google的grpc在golang中的使用
GRPC是google开源的一个高性能、跨语言的RPC框架,基于HTTP2协议,基于protobuf 3.x,基于Netty 4.x。
前面写过一篇golang标准库的rpc包的用法,这篇文章接着讲一下google的grpc。
介绍
在 gRPC 里客户端应用可以像调用本地对象一样直接调用另一台不同的机器上服务端应用的方法,使得您能够更容易地创建分布式应用和服务。
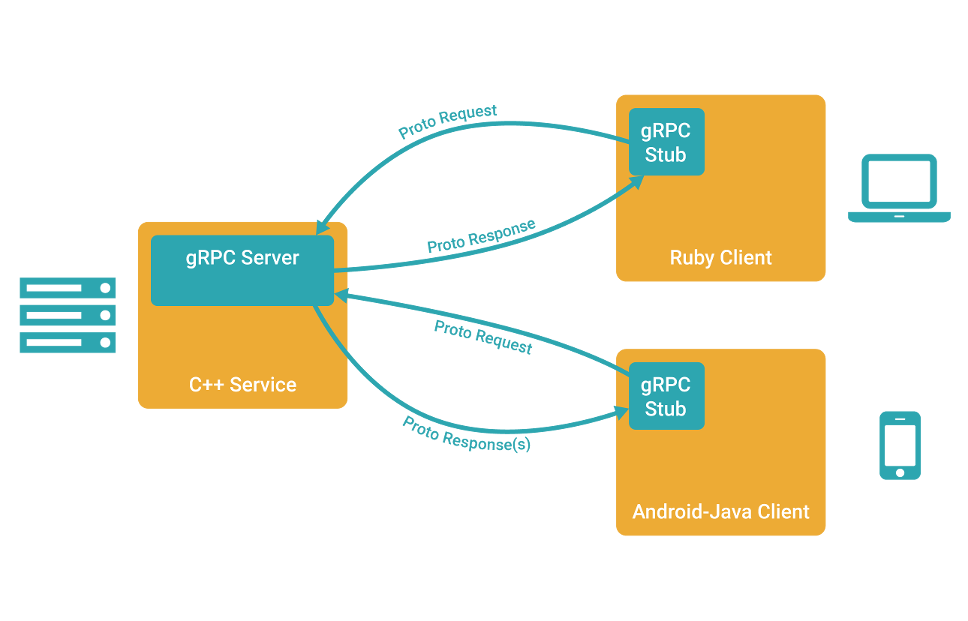
使用grpc的优点很多,支持多种语言,二进制的数据可以加快传输速度,基于http2的多路复用可以减少服务之间的连接次数,和函数一样的调用方式也有效的提升了开发效率。
grpc提供有go版本,下面介绍一下grpc在golang中的使用。
安装
grpc支持1.5及以上版本。
用以下命令安装grpc-go:
go get google.golang.org/grpc
安装Protocol Buffers v3
去https://github.com/google/protobuf/releases下载最新的稳定的版本,然后解压缩,把里面的文件放到$PATH中。
安装插件
go get -u github.com/golang/protobuf/{proto,protoc-gen-go}
别忘了将$GOPATH/bin添加到$PATH中:
export PATH=$PATH:$GOPATH/bin
示例
示例代码获取地址:https://github.com/andyidea/go-example。
代码文件结构如下
├── bin
│ ├── grpc-client
│ └── grpc-server
└── src
└── grpc-helloworld
├── greeter_client
│ └── main.go
├── greeter_server
│ └── main.go
└── helloworld
├── helloworld.pb.go
└── helloworld.proto
grpc-helloworld里有三个包,greeter_client是客户端代码,greeter_server是服务端代码,helloworld是协议文件。
先看下协议。
helloworld.proto
syntax = "proto3";
option java_multiple_files = true;
option java_package = "io.grpc.examples.helloworld";
option java_outer_classname = "HelloWorldProto";
package helloworld;
// The greeting service definition.
service Greeter {
// Sends a greeting
rpc SayHello (HelloRequest) returns (HelloReply) {}
}
// The request message containing the user's name.
message HelloRequest {
string name = 1;
}
// The response message containing the greetings
message HelloReply {
string message = 1;
}
协议中定义了两个结构体HelloRequest和HelloReply,还有一个函数SayHello,函数的参数是HelloRequest,返回HelloReply。
在src/下用下面命令生成协议的go文件:
protoc -I helloworld/ helloworld/helloworld.proto --go_out=plugins=grpc:helloworld
这样就生成了helloworld.pb.go协议文件。
接着我们看下服务器端的代码:
package main
import (
"log"
"net"
"golang.org/x/net/context"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
pb "grpc-helloworld/helloworld"
"google.golang.org/grpc/reflection"
)
const (
port = ":50051"
)
// server is used to implement helloworld.GreeterServer.
type server struct{}
// SayHello implements helloworld.GreeterServer
func (s *server) SayHello(ctx context.Context, in *pb.HelloRequest) (*pb.HelloReply, error) {
return &pb.HelloReply{Message: "Hello " + in.Name}, nil
}
func main() {
lis, err := net.Listen("tcp", port)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to listen: %v", err)
}
s := grpc.NewServer()
pb.RegisterGreeterServer(s, &server{})
// Register reflection service on gRPC server.
reflection.Register(s)
if err := s.Serve(lis); err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to serve: %v", err)
}
}
服务器端主要逻辑就是实现之前协议中的SayHello方法,这里是将字符串Hello和参数拼接在一起返回。
协议生成的go文件给了一个RegisterGreeterServer方法,我们用这个方法绑定实现函数的结构体和server。
然后是客户端代码:
package main
import (
"log"
"os"
"golang.org/x/net/context"
"google.golang.org/grpc"
pb "grpc-helloworld/helloworld"
)
const (
address = "localhost:50051"
defaultName = "world"
)
func main() {
// Set up a connection to the server.
conn, err := grpc.Dial(address, grpc.WithInsecure())
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("did not connect: %v", err)
}
defer conn.Close()
c := pb.NewGreeterClient(conn)
// Contact the server and print out its response.
name := defaultName
if len(os.Args) > 1 {
name = os.Args[1]
}
r, err := c.SayHello(context.Background(), &pb.HelloRequest{Name: name})
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("could not greet: %v", err)
}
log.Printf("Greeting: %s", r.Message)
}
客户端的思路也很清晰,建立一个rpc客户端连接,将这个连接用pb.NewGreeterClient和协议绑定,返回一个client对象,用这个对象就可以调用远程的函数了。
调用输出如下:
Greeting: Hello world
示例到此结束。示例代码获取地址:https://github.com/andyidea/go-example。



