Vuex极速入门

01、什么是Vuex?
1.1、为什么需要状态管理?
在复杂的系统中,我们会把系统按照业务逻辑拆分为多个层次、多个模块,采用组件式的开发方式。而此时不同模块、父子模块之间的通信就成了一个问题。
为了解决这个问题,就有了状态管理,核心概念就是把大家共享的状态(数据)抽出来,放到一个全局共享的仓库里,按照一定约定统一管理,让状态的变化可预测。这就有两个关键点:
- 统一存储:共享的状态统一存储,全局共享。
- 可预测:共享的状态不可随意修改,需要按照约定的规则修改,才能监测状态变更、通知更新。
1.2、Vuex简介
Vuex 就是面向Vue的状态管理组件,采用集中式存储+管理应用的所有共享状态。Vuex只能在Vue中使用,深度使用了Vue的能力,如用Vue来实现state的响应式特性。
Vue2.*版本 ▶ 对应Vuex3.*版本,Vuex3.* 中文文档Vue3.*版本 ▶ 对应Vuex4.*版本,Vuex4.* 中文文档
简单来说,就是Vuex有一个全局公共的store(类似Vue里的data),作为公共数据仓库,保存了大家共享的状态(数据)。这个数据仓库store实现了数据响应、自动通知更新,这样就很容易实现了各个组件间的数据通信了。
其实,对于简单的应用不一定需要Vuex,不过Vuex文件并不大(gzip压缩后10K左右)。
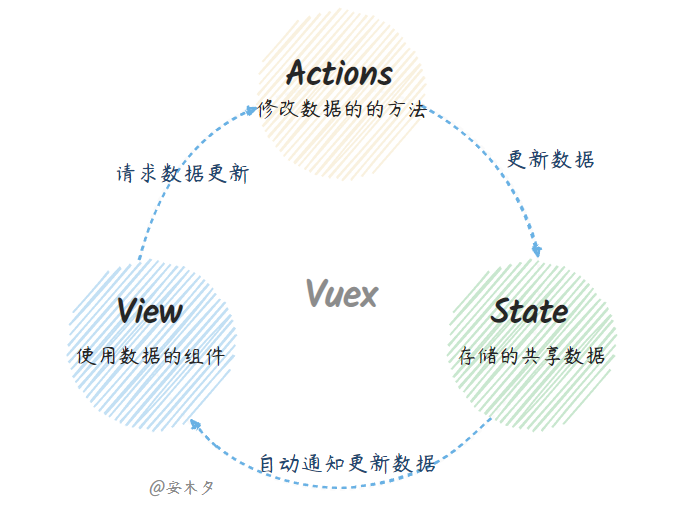
Vuex主要特点就是:单向数据流+单一数据源。
- state:存储数据仓库,类似Vue的
data,也是响应式的,变更后会自动通知View。 - views:组件视图,就是使用
state的Vue组件。 - actions:更新state状态,为了规范管理,state不能直接修改,必须通过
action进行提交。Vuex中分为同步Mutation、和异步Action。
02、安装使用
- 通过
<script>标签直接引用vuex.js:
<script src="https://cdn.jsdelivr.net/npm/vue@2/dist/vue.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vuex@3/dist/vuex.js"></script>
// 注册插件
Vue.use(Vuex);
- 通过
vue-cli脚手架搭建vue的开发框架,集成了vuex组件。 - 注册插件:
Vue.use(Vuex)
调试已经被集成在了Vue的调试工具Devtools中了。
03、Vuex3入门
3.1、Vuex选项&实例
| Store构造器选项 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| state | Vuex store 实例的根 state 对象 |
| mutations | 注册 mutation,就是修改数据的方法,参数为state。不支持异步,通过store.commit(name)调用 |
| actions | 注册 action,参数为context,同store实例,但不是她。支持异步,通过store.dispatch(name)调用 |
| getters | 注册 getter,{ [key: string]: Function },参数为state,定义、使用同计算属性 |
| modules | 子模块的对象,分割管理store,{ key(moduleName) : {state, namespaced?, mutations?, actions? ... }} |
| strict | 是否严格模式,默认false,true=严格模式下,任何 mutation 处理函数以外修改state 都会抛出错误。 |
| ✅store实例属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| state | 数据源state根对象 |
| getters | 所有注册的getter |
| ✅store 实例方法 | |
| commit(name, arg?, options?) | 提交 mutation 执行申请,name为mutation注册的方法名 |
| dispatch(name, arg?, options?) | 提交 action 执行申请,name为action注册的方法名 |
| replaceState(state: Object) | 替换 store 的根状态,用于合并状态,如加载持久化的state数据。 |
| watch(fn, callback) | 响应式地侦听 fn 的返回值,当值改变时调用回调函数 |
| subscribe(handler, option?) | 订阅 store 的 mutation,每一个mutation执行完调用 |
| subscribeAction(handler, option?) | 订阅 store 的 action |
| registerModule(path, module) | 注册一个动态模块 |
| unregisterModule(path) | 卸载一个动态模块 |
| hasModule(path) | 检查模块是否以注册 |
| hotUpdate(newOptions: Object) | 热替换新的 action 和 mutation |
const store = new Vuex.Store({
strict:false,
state: { //定义数据结构-数据仓库
points: 1000,
user: { id: '001', name: 'sam' }
},
mutations: { //修改数据的方法
setUser(state, obj) {
state.user.id = obj.uid;
state.user.name = obj.uname;
},
},
actions: { //修改数据的方法-异步
set(context, obj) { context.commit('setUser', obj) }
},
getters: { //获取数据的计算属性
userExist(state) { return state.user.id != ''; }
}
})
//提交数据修改
store.commit('setUser',{uid:'007',uname:'zhangsan'});
console.log(store.state.user); //id : "007" name : "zhangsan"
console.log(store.getters.userExist); //true
3.2、Vuex核心流程
Vuex核心概念:
- 🔹Store 单一状态树:一个应用程序中只有一个Store实例(单例模式),Store包含了
state、actions、mutations、getter、modules。一般会在根Vue注册store实例,这样组件内所有地方都可以this.$store访问了。 - 🔸State 数据源:实现了响应式监听,可用
mapState辅助函数包装为计算属性访问。 - 🔹Getter 访问属性:返回对
state状态数据进行加工后的结果,类似Vue中的计算属性、过滤器,区别就是这是全局共享的。 - 🔸Mutation 修改数据:Vuex中用于修改状态数据的主要方式,是唯一修改
state数据的合理途径了。通过store.commit()调用mutation。(mutation /mjuːˈteɪʃ(ə)n/ 改变) - 🔹Action 异步操作:类似Vue的
methods,支持异步操作。通过store.dispatch()调用,实际修改数据也是要调用mutation的。Action 可用来发起异步ajax请求获取处理 state的数据,这是和mutation最大的不同了。 - 🔹Module 模块:当Store很复杂时,用Module拆分为多个模块管理,每个模块里有自己的
state、actions、mutations、getter、modules。
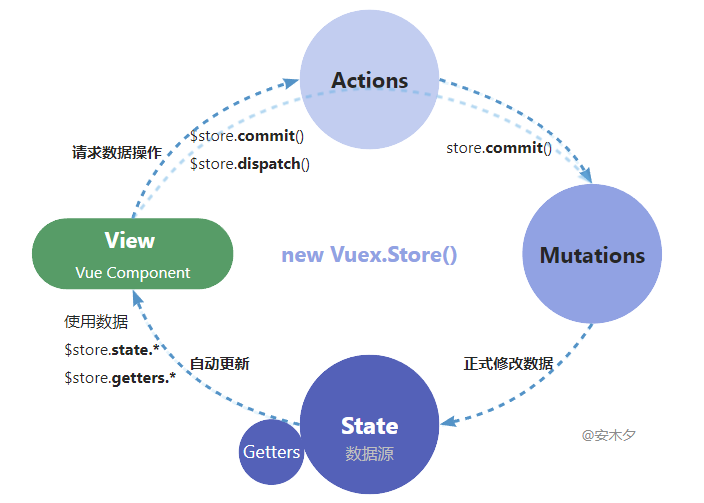
🔸基本流程:
❶ 定义数据 state,和data一样,预先定义好数据结构,以及数据更新的mutation方法。
❷ 使用数据 state
- 在根组件注入
store实例,组件内所有地方(包括后代组件)都可以this.$store访问了。 - 通过计算属性
computed包装所需的state数据。如果state数据需要双向绑定到表单元素,则需要用计算属性实现get、set来代理实现。 - 通过方法
methods包装数据的更新store.mutation。 - 在
View上绑定使用,可以绑定包装后的计算属性、方法,也可以直接绑定注入的$store。
❸ 触发更新,根据业务需要更新state数据。
- store.commit(name, arg?, options?)
- store.dispatch(name, arg?, options?)
❹ 正式修改state数据,并触发 View 自动更新。
<div id="app">
<button @click="login">登录</button>
<p>用户:{{$store.state.user.name}}({{$store.state.user.id}})</p>
<p v-text="`用户:${$store.state.user.name}(${$store.state.user.id})`"></p>
</div>
<script>
// 注册插件
Vue.use(Vuex);
//申明全局store
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: { user: { id: '', name: '' } },
mutations: { setUser(state, obj) { state.user.id = obj.uid; state.user.name = obj.uname; }, },
getters: { userExist(state) { return state.user.id != ''; } }
})
//根Vue
let app = new Vue({
el: '#app',
data: {},
store: store, //在根组件注入store实例,组件内所有地方都可以 this.$store 通过访问了
methods: {
login() { this.$store.commit('setUser',{ uid: '007', uname: 'zhangsan' }) }
}
})
</script>

3.3、创建Vuex()-购物车案例
- 注册插件:
Vue.use(Vuex) - 创建全局共享的
Store实例,并配置数据、方法。 - 注入
store,在根Vue组件上注入store实例。 - 愉快的使用了。
<script>
// 注册插件
Vue.use(Vuex);
//申明全局store
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: { cart: ['汽车01', '苹果', '梨子'] },
mutations: {
add(state, item) { state.cart.push(item); },
delete(state, index) { state.cart.splice(index,1) }
},
actions: { add(context, item) { context.commit('add', item) } },
getters: { cartTotal(state) { return state.cart.length; } }
})
</script>
<div id="app1">
<p>购物车({{this.$store.getters.cartTotal}})(直接绑定)</p>
<p>购物车({{cartTotal}}) <button @click="add">添加商品</button></p>
<cart-box></cart-box>
</div>
<template id="cardBoxTemplate"> <!--购物列表模板-->
<ul>
<li v-for="(item,index) in cartList">{{item}} <button v-on:click="deleteItem(index)">删除</button></li>
</ul>
</template>
<script>
let app1 = new Vue({
el: "#app1",
data: {},
store: store, //在根组件注入store实例,组件内所有地方都可以 this.$store 访问了
computed: {
cartTotal: function () { return this.$store.getters.cartTotal; }
},
methods: { add: function (item) { this.$store.dispatch('add', "西瓜") } },
components: { //购物车组件
'cart-box': {
computed: { cartList() { return this.$store.state.cart; } },
template: '#cardBoxTemplate',
methods: { deleteItem: function (index) { this.$store.commit("delete", index); } }
}
}
})
</script>

3.4、...mapState语法糖
mpaState是state的一种Vuex提供的 “语法糖”,主要作用是简化代码。比如当state有多个状态属性,在组件中都要用就得一个一个包装,代码冗余。这时,mapState就可以简化这个重复、无聊的代码了。
<script>
let app1 = new Vue({
el: "#app1",
data: {},
store: store,
computed: { //做一个简单包装,使用时更方便
card() { return $store.state.card; },
user() { return $store.state.user; }
},
computed: Vuex.mapState(['card', 'user']), //直接赋值,效果同上,简化了包装代理代码
computed: {
cartTotal: function () { return this.$store.getters.cartTotal; },
//展开运算符展开
...Vuex.mapState({
'cart': 'cart', //计算属性名称:state状态名称
currentUserId: 'user',
}),
...Vuex.mapState(['cart', 'user']) //更简洁的写法
},
})
</script>
- mpaState() 是Vuex提供一个辅助函数,帮助生成计算属性。返回的是一个对象(结构同计算属性
computed)。
mapState(namespace?: string, map: Array<string> | Object<string | function>): Object
- ...mapState,三个点
...是ES6的展开运算符,把对象展开混入当前环境。
其他还有 mapGetters、mapActions、mapMutations 都是类似作用和用法。
3.5、Module模块化
当共享的数据和操作太多时,就需要分模块管理了,如下模块示例。
const moduleA = {
state: { ... },
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... },
getters: { ... }
}
const moduleB = {
state: { ... },
mutations: { ... },
actions: { ... }
}
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
a: moduleA,
b: moduleB
}
})
store.state.a // -> moduleA 的状态
store.state.b // -> moduleB 的状态
每个模块 module 都包含完整的store结构。
module定义结构:
{ key(moduleName) : {state, namespaced?, mutations?, actions?, getters? modules? }}
- key:就是模块的名称,也是模块的命名空间。
- value,就是一个和
store结构相同的对象,存放模块的store信息。模块里方法的参数state、context都是命名空间内的局部对象。
模块化的项目结构:
├── index.html
├── main.js
├── api
│ └── ... # 抽取出API请求
├── components
│ ├── App.vue
│ └── ...
└── store
├── index.js # 我们组装模块并导出 store 的地方
├── actions.js # 根级别的 action
├── mutations.js # 根级别的 mutation
└── modules
├── cart.js # 购物车模块
└── products.js # 产品模块
04、Vuex4区别
几乎所有的 Vuex 4 API 都与 Vuex 3 保持不变,有少量差异。
- 创建方式不同,Vuex4 使用
createStore({})函数创建store对象,之前的方式依然支持。 - 安装方式,
app.use(store),已经注入了store实例,不用再注册store实例了。 - 打包产物已经与 Vue 3 配套。
- 新特性:
useStore组合式函数。//TODO
05、一些问题
❓Vuex的持久化?
如果用户刷新页面,导致页面的各种实例重新初始化,之前的全局状态就会丢失。解决方法就是把state数据仓库存起来,当刷新页面的时候读取出来,如果关闭页面就不用管了。
- 持久化
state:在页面刷新时的beforeunload事件中保存state到sessionStorage里。sessionStorage刷新页面不会丢失,关闭才清除。 - 加载
state:Vuecreate中加载持久化的state,并清除持久化的state数据。
created: function () {
window.addEventListener('beforeunload', () => {
sessionStorage.setItem('vstore', JSON.stringify(this.$store.state));
});
try {
const vstore = sessionStorage.getItem('vstore')
if (vstore)
this.$store.replaceState(Object.assign({}, this.$store.state, JSON.parse(vstore)));
}
catch (ex) { console.log(ex) }
sessionStorage.removeItem('vstore');
}
©️版权申明:版权所有@安木夕,本文内容仅供学习,欢迎指正、交流,转载请注明出处!原文编辑地址-语雀
 Vuex就是面向Vue的状态管理组件,采用集中式存储+管理应用的所有共享状态。目的是解决复杂系统中不同模块、父子模块之间的通信问题。
Vuex就是面向Vue的状态管理组件,采用集中式存储+管理应用的所有共享状态。目的是解决复杂系统中不同模块、父子模块之间的通信问题。

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号