ACM学习历程—HDU1028 Ignatius and the Princess(组合数学)
Ignatius and the Princess
Description
"Well, it seems the first problem is too easy. I will let you know how foolish you are later." feng5166 says.
"The second problem is, given an positive integer N, we define an equation like this: N=a[1]+a[2]+a[3]+...+a[m]; a[i]>0,1<=m<=N; My question is how many different equations you can find for a given N. For example, assume N is 4, we can find: 4 = 4; 4 = 3 + 1; 4 = 2 + 2; 4 = 2 + 1 + 1; 4 = 1 + 1 + 1 + 1; so the result is 5 when N is 4. Note that "4 = 3 + 1" and "4 = 1 + 3" is the same in this problem. Now, you do it!"
"The second problem is, given an positive integer N, we define an equation like this: N=a[1]+a[2]+a[3]+...+a[m]; a[i]>0,1<=m<=N; My question is how many different equations you can find for a given N. For example, assume N is 4, we can find: 4 = 4; 4 = 3 + 1; 4 = 2 + 2; 4 = 2 + 1 + 1; 4 = 1 + 1 + 1 + 1; so the result is 5 when N is 4. Note that "4 = 3 + 1" and "4 = 1 + 3" is the same in this problem. Now, you do it!"
Input
The input contains several test cases. Each test case contains a positive integer N(1<=N<=120) which is mentioned above. The input is terminated by the end of file.
Output
For each test case, you have to output a line contains an integer P which indicate the different equations you have found.
Sample Input
4
10
20
刚看到题目是k个数相加为n的题目,第一反应是求1到n元的一次不定方程求解,用插板的方法就能求出通项,但是考虑到这k元未知数是没有先后关系的,也就是说任意(a,a)和(a,a)是相同的。于是不能这样考虑。
然后考虑到每组解必然有个最大值,于是设了这样一个函数(或者数组)f(n,k),表示和为n且最大数为k的上述元数不定的方程的解的个数。这样一来题目要求求得就是f(n,1)到f(n,n)的和了。
然后我们考虑,对于f(n,k)如果去掉最大值k,那么其子问题就是求和为n-k且最大值小于等于k的上述方程的解的个数。 于是得到递推方程:
![]()
![]()
Sample Output
5
42
627
刚看到题目是k个数相加为n的题目,第一反应是求1到n元的一次不定方程求解,用插板的方法就能求出通项,但是考虑到这k元未知数是没有先后关系的,也就是说任意(a,a)和(a,a)是相同的。于是不能这样考虑。
然后考虑到每组解必然有个最大值,于是设了这样一个函数(或者数组)f(n,k),表示和为n且最大数为k的上述元数不定的方程的解的个数。这样一来题目要求求得就是f(n,1)到f(n,n)的和了。
然后我们考虑,对于f(n,k)如果去掉最大值k,那么其子问题就是求和为n-k且最大值小于等于k的上述方程的解的个数。 于是得到递推方程:
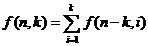
但是考虑到n-k或许会比k还要小,于是更新递推方程为:
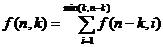
然后打表求f(n,k)即可,此外用f(n,0)来存所有f(n,i)的和。用数组实现。
代码:
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <cmath>
#include <algorithm>
#include <set>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
#define inf 0x3fffffff
using namespace std;
int a[125][125];
int main()
{
//freopen ("test.txt", "r", stdin);
memset (a, 0, sizeof(a));
for (int i = 1; i <= 120; ++i)
{
for (int j = 1; j <= i; ++j)
{
if (i == 1 || i == j)
{
a[i][j] = 1;
}
else
{
for (int k = 1; k <= j && k <= i-j; ++k)
{
a[i][j] += a[i-j][k];
}
}
a[i][0] += a[i][j];
}
}
int n;
while(scanf("%d", &n) != EOF)
{
printf ("%d\n", a[n][0]);
}
return 0;
}
把每一道题当作难题去做。
posted on 2014-11-16 19:14 AndyQsmart 阅读(241) 评论(0) 收藏 举报


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号