我的理解是,子线程要和主线程通讯,就需要Handler+Message-消息机制

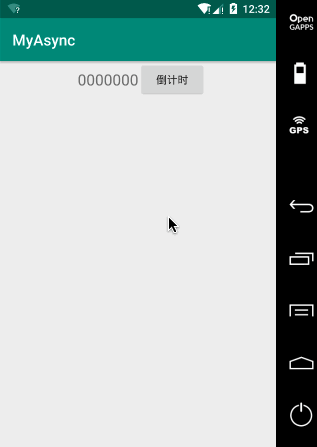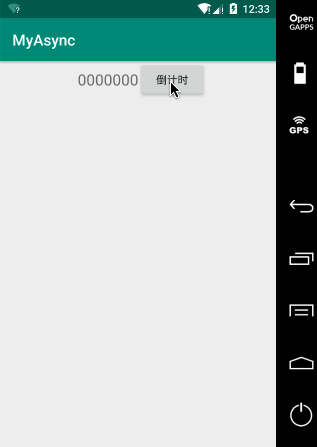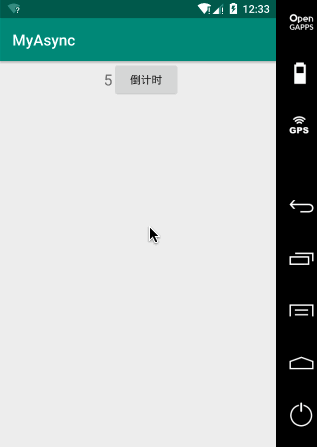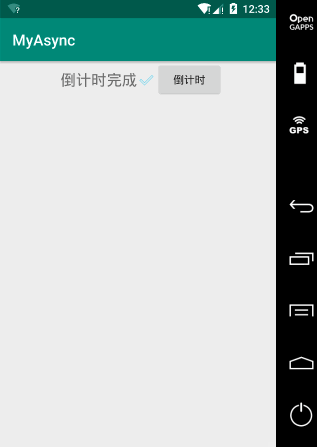
案例一:倒计时Demo(子线程+Handler+Message)
package liudeli.async; import android.os.Handler; import android.os.Message; import android.os.SystemClock; import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity; import android.os.Bundle; import android.view.View; import android.widget.TextView; public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { private TextView tvInfo; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); tvInfo = findViewById(R.id.tv_info); } /** * 定义Handler */ private Handler mHandler = new Handler(){ @Override public void handleMessage(Message msg) { super.handleMessage(msg); if (msg.obj != null) { tvInfo.setText(msg.obj.toString()); return; } tvInfo.setText(msg.what + ""); } }; /** * 耗时操作不能在主线程 定义主线程 */ private class MyTimeing implements Runnable { @Override public void run() { for (int i = 10; i >= 0; i--) { // mHandler.obtainMessage(i); 这种消息池方式获取Message消耗小 Message message = mHandler.obtainMessage(i); // what 其实就是ID的意思,唯一标示 if (i <= 0) { // obj 是Object 什么类型都可以传递: 传递T类型,获取的时候就强转T类型 message.obj = "倒计时完成✅"; } // 用Android提供的睡眠方法,其实是封装来Thread.sleep SystemClock.sleep(1000); // 从子线程 发送消息 到---> 主线程的handleMessage方法 mHandler.sendMessage(message); } } } /** * 执行倒计时 * @param view */ public void timeing(View view) { // 主线程被阻塞 5秒 未响应,系统就会自动报错 ANR Application Not Responding /** * Android系统中,ActivityManagerService(简称AMS) 和 WindowManagerService(简称WMS)会检测App的响应时间 * 如果App在特定时间无法响应屏幕触摸或键盘输入事件,或者特定事件没有处理完毕,就会出现ANR */ // 启动自行车来做耗时操作 new Thread(new MyTimeing()).start(); } }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".MainActivity"> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="horizontal" android:gravity="center"> <TextView android:id="@+id/tv_info" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="0000000" android:layout_gravity="center_vertical" android:textSize="20sp" android:layout_marginLeft="10dp" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="倒计时" android:onClick="timeing" android:layout_gravity="right" /> </LinearLayout> </RelativeLayout>
案例二:文字变化(Handler+Message)
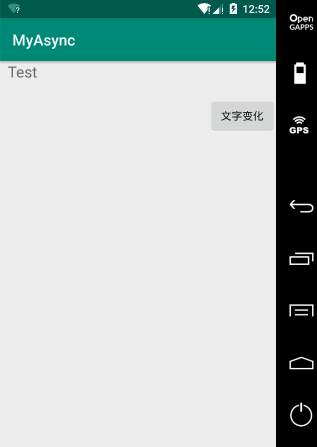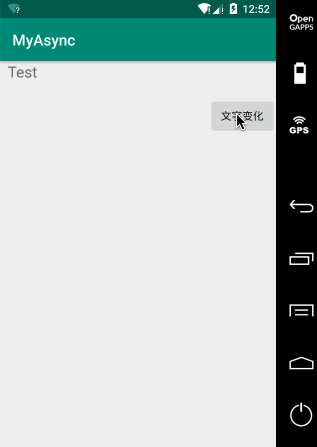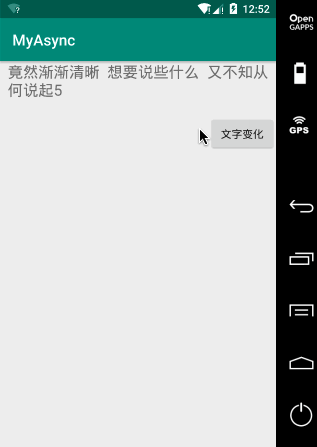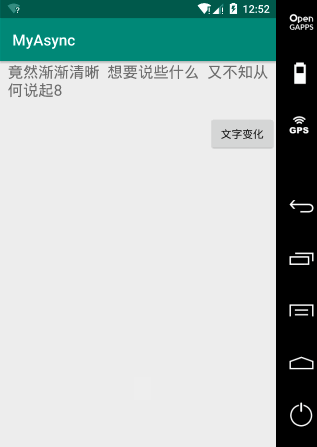
package liudeli.async; import android.os.Bundle; import android.os.Handler; import android.os.Message; import android.os.SystemClock; import android.support.v7.app.AppCompatActivity; import android.view.View; import android.widget.TextView; public class MainActivity2 extends AppCompatActivity { private TextView tvInfo; @Override protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.activity_main2); tvInfo = findViewById(R.id.tv_info); } private int count; /** * 定义Handler */ private Handler mHandler = new Handler(){ @Override public void handleMessage(Message msg) { super.handleMessage(msg); if (msg.obj == null) { return; } if (msg.what <= 7) { tvInfo.setText(msg.obj.toString() + ""); Message message = mHandler.obtainMessage(); message.what = count++; message.obj = "竟然渐渐清晰 想要说些什么 又不知从何说起" + count; mHandler.sendMessageDelayed(message, 900); } } }; /** * 执行文字变化 * @param view */ public void textChange(View view) { // mHandler.obtainMessage(i); 这种消息池方式获取Message消耗小 Message message = mHandler.obtainMessage(); message.what = 1; message.obj = "从那遥远海边 慢慢消失的你 本来模糊的脸"; // 从主线程 发送消息 到---> 主线程的handleMessage方法 mHandler.sendMessageDelayed(message, 800); count = 0; } }
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" tools:context=".MainActivity"> <LinearLayout android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:orientation="vertical" android:gravity="center"> <TextView android:id="@+id/tv_info" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Test" android:layout_gravity="center_vertical" android:textSize="20sp" android:layout_marginLeft="10dp" /> <Button android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="文字变化" android:onClick="textChange" android:layout_gravity="right" android:layout_marginTop="20dp" /> </LinearLayout> </RelativeLayout>
注意:⚠️在Activity的 onDestroy() 方法中,一定要记得回收
postDelayed 看似子线程,其实是属于主线程,postDelayed能延时run,但不能在子线程中执行,否则报错
这个开启的Runnable会在这个Handler所依附线程中运行,而这个Handler是在UI线程中创建的,所以自然地依附在主线程中了。
/** * 参数一:可以在Runnable中执行UI操作 * 参数二:延时时间 毫秒 * new Handler().postDelayed(Runnable r, long delayMillis); * @param view */ public void test(View view) { new Handler().postDelayed(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { Toast.makeText(MainActivity2.this, "postDelayed", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show(); } }, 2000); }
子线程 send 到 主线程 的常用方法
// 参数一:Message消息,可传递数据 // 参数二:delayMillis延时时间,延时多久才send,毫秒为单位 // 特点是:send Message消息,并可设置延时时间 // sendMessageDelayed(Message msg, long delayMillis) // 参数一:Message消息,可传递数据 // 特点是:立即send,不延时 // mHandler.sendMessage(Message msg) // 参数一:唯一标识what // 参数二:delayMillis延时时间,延时多久才send,毫秒为单位 // 特点是:send 唯一标识what,并可设置延时时间 // mHandler.sendEmptyMessageDelayed(int what, long delayMillis) // 参数一:唯一标识what // 特点是:send 唯一标识what,立即send // mHandler.sendEmptyMessage(int what)
消息池的概念:
Android操作系统启动后默认会有很多的消息池,这样的方式直接到系统里面消息池拿消息mHandler.obtainMessage(), 而new Message(); 是实例化消息(消耗多些)
推荐用mHandler.obtainMessage()方式
面试题:postDelayed(Runnable r) Runnable 是属于子线程吗?
答:和子线程没有半毛钱关系,命名叫Runnable而已,子线程必须是 有run方法,有.start();
new Thread(){ @Override public void run() { super.run(); } }.start();
按原理来说:子线程是不能执行UI操作,确实不能执行UI操作,但Android设计了API看起来可以在子线程(这是假象),实际是对Handler+Message进行了封装
/** * 在子线程中操作UI * @param view */ public void uiRun(View view) { new Thread(){ @Override public void run() { super.run(); /** * 第一种方式 */ runOnUiThread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { Toast.makeText(MainActivity2.this, "runOnUiThread", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show(); } }); /** * 第二种方式 */ Looper.prepare(); Toast.makeText(MainActivity2.this, "Looper", Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show(); Looper.loop(); } }.start(); }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号