适配器模式的理解,在生活当中就有很多的适配器,例如:笔记本电脑的适配器(充电器),在其他国家地方给笔记本电脑充电的电压是不一样的,
例如在外国220V电压,在中国110V电压,电压不一样去给笔记本电脑充电是不行的,这就需要一个适配过程,于是就有了充电适配器,来适配给笔记本电脑充电的处理;
通俗易懂的来讲,其实适配器模式是给不符合使用的(类,抽象类,接口,行为 …),完成一个匹配的过程。
注意:大部分情况下(适配器模式是在维护阶段发现某些对象无法匹配才用适配器模式,而不是开始设计就用适配器模式),乱用设计模式,还不如不用。
以下代码举例来分析:
案例一(不使用适配器):
package coom.oop.demo4;
/**
* 抽象出充电抽象类
* @author Liudeli
*
*/
public abstract class ACharge {
/**
* 得到电压数
*/
public abstract int getCharge();
}
package coom.oop.demo4;
/**
* 英国具体对象
* @author Liudeli
*
*/
public class Britain extends ACharge{
/**
* 模拟英国24V电压
*/
public int getCharge() {
return 24;
}
}
package coom.oop.demo4;
/**
* 中国具体对象
* @author Liudeli
*
*/
public class China extends ACharge{
/**
* 在中国24V电压
*/
public int getCharge() {
return 24;
}
}
package coom.oop.demo4;
/**
* 法国具体对象
* @author Liudeli
*
*/
public class France extends ACharge{
/**
* 模拟在法国240V电压
*/
public int getCharge() {
return 240;
}
}
package coom.oop.demo4;
/**
* 具体电脑对象
* @author Liudeli
*
*/
public class Computer {
/**
* 电脑充电电压标准为 24V
*/
private static final int VOLTAGE = 24;
/**
* 电脑具备充电的行为
* @param value 电压V
*/
public void charge(ACharge aCharge) {
if (VOLTAGE == aCharge.getCharge()) {
System.out.println("充电成功 success √");
} else {
System.out.println("电压不对,无法充电,请尽快拔掉充电插头!! ×");
}
}
}
/**
* 测试程序
* @author Liudeli
*
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 不使用适配器去充电
Computer computer = new Computer();
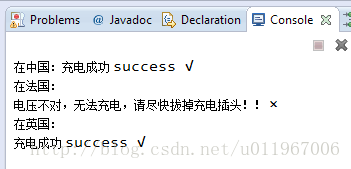
System.out.print("在中国:");
computer.charge(new China());
System.out.print("在法国:");
computer.charge(new France());
System.out.print("在英国:");
computer.charge(new Britain());
}
}运行结果:
案例二(使用适配器):
增加适配器:
package coom.oop.demo4;
/**
* 定义法国专用的适配器
* @author Liudeli
*
*/
public class FranceAdapter extends ACharge{
private France france;
public FranceAdapter(France france) {
this.france = france;
}
public int getCharge() {
return (france.getCharge() / 10);
}
}
测试程序:
private static void test() {
// 使用适配器
Computer computer = new Computer();
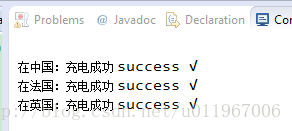
System.out.print("在中国:");
computer.charge(new China());
System.out.print("在法国:");
// 法国电压不符合笔记本电脑的标准,所以使用适配器
computer.charge(new FranceAdapter(new France()));
System.out.print("在英国:");
computer.charge(new Britain());
}运行结果:
谢谢大家的观看,更多精彩技术博客,会不断的更新,请大家访问,
刘德利CSDN博客, http://blog.csdn.net/u011967006


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号