
select * from table_name where field_name like '%n%';- 返回field_name中,与'%n%'匹配的数据;%可以放在任意位置。
-
示例:
-
select * from houses where purchasing_year like '19%';- %表示如果前面匹配到了字符19,则后面字符任意,包括0个、一个、多个。
-
select * from houses where purchasing_year like '19';- 没有%,即只有指定字段的值为'19'时才符合。
-
select * from houses where purchasing_year like '%19%';- %放在'19'的前面,%位置表示0个或1个或多个任意字符。
-
带关键字IS NULL空值查询
-
where后的查询条件中,用IS NULL或者IS NOT NULL进行空值或者非空值查询
- 作用:筛选过滤。
-
语法:
select * from table_name where purchasing_year is null / is not null;- 返回符合条件且为空值或者非空值的数据。
-
示例:
-
select * from houses where purchasing_year is null;- 查询空值。
-
select * from houses where purchasing_year is not null;- 查询非空值。
-
带关键字AND的多条件查询
-
where后的查询条件中,用AND连接多条查询条件语句,并返回同时满足多条语句的数据。
-
语法:
select * from table_name where field_name1='x' and field_name2='y';- 返回同时满足两个条件的数据;and可使用多次,以连接多条语句。
-
示例:
-
select * from houses where name='甲' and purchasing_year='1997';- 查询同时符合两个条件的数据。
-
select * from houses where name='甲' and purchasing_year='1997' and location='天河';- 查询同时符合多个条件的数据。
-
带关键字OR的多条件查询
-
where后的查询条件中,用OR连接多条查询条件语句,并返回符合其中任一条件的数据。
-
语法:
select * from table_name where field_name1='x' or field_name2='y';- 返回满足任一条件的数据;or可使用多次,以连接多条语句。
-
示例:
-
select * from houses where name='甲' or purchasing_year='1997';- 查询符合两个条件中任意一条的数据。
-
select * from houses where name='甲' or purchasing_year='1997' or location='天河';- 查询同时符合多个条件中任意一条的数据。
-
select * from houses where name='甲' or (purchasing_year='1997' or location='天河');- AND 和 OR混合嵌套使用。
-
用关键字DISTINCT去除结果集重复行
-
用在select之后,字段名之前,返回去重的结果
-
语法:
select distinct field_name from table_name;- 注意distinct的使用位置:select后,from前,放在字段名前面。
-
示例:
select distinct name from houses;- 将表houses中的字段为name的所有数值去重后返回,避免了某个数值出现多次的情况。
用关键字ORDER BY对查询结果排序
-
用在
select xxx 表名之后,字段名之前,将结果以字段名为准进行排序,可设置正序、逆序。- 注:默认是升序,asc可省略;如需降序,最后添加desc。
- 注:不使用order by排序时,数据的顺序未知,可能和取数据的顺序等有关系。
-
语法:
select * from table_name order by field_name + asc/desc;- 将结果按照指定字段排序后返回,用asc/desc规定按照正序/逆序进行排序。
-
示例:
-
select * from houses order by purchasing_year;- 默认升序,从小到大。
-
select * from houses order by purchasing_year asc;- asc表示升序,从小到大;可省略
-
select * from houses order by purchasing_year desc;- desc表示降序,从大到小。
-
用关键字LIMIT限制查询结果的数量
-
用在select语句的最后,limit+N,N表示展示的语句数量的最大值;如果N>数据总数,仅返回所有数据。
- 注:limit后的参数可以指定起始位置和数据条数。
-
语法:
select * from tableName limit i,n- i:为查询结果的索引值(默认从0开始),当i=0时可省略i; n:为查询结果返回的数量,i与n之间使用英文逗号","隔开
- limit n 等同于 limit 0,n
-
示例:
-
select * from houses limit 2;- 返回两条数据,不写起始位置的索引值,即默认从索引值为0的位置开始,包含索引值为0的数据。
-
select * from houses limit 2,3;- 从索引值为2的位置开始,返回3条数据,包含索引值为2的数据。
-
========================================================
连接查询
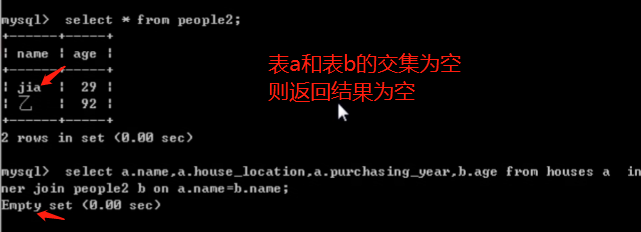
内连接查询
-
概述
- 获取两个表中字段匹配关系的记录。
- 注意:只有两张表都存在的记录才会被查询出来。
-
关键字
- inner join
- on
-
示例
select a.name, a.house_location,a.purchasing_year, b.age from house a /*设置返回结果包含的字段*/inner join people b /*与表b进行内连接*/on a.name = b.name; /*当满足这个条件时返回结果*/

外连接查询
-
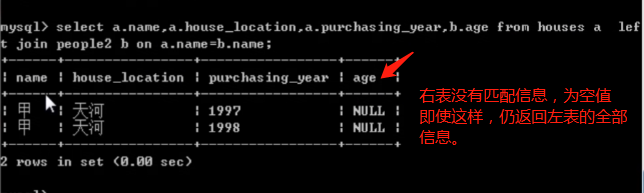
左连接
- 获取左表的所有记录,即使右表没有对应匹配的记录。

- 获取左表的所有记录,即使右表没有对应匹配的记录。
-
左连接关键字与代码示例
- 关键字:left join;on
- 代码示例:
select a.name,a.house_location,a.purchasing_year,b.age from house a left join people b on a.name=b.name;
-
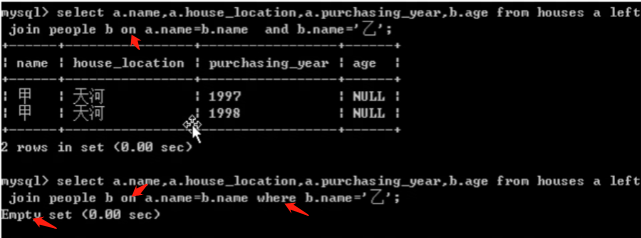
左连接中用on和用where的区别:


-
右连接
- 与left join相反,用于获取右表的所有记录,即使左表没有对应匹配的记录。

- 与left join相反,用于获取右表的所有记录,即使左表没有对应匹配的记录。
-
右连接关键字与代码示例
- right join;on
- 代码示例:
select a.name,a.house_location,a.purchasing_year,b.age from house a right join people b on a.name=b.name;
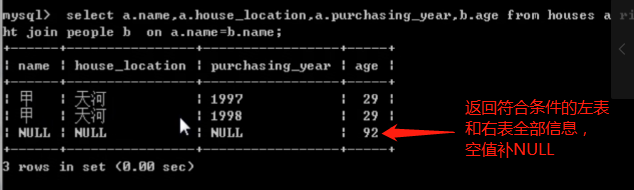
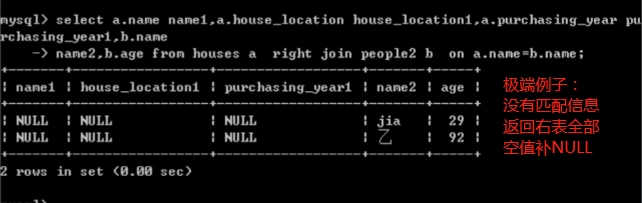
复合连接查询
-
语法:
SELECT A.字段1, B.字段2, C.字段3, D.字段4,FROM 表ALEFT JOIN 表BLEFT JOIN 表CRIGHT JOIN 表DON <查询条件>;
-
示例
select a.name,a.house_location,a.purchasing_year,b.age,c.pricefrom houses ainner join people b /*内连接*/right join housingprice c /*右连接*/on a.name=b.nameand a.house_location=c.house_location;
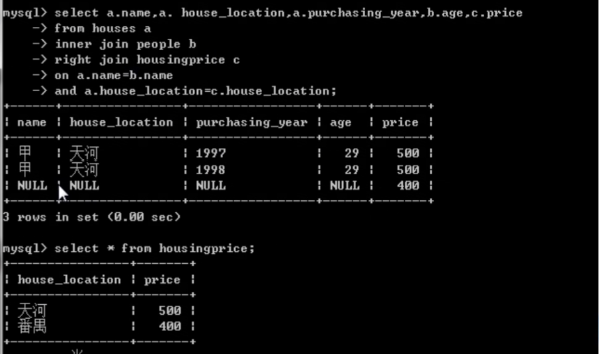
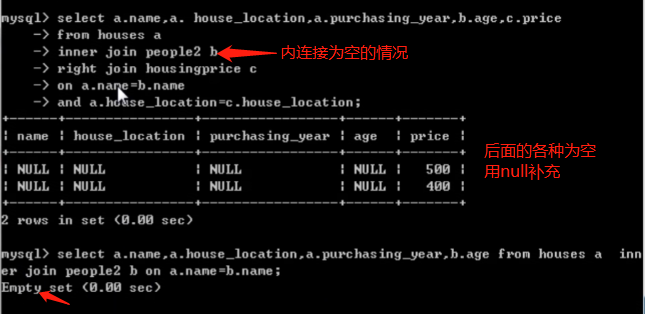
=======================================================
其他类型的查询
子查询/嵌套查询
-
多条查询语句的嵌套。
-
示例:
-
select * from houses where name in (select name from poople where age < 30); /*子句结果的name为甲*/ -
select * from houses where name in (select name from poople where age > 30); /*子句结果为空*/

-
分组查询
-
概述:对查询结果按照某字段进行排序后返回。
-
关键字:group by
-
示例:
select house_location from houses group by house_location;
聚合查询
-
概述:将关键字作为结果的字段之一返回查询结果。
-
关键字:count(), sum(), max(), min()
-
示例
-
select house_location, count(*) as total from houses group by house_location;
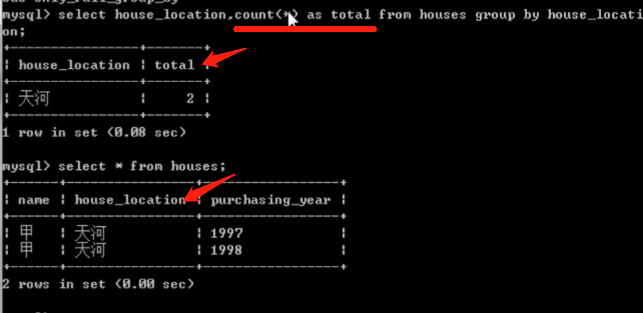
-
select sum(age) from people;
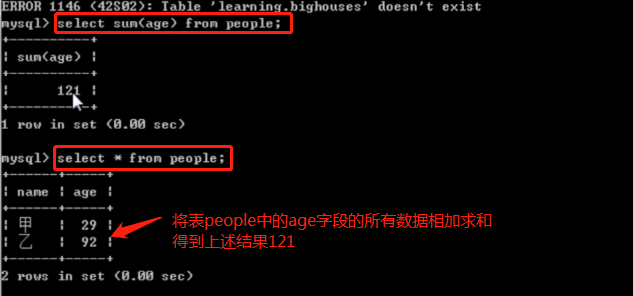
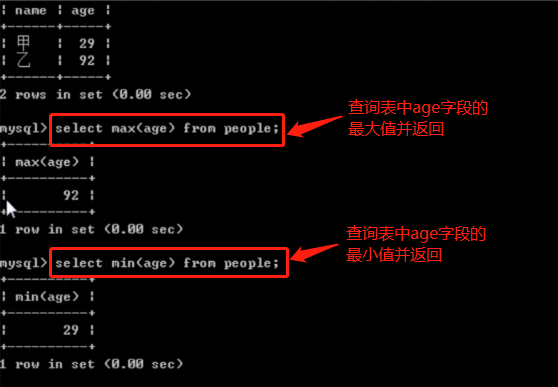
-
组合查询
-
概述:使用union将多条查询语句连接,即返回多条查询语句分别的结果的组合。
-
关键字:union
-
union:默认同加distinct的结果,即去重 -
union distinct:将结果去重后返回 -
union all:将所有结果返回
-
-
示例:
-
select name from houses union distinct select name from people;

-
select name from houses union all select name from people;
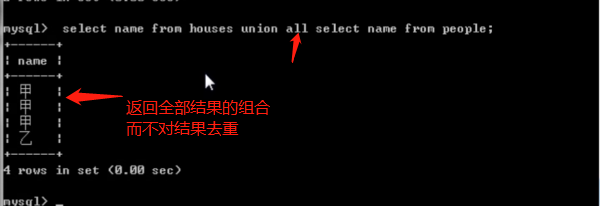
-
select name from houses union select name from people;

-
=======================================================



