ArrayList源码解析
ArrayList
总体介绍
ArrayList实现了List接口,是顺序容器,即元素存放的数据与放进去的顺序相同,允许放入null元素,底层通过数组实现。除该类未实现同步外,其余跟Vector大致相同。每个ArrayList都有一个容量(capacity),表示底层数组的实际大小,容器内存储元素的个数不能多于当前容量。当向容器中添加元素时,如果容量不足,容器会自动增大底层数组的大小。前面已经提过,Java泛型只是编译器提供的语法糖,所以这里的数组是一个Object数组,以便能够容纳任何类型的对象。
ArrayList 容器能够自动的扩展它自身的容量以便能够存放更多的元素。
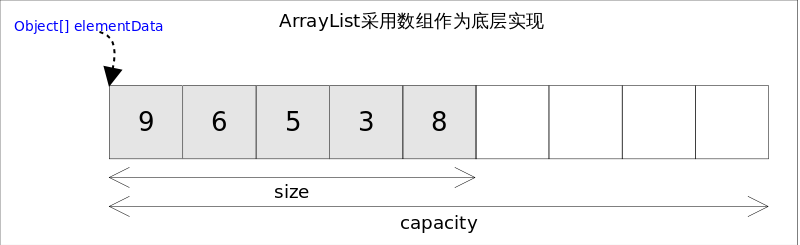
size(), isEmpty(), get(), set()方法均能在常数时间内完成,add()方法的时间开销跟插入位置有关,addAll()方法的时间开销跟添加元素的个数成正比。其余方法大都是线性时间。
为追求效率,ArrayList没有实现同步(synchronized),如果需要多个线程并发访问,用户可以手动同步,也可使用Vector替代。
主要变量和三个构造方法
ArrayList的内部存储结构就是一个Object类型的数组,因此它可以存放任意类型的元素。在构造ArrayList的时候,如果传入初始大小那么它将新建一个指定容量的Object数组,如果不设置初始大小那么它将不会分配内存空间而是使用空的对象数组,在实际要放入元素时再进行内存分配。
private static final long serialVersionUID = 8683452581122892189L;
/**
* Default initial capacity.默认初始化容量
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10;
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for empty instances.//空对象数组
*/
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for default sized empty instances. We
* distinguish this from EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA to know how much to inflate when
* first element is added.
*/
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {};
/**
* The array buffer into which the elements of the ArrayList are stored.
* The capacity of the ArrayList is the length of this array buffer. Any
* empty ArrayList with elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
* will be expanded to DEFAULT_CAPACITY when the first element is added.
*/
transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access
/**
* The size of the ArrayList (the number of elements it contains).集合元素个数
*
* @serial
*/
private int size;
/**
* Constructs an empty list with the specified initial capacity. 传入初始容量的构造方法
*
* @param initialCapacity the initial capacity of the list
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if the specified initial capacity
* is negative
*/
public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) {
//新建指定容量的Object类型数组
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
}
}
/**
* Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten.不带参数的构造方法
*/
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
/**
* Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's
* iterator.
* 传入外部集合的构造方法
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
//持有传入集合的内部数组的引用
elementData = c.toArray();
//更新集合元素个数大小
if ((size = elementData.length) != 0) {
// c.toArray might (incorrectly) not return Object[] (see 6260652)
//判断引用的数组类型, 并将引用转换成Object数组引用
if (elementData.getClass() != Object[].class)
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, size, Object[].class);
} else {
// replace with empty array.
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
}
方法剖析
set()
既然底层是一个数组ArrayList的set()方法也就变得非常简单,直接对数组的指定位置赋值即可。
/**
* Replaces the element at the specified position in this list with
* the specified element.
* 替换index位置的元素
* @param index index of the element to replace
* @param element element to be stored at the specified position
* @return the element previously at the specified position
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E set(int index, E element) {
//index不能大于size
rangeCheck(index);
//替换成新元素
E oldValue = elementData(index);
elementData[index] = element;
return oldValue;
}
get()
get()方法同样很简单,唯一要注意的是由于底层数组是Object[],得到元素后需要进行类型转换。
/**
* Returns the element at the specified position in this list.
*
* @param index index of the element to return
* @return the element at the specified position in this list
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public E get(int index) {
//index不能大于size
rangeCheck(index);
//返回指定位置元素
return elementData(index);//注意类型转换,无需遍历
}
add()
跟C++ 的vector不同,ArrayList没有push_back()方法,对应的方法是add(E e),ArrayList也没有insert()方法,对应的方法是add(int index, E e)。这两个方法都是向容器中添加新元素,这可能会导致capacity不足,因此在添加元素之前,都需要进行剩余空间检查,如果需要则自动扩容。扩容操作最终是通过grow()方法完成的。
/**
* 增(添加)
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return <tt>true</tt> (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
//添加前先检查是否需要拓展数组, 此时数组长度最小为size+1
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
//将元素添加到数组末尾
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
/**
* 增(插入)
*
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* @param element element to be inserted
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
//插入位置范围检查
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
//检查是否需要扩容
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
//挪动插入位置后面的元素
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + 1,
size - index);
//在要插入的位置赋上新值
elementData[index] = element;
size++;
}
/**
*增加数组长度
* ensureCapacityInternal -->ensureCapacityInternal -->ensureExplicitCapacity -->grow最后调用这个方法
*/
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
//获取数组原先的容量
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
//新数组的容量, 在原来的基础上增加一半
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
//检验新的容量是否小于最小容量
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) {
newCapacity = minCapacity;
}
//检验新的容量是否超过最大数组容量
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) {
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
}
//拷贝原来的数组到新数组
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
由于Java GC自动管理了内存,这里也就不需要考虑源数组释放的问题。

空间的问题解决后,插入过程就显得非常简单。
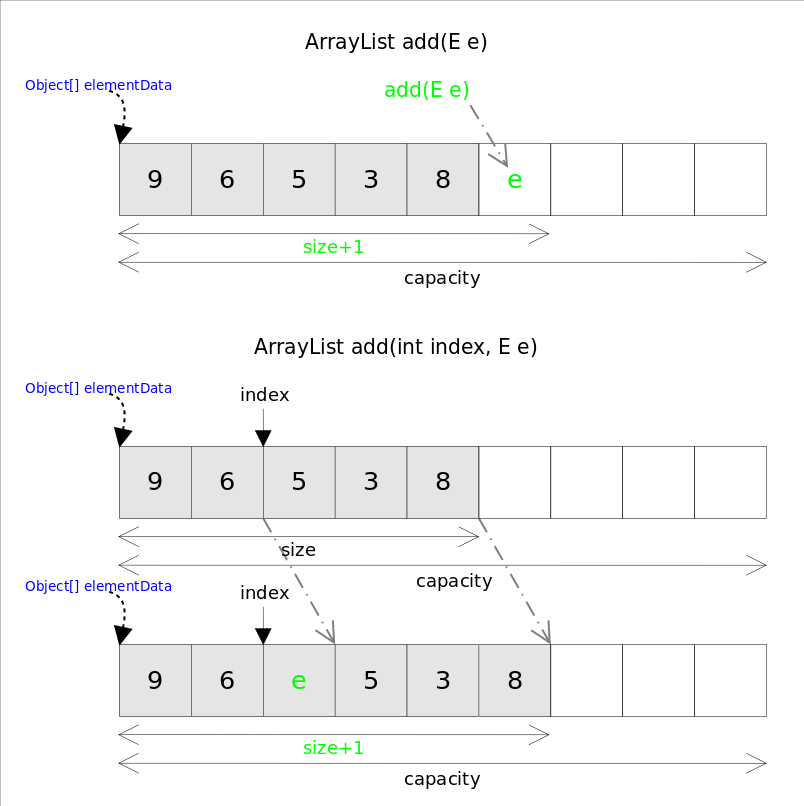
add(int index, E e)需要先对元素进行移动,然后完成插入操作,也就意味着该方法有着线性的时间复杂度。
addAll()
addAll()方法能够一次添加多个元素,根据位置不同也有两个把本,一个是在末尾添加的addAll(Collection<? extends E> c)方法,一个是从指定位置开始插入的addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c)方法。跟add()方法类似,在插入之前也需要进行空间检查,如果需要则自动扩容;如果从指定位置插入,也会存在移动元素的情况。
addAll()的时间复杂度不仅跟插入元素的多少有关,也跟插入的位置相关。
public boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) {
//插入位置范围检查
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
//集合转化为对象数组
Object[] a = c.toArray();
//获取数组长度
int numNew = a.length;
//检查是否需要扩容
ensureCapacityInternal(size + numNew); // Increments modCount
int numMoved = size - index;
if (numMoved > 0)
//挪动插入位置后面的元素
System.arraycopy(elementData, index, elementData, index + numNew,
numMoved);
System.arraycopy(a, 0, elementData, index, numNew);
size += numNew;
return numNew != 0;
}
remove()
remove()方法也有两个版本,一个是remove(int index)删除指定位置的元素,另一个是remove(Object o)删除第一个满足o.equals(elementData[index])的元素。删除操作是add()操作的逆过程,需要将删除点之后的元素向前移动一个位置。需要注意的是为了让GC起作用,必须显式的为最后一个位置赋null值。
public E remove(int index) {
rangeCheck(index);
modCount++;
E oldValue = elementData(index);
int numMoved = size - index - 1;
if (numMoved > 0)
System.arraycopy(elementData, index+1, elementData, index, numMoved);
elementData[--size] = null; //清除该位置的引用,让GC起作用
return oldValue;
}
ArrayList扩容方法:
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
//如果此时还是空数组
if (elementData == EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
//和默认容量比较, 取较大值
minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
//数组已经初始化过就执行这一步
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
//如果最小容量大于数组长度就扩增数组
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0) {
grow(minCapacity);
}
}
//集合最大容量
private static final int MAX_ARRAY_SIZE = Integer.MAX_VALUE - 8;
//增加数组长度
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
//获取数组原先的容量
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
//新数组的容量, 在原来的基础上增加一半
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
//检验新的容量是否小于最小容量
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0) {
newCapacity = minCapacity;
}
//检验新的容量是否超过最大数组容量
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0) {
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
}
//拷贝原来的数组到新数组
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
关于Java GC这里需要特别说明一下,有了垃圾收集器并不意味着一定不会有内存泄漏。对象能否被GC的依据是是否还有引用指向它,上面代码中如果不手动赋null值,除非对应的位置被其他元素覆盖,否则原来的对象就一直不会被回收。





