【朝花夕拾】Android自定义View篇之(十一)View的滑动,弹性滑动与自定义PagerView
前言
转载请声明,转载自【https://www.cnblogs.com/andy-songwei/p/11213718.html】,谢谢!
由于手机屏幕尺寸有限,但是又经常需要在屏幕中显示大量的内容,这就使得必须有部分内容显示,部分内容隐藏。这就需要用一个Android中很重要的概念——滑动。滑动,顾名思义就是view从一个地方移动到另外一个地方,我们平时看到的各种很炫的移动效果,都是在基本的滑动基础上加入一些动画技术实现的。在Android中实现滑动的方式有多种,比如通过scrollTo/scrollBy,动画位移,修改位置参数等。本文主要介绍通过scrollTo/scrollBy方式来实现View的滑动,并通过该方法来实现一个自定义PagerView。
本文的主要内容如下:

一、 scrollTo/scrollBy实际滑动的是控件的内容
这里我们必须要先理解一个基本概念:使用scrollTo/scrollBy来实现滑动时,滑动的不是控件本身的位置,而是控件的内容。理解这一点,可以结合ScrollView控件,我们平时使用的使用会在xml布局文件中固定ScrollView的大小和位置,这也是我们肉眼看到的信息。但是如果我们左右/上下滑动滚动条,会发现里面原来还“藏”了许多“风景”。控件就像一个窗户,我们看到的只有窗户大小的内容,实际上窗户中“另有乾坤”。就像下面这张图显示的一样:
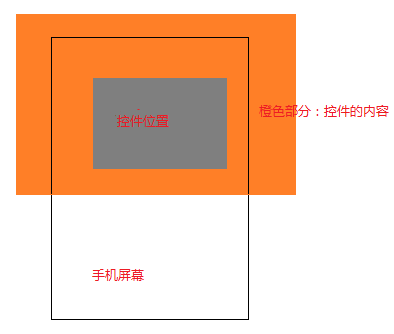
当我们手指在控件上滑动时,移动的其实是橙色部分表示的内容,而不是灰色部分表示的控件位置。
二、scrollBy实际上通过调用scrollTo来实现
scrollTo(int x, int y)方法的作用是:滑动到(x,y)这个坐标点,是一个绝对位置。
scrollBy(int x, int y)方法的作用是:在原来的位置上,水平方向向左滑动x距离,竖直方向向上滑动的y距离(滑动方向问题我们后面会详细讲),是一个相对位置。
这里我们先看看这两个函数的源码:
1 //===========View.java========= 2 /** 3 * Set the scrolled position of your view. This will cause a call to 4 * {@link #onScrollChanged(int, int, int, int)} and the view will be 5 * invalidated. 6 * @param x the x position to scroll to 7 * @param y the y position to scroll to 8 */ 9 public void scrollTo(int x, int y) { 10 if (mScrollX != x || mScrollY != y) { 11 int oldX = mScrollX; 12 int oldY = mScrollY; 13 mScrollX = x; 14 mScrollY = y; 15 invalidateParentCaches(); 16 onScrollChanged(mScrollX, mScrollY, oldX, oldY); 17 if (!awakenScrollBars()) { 18 postInvalidateOnAnimation(); 19 } 20 } 21 } 22 23 /** 24 * Move the scrolled position of your view. This will cause a call to 25 * {@link #onScrollChanged(int, int, int, int)} and the view will be 26 * invalidated. 27 * @param x the amount of pixels to scroll by horizontally 28 * @param y the amount of pixels to scroll by vertically 29 */ 30 public void scrollBy(int x, int y) { 31 scrollTo(mScrollX + x, mScrollY + y); 32 }
注释中也说明了这两个方法的功能,也可以看到scrollBy,就是调用的scrollTo来实现的,所以实际上这两个方法功能一样,实际开发中看那个方便就用那个。这部分源码逻辑比较简单,这里就不啰嗦了,需要注意的是mScrollX/mScrollY这两个变量,后面会用到,它们表示当前内容已经滑动的距离(向左/上滑动为正,向右/下滑动为负,方向问题下面详细讲)。
三、滑动坐标系和View坐标系正好相反
上面一节中介绍过,内容向左/上滑动时mScrollX/mScrollY为正,向右/下滑动时为负,这似乎和我们所理解的正好相反。我们平时理解的是基于View的坐标系,水平向右为X轴正方向,竖直向下为Y轴正方向。但是滑动坐标系和View坐标系正好相反,对于滑动而言,水平向左为X轴正方向,竖直向上为Y轴正方向,原点都还是View控件的左上角顶点。如下图所示:
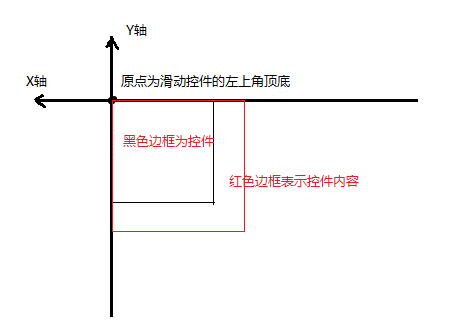
仅从数值上看,mScrollX表示控件内容左边缘到控件左边缘的偏移距离,mScrollY表示控件内容上边缘的距离与控件上边缘的偏移距离。在实际开发中,经常通过getScrollX()/getScrollY()来获取mScrollX/mScrollY的值。
1 //===========View.java========= 2 public final int getScrollX() { 3 return mScrollX; 4 } 5 ...... 6 public final int getScrollY() { 7 return mScrollY; 8 }
对于其值的正负问题,读者可以自己通过打印log的方式来演示一下,比较简单,此处不赘述了。这里再提供几个图来体会一下滑动方向的问题。

水平方向的滑动
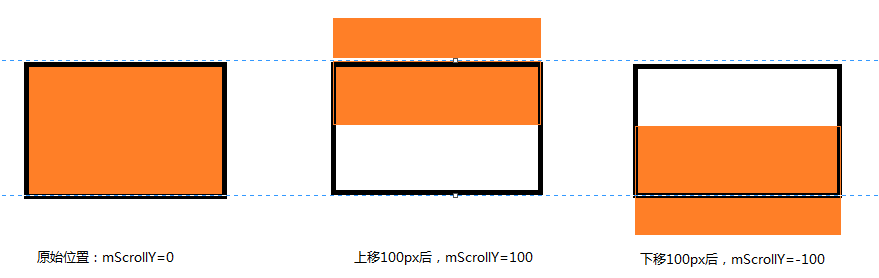
竖直方向的滑动
四、通过Scroller实现弹性滑动
通过scrollTo/scrollBy实现滑动时,是一瞬间来实现的。这样看起来会比较生硬和突兀,用户体验显然是不友好的,很多场景下,我们希望这个滑动是一个渐近式的,在给定的一段时间内缓慢移动到目标坐标。Android提供了一个Scroller类,来辅助实现弹性滑动,至于它的使用方法,下一点的代码中有详细演示,红色加粗的文字部分显示了使用步骤,这里结合该示例进行讲解。
通过Scroller实现弹性滑动的基本思想是,将一整段的滑动分为很多段微小的滑动,并在一定时间段内一一完成。
我们来看看CustomPagerView中第111行startScroll方法的源码:
1 //===================Scroller.java================== 2 /** 3 * Start scrolling by providing a starting point, the distance to travel, 4 * and the duration of the scroll. 5 * 6 * @param startX Starting horizontal scroll offset in pixels. Positive 7 * numbers will scroll the content to the left. 8 * @param startY Starting vertical scroll offset in pixels. Positive numbers 9 * will scroll the content up. 10 * @param dx Horizontal distance to travel. Positive numbers will scroll the 11 * content to the left. 12 * @param dy Vertical distance to travel. Positive numbers will scroll the 13 * content up. 14 * @param duration Duration of the scroll in milliseconds. 15 */ 16 public void startScroll(int startX, int startY, int dx, int dy, int duration) { 17 mMode = SCROLL_MODE; 18 mFinished = false; 19 mDuration = duration; 20 mStartTime = AnimationUtils.currentAnimationTimeMillis(); 21 mStartX = startX; 22 mStartY = startY; 23 mFinalX = startX + dx; 24 mFinalY = startY + dy; 25 mDeltaX = dx; 26 mDeltaY = dy; 27 mDurationReciprocal = 1.0f / (float) mDuration; 28 }
startScroll方法实际上没有做移动的操作,只是提供了本次完整滑动的开始位置,需要滑动的距离,以及完成这次滑动所需要的时间。
第113行的invalidate()方法会让CustomPagerView重绘,这会调用View中的draw(...)方法,
1 boolean draw(Canvas canvas, ViewGroup parent, long drawingTime) { 2 ...... 3 computeScroll(); 4 ...... 5 } 6 ...... 7 /** 8 * Called by a parent to request that a child update its values for mScrollX 9 * and mScrollY if necessary. This will typically be done if the child is 10 * animating a scroll using a {@link android.widget.Scroller Scroller} 11 * object. 12 */ 13 public void computeScroll() { 14 }
draw()方法调用了computeScroll(),这是一个空方法,在CustomPagerView的126行重写了该方法,重绘时会进入到这个方法体中。第127行中有一个判断条件,看看它的源码:
1 /** 2 * Call this when you want to know the new location. If it returns true, 3 * the animation is not yet finished. 4 */ 5 public boolean computeScrollOffset() { 6 if (mFinished) { 7 return false; 8 } 9 10 int timePassed = (int)(AnimationUtils.currentAnimationTimeMillis() - mStartTime); 11 12 if (timePassed < mDuration) { 13 switch (mMode) { 14 case SCROLL_MODE: 15 final float x = mInterpolator.getInterpolation(timePassed * mDurationReciprocal); 16 mCurrX = mStartX + Math.round(x * mDeltaX); 17 mCurrY = mStartY + Math.round(x * mDeltaY); 18 break; 19 case FLING_MODE: 20 ...... 21 break; 22 } 23 } 24 else { 25 mCurrX = mFinalX; 26 mCurrY = mFinalY; 27 mFinished = true; 28 } 29 return true; 30 }
这个判断语句是在判断本次滑动是否在在继续,如果还没结束,会返回false,重写的computeScroll()中第130~135行会继续执行,直到滑动完成为止。同时这个方法还会根据已经滑动的时间来更新当前需要移动到位置mCurrX/mCurrY。所以我们可以看到,在滑动还没结束时,第134行就执行scrollTo方法来滑动一段距离。第134行又是一个刷新,让CustomPagerView重绘,又会调用draw(...)方法,computeScroll方法又被调用了,这样反复调用,直到整个滑动过程结束。(至于多长时间会执行一直刷新,笔者目前还没找到更深入的代码,有兴趣的读者可以自己再深入研究研究)
最后这里做个总结,Scroller辅助实现弹性滑动的原理为: Scroller本身不能实现滑动,而是通过startScroll方法传入起始位置、要滑动的距离和执行完滑动所需的时间,再通过invalidate刷新界面来调用重写的computeScroll方法,在没有结束滑动的情况下,computeScroll中执行scrollTo方法来滑动一小段距离,并再次刷新界面调用重写的computeScroll方法,如此反复,直到滑动过程结束。
五、实现一个自定义PagerView
本示例结合了该系列前面文章中提到的自定义View,View的绘制流程,触摸事件处理,速度等方面的知识,不明白的可以先去看看这些文章,打一下基础。本示例的项目结构非常简单,这里就不提供下载地址了。
这里先看看效果,一睹为快吧。

自定义一个view,继承自ViewGroup
1 public class CustomPagerView extends ViewGroup { 2 3 private static final String TAG = "songzheweiwang"; 4 private Scroller mScroller; 5 private VelocityTracker mVelocityTracker; 6 private int mMaxVelocity; 7 private int mCurrentPage = 0; 8 private int mLastX = 0; 9 private List<Integer> mImagesList; 10 11 public CustomPagerView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) { 12 super(context, attrs); 13 init(context); 14 } 15 16 private void init(Context context) { 17 //第一步:实例化一个Scroller实例 18 mScroller = new Scroller(context); 19 mVelocityTracker = VelocityTracker.obtain(); 20 mMaxVelocity = ViewConfiguration.get(context).getScaledMinimumFlingVelocity(); 21 Log.i(TAG, "mMaxVelocity=" + mMaxVelocity); 22 } 23 24 //添加需要显示的图片,并显示 25 public void addImages(Context context, List<Integer> imagesList) { 26 if (imagesList == null) { 27 mImagesList = new ArrayList<>(); 28 } 29 mImagesList = imagesList; 30 showViews(context); 31 } 32 33 private void showViews(Context context) { 34 if (mImagesList == null) { 35 return; 36 } 37 for (int i = 0; i < mImagesList.size(); i++) { 38 ImageView imageView = new ImageView(context); 39 LayoutParams params = new LayoutParams(LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT); 40 imageView.setLayoutParams(params); 41 imageView.setBackgroundResource(mImagesList.get(i)); 42 addView(imageView); 43 } 44 } 45 46 @Override 47 protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { 48 super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); 49 int count = getChildCount(); 50 for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { 51 View childView = getChildAt(i); 52 childView.measure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); 53 } 54 } 55 56 @Override 57 protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) { 58 int count = getChildCount(); 59 for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) { 60 View childView = getChildAt(i); 61 childView.layout(i * getWidth(), t, (i + 1) * getWidth(), b); 62 } 63 } 64 65 @Override 66 public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) { 67 mVelocityTracker.addMovement(event); 68 int x = (int) event.getX(); 69 switch (event.getActionMasked()) { 70 case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN: 71 //如果动画没有结束,先停止动画 72 if (!mScroller.isFinished()) { 73 mScroller.abortAnimation(); 74 } 75 mLastX = x; 76 break; 77 case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE: 78 int dx = x - mLastX; 79 //滑动坐标系正好和View坐标系是反的,dx为负数表示向右滑,为正表示向左滑 80 scrollBy(-dx, 0); 81 mLastX = x; 82 break; 83 case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP: 84 mVelocityTracker.computeCurrentVelocity(1000); 85 int xVelocity = (int) mVelocityTracker.getXVelocity(); 86 Log.i(TAG, "xVelocity=" + xVelocity); 87 if (xVelocity > mMaxVelocity && mCurrentPage > 0) { 88 //手指快速右滑后抬起,且当前页面不是第一页 89 scrollToPage(mCurrentPage - 1); 90 } else if (xVelocity < -mMaxVelocity && mCurrentPage < getChildCount() - 1) { 91 //手指快速左滑后抬起,且当前页面不是最后一页 92 scrollToPage(mCurrentPage + 1); 93 } else { 94 slowScrollToPage(); 95 } 96 break; 97 } 98 return true; 99 } 100 101 private void scrollToPage(int pageIndex) { 102 mCurrentPage = pageIndex; 103 if (mCurrentPage > getChildCount() - 1) { 104 mCurrentPage = getChildCount() - 1; 105 } 106 int scrollX = getScrollX(); 107 int dx = mCurrentPage * getWidth() - scrollX; 108 int duration = Math.abs(dx) * 2; 109 Log.i(TAG, "[scrollToPage]scrollX=" + scrollX + ";dx=" + dx + ";duration=" + duration); 110 //第二步:调用startScroll方法,指定起始坐标,目的坐标和滑动时长 111 mScroller.startScroll(scrollX, 0, dx, 0, duration); 112 //第三步:让界面重绘 113 invalidate(); 114 } 115 116 private void slowScrollToPage() { 117 int scrollX = getScrollX(); 118 //缓慢滑动式,滑动一半以上后自动换到下一张,滑动不到一半则还原 119 int whichPage = (scrollX + getWidth() / 2) / getWidth(); 120 Log.i(TAG, "[slowScrollToPage]scrollX=" + scrollX + ";whichPage=" + whichPage); 121 scrollToPage(whichPage); 122 } 123 124 //第四步:重写computeScroll方法,在该方法中通过scrollTo方法来完成滑动,并重绘 125 @Override 126 public void computeScroll() { 127 boolean isAnimateRun = mScroller.computeScrollOffset(); 128 Log.i(TAG, "[computeScroll]isAnimateRun=" + isAnimateRun); 129 if (isAnimateRun) { 130 //当前页面的右上角,相对于第一页右上角的坐标 131 int curX = mScroller.getCurrX(); 132 int curY = mScroller.getCurrY(); 133 Log.i(TAG, "[computeScroll]curX=" + curX + ";curY=" + curY); 134 scrollTo(curX, curY); 135 postInvalidate(); 136 } 137 } 138 139 @Override 140 protected void onDetachedFromWindow() { 141 super.onDetachedFromWindow(); 142 if (mVelocityTracker != null) { 143 mVelocityTracker.recycle(); 144 mVelocityTracker = null; 145 } 146 } 147 }
代码看起来有点长,其实逻辑很简单。基本思路是,使用者添加要显示的图片资源id列表,在CustomPagerView中为每一个要显示的图片实例一个ImageView进行显示。在滑动的过程中,如果速度比较快(大于某个阈值),手指抬起后,就会滑动下一页。如果速度很慢,手指抬起时,如果手指滑动的距离超过了屏幕的一半,则自动滑到下一页,如果没滑到一半,本次就不翻页,仍然停留在本页。
在布局文件中引入该控件
1 //=========activity_scroller_demo.xml========= 2 <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> 3 <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" 4 android:layout_width="match_parent" 5 android:layout_height="match_parent" 6 android:orientation="vertical"> 7 8 <com.example.demos.customviewdemo.CustomPagerView 9 android:id="@+id/viewpager" 10 android:layout_width="match_parent" 11 android:layout_height="300dp" /> 12 </LinearLayout>
在Activity中使用该控件
1 public class ScrollerDemoActivity extends AppCompatActivity { 2 3 private static final String TAG = "ScrollerDemoActivity"; 4 5 @Override 6 protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { 7 super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); 8 setContentView(R.layout.activity_scroller_demo); 9 initViews(); 10 } 11 12 private void initViews() { 13 List<Integer> mImageList = new ArrayList<>(); 14 mImageList.add(R.drawable.dog); 15 mImageList.add(R.drawable.test2); 16 mImageList.add(R.drawable.test3); 17 mImageList.add(R.drawable.test4); 18 CustomPagerView customPagerView = findViewById(R.id.viewpager); 19 customPagerView.addImages(this, mImageList); 20 } 21 }
这里再啰嗦一句,本示例很好地演示了一个自定义View的开发,包含了不少自定义View需要掌握的基础知识点。通过该代码,希望能够强化理解前面文章中介绍的相关知识。
六、其他实现滑动及弹性滑动的方法
前面只介绍了通过scrollTo/scrollBy,并结合Scroller来实现滑动和弹性滑动的方式,实际上还有很多方式来实现这些效果。比如,要实现滑动,还有使用动画以及修改控件位置参数等方式。要实现弹性滑动,已经知道了基本思路是把一整段滑动分为很多小段滑动来一一实现,那么还可以使用定时器,Handler,Thread/sleep等方式来实现。这些方法就不一一介绍了,在使用时可以根据实际的场景和需求选择实现方式。
结语
本文主要介绍通过scrollTo/scrollBy来实现控件内容的滑动,以及结合Scroller实现弹性滑动的方式。由于笔者水平和经验有限,有描述不准确或不正确的地方,欢迎来拍砖,谢谢!
参考资料
《Android开发艺术探索》





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· Manus的开源复刻OpenManus初探
· AI 智能体引爆开源社区「GitHub 热点速览」
· 三行代码完成国际化适配,妙~啊~
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?