- 作者: Laruence(




 )
) - 本文地址: http://www.laruence.com/2008/08/12/180.html
- 转载请注明出处
SAPI: Server abstraction API,研究过PHP架构的同学应该知道这个东东的重要性,它提供了一个接口,使得PHP可以和其他应用进行交互数据。 本文不会详细介绍每个PHP的SAPI,只是针对最简单的CGI SAPI,来说明SAPI的机制。
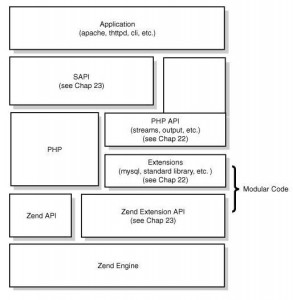
首先,我们来看看PHP的架构图:
SAPI提供了一个和外部通信的接口, 对于PHP5.2,默认提供了很多种SAPI, 常见的给apache的mod_php5,CGI,给IIS的ISAPI,还有Shell的CLI,本文就从CGI SAPI入手 ,介绍SAPI的机制。 虽然CGI简单,但是不用担心,它包含了绝大部分内容,足以让你深刻理解SAPI的工作原理。
要定义个SAPI,首先要定义个sapi_module_struct, 查看 PHP-SRC/sapi/cgi/cgi_main.c:
- */
- static sapi_module_struct cgi_sapi_module = {
- #if PHP_FASTCGI
- "cgi-fcgi", /* name */
- "CGI/FastCGI", /* pretty name */
- #else
- "cgi", /* name */
- "CGI", /* pretty name */
- #endif
- php_cgi_startup, /* startup */
- php_module_shutdown_wrapper, /* shutdown */
- NULL, /* activate */
- sapi_cgi_deactivate, /* deactivate */
- sapi_cgibin_ub_write, /* unbuffered write */
- sapi_cgibin_flush, /* flush */
- NULL, /* get uid */
- sapi_cgibin_getenv, /* getenv */
- php_error, /* error handler */
- NULL, /* header handler */
- sapi_cgi_send_headers, /* send headers handler */
- NULL, /* send header handler */
- sapi_cgi_read_post, /* read POST data */
- sapi_cgi_read_cookies, /* read Cookies */
- sapi_cgi_register_variables, /* register server variables */
- sapi_cgi_log_message, /* Log message */
- NULL, /* Get request time */
- STANDARD_SAPI_MODULE_PROPERTIES
- };
这个结构,包含了一些常量,比如name, 这个会在我们调用php_info()的时候被使用。一些初始化,收尾函数,以及一些函数指针,用来告诉Zend,如何获取,和输出数据。
- static int php_cgi_startup(sapi_module_struct *sapi_module)
- {
- if (php_module_startup(sapi_module, NULL, 0) == FAILURE) {
- return FAILURE;
- }
- return SUCCESS;
- }
- static int sapi_cgi_deactivate(TSRMLS_D)
- {
- /* flush only when SAPI was started. The reasons are:
- 1. SAPI Deactivate is called from two places: module init and request shutdown
- 2. When the first call occurs and the request is not set up, flush fails on
- FastCGI.
- */
- if (SG(sapi_started)) {
- sapi_cgibin_flush(SG(server_context));
- }
- return SUCCESS;
- }
- static inline size_t sapi_cgibin_single_write(const char *str, uint str_length TSRMLS_DC)
- {
- #ifdef PHP_WRITE_STDOUT
- long ret;
- #else
- size_t ret;
- #endif
- #if PHP_FASTCGI
- if (fcgi_is_fastcgi()) {
- fcgi_request *request = (fcgi_request*) SG(server_context);
- long ret = fcgi_write(request, FCGI_STDOUT, str, str_length);
- if (ret <= 0) {
- return 0;
- }
- return ret;
- }
- #endif
- #ifdef PHP_WRITE_STDOUT
- ret = write(STDOUT_FILENO, str, str_length);
- if (ret <= 0) return 0;
- return ret;
- #else
- ret = fwrite(str, 1, MIN(str_length, 16384), stdout);
- return ret;
- #endif
- }
- static int sapi_cgibin_ub_write(const char *str, uint str_length TSRMLS_DC)
- {
- const char *ptr = str;
- uint remaining = str_length;
- size_t ret;
- while (remaining > 0) {
- ret = sapi_cgibin_single_write(ptr, remaining TSRMLS_CC);
- if (!ret) {
- php_handle_aborted_connection();
- return str_length - remaining;
- }
- ptr += ret;
- remaining -= ret;
- }
- return str_length;
- }
把真正的写的逻辑剥离出来,就是为了简单实现兼容fastcgi的写方式。
- static char *sapi_cgibin_getenv(char *name, size_t name_len TSRMLS_DC)
- {
- #if PHP_FASTCGI
- /* when php is started by mod_fastcgi, no regular environment
- is provided to PHP. It is always sent to PHP at the start
- of a request. So we have to do our own lookup to get env
- vars. This could probably be faster somehow. */
- if (fcgi_is_fastcgi()) {
- fcgi_request *request = (fcgi_request*) SG(server_context);
- return fcgi_getenv(request, name, name_len);
- }
- #endif
- /* if cgi, or fastcgi and not found in fcgi env
- check the regular environment */
- return getenv(name);
- }
- static int sapi_cgi_send_headers(sapi_headers_struct *sapi_headers TSRMLS_DC)
- {
- char buf[SAPI_CGI_MAX_HEADER_LENGTH];
- sapi_header_struct *h;
- zend_llist_position pos;
- if (SG(request_info).no_headers == 1) {
- return SAPI_HEADER_SENT_SUCCESSFULLY;
- }
- if (cgi_nph || SG(sapi_headers).http_response_code != 200)
- {
- int len;
- if (rfc2616_headers && SG(sapi_headers).http_status_line) {
- len = snprintf(buf, SAPI_CGI_MAX_HEADER_LENGTH,
- "%s\r\n", SG(sapi_headers).http_status_line);
- if (len > SAPI_CGI_MAX_HEADER_LENGTH) {
- len = SAPI_CGI_MAX_HEADER_LENGTH;
- }
- } else {
- len = sprintf(buf, "Status: %d\r\n", SG(sapi_headers).http_response_code);
- }
- PHPWRITE_H(buf, len);
- }
- h = (sapi_header_struct*)zend_llist_get_first_ex(&sapi_headers->headers, &pos);
- while (h) {
- /* prevent CRLFCRLF */
- if (h->header_len) {
- PHPWRITE_H(h->header, h->header_len);
- PHPWRITE_H("\r\n", 2);
- }
- h = (sapi_header_struct*)zend_llist_get_next_ex(&sapi_headers->headers, &pos);
- }
- PHPWRITE_H("\r\n", 2);
- return SAPI_HEADER_SENT_SUCCESSFULLY;
- }
- static int sapi_cgi_read_post(char *buffer, uint count_bytes TSRMLS_DC)
- {
- uint read_bytes=0, tmp_read_bytes;
- #if PHP_FASTCGI
- char *pos = buffer;
- #endif
- count_bytes = MIN(count_bytes, (uint) SG(request_info).content_length - SG(read_post_bytes));
- while (read_bytes < count_bytes) {
- #if PHP_FASTCGI
- if (fcgi_is_fastcgi()) {
- fcgi_request *request = (fcgi_request*) SG(server_context);
- tmp_read_bytes = fcgi_read(request, pos, count_bytes - read_bytes);
- pos += tmp_read_bytes;
- } else {
- tmp_read_bytes = read(0, buffer + read_bytes, count_bytes - read_bytes);
- }
- #else
- tmp_read_bytes = read(0, buffer + read_bytes, count_bytes - read_bytes);
- #endif
- if (tmp_read_bytes <= 0) {
- break;
- }
- read_bytes += tmp_read_bytes;
- }
- return read_bytes;
- }
- static char *sapi_cgi_read_cookies(TSRMLS_D)
- {
- return sapi_cgibin_getenv((char *) "HTTP_COOKIE", sizeof("HTTP_COOKIE")-1 TSRMLS_CC);
- }
- static void sapi_cgi_register_variables(zval *track_vars_array TSRMLS_DC)
- {
- /* In CGI mode, we consider the environment to be a part of the server
- * variables
- */
- php_import_environment_variables(track_vars_array TSRMLS_CC);
- /* Build the special-case PHP_SELF variable for the CGI version */
- php_register_variable("PHP_SELF", (SG(request_info).request_uri ? SG(request_info).request_uri : ""), track_vars_array TSRMLS_CC);
- }
- static void sapi_cgi_log_message(char *message)
- {
- #if PHP_FASTCGI
- if (fcgi_is_fastcgi() && fcgi_logging) {
- fcgi_request *request;
- TSRMLS_FETCH();
- request = (fcgi_request*) SG(server_context);
- if (request) {
- int len = strlen(message);
- char *buf = malloc(len+2);
- memcpy(buf, message, len);
- memcpy(buf + len, "\n", sizeof("\n"));
- fcgi_write(request, FCGI_STDERR, buf, len+1);
- free(buf);
- } else {
- fprintf(stderr, "%s\n", message);
- }
- /* ignore return code */
- } else
- #endif /* PHP_FASTCGI */
- fprintf(stderr, "%s\n", message);
- }
经过分析,我们已经了解了一个SAPI是如何实现的了, 分析过CGI以后,我们也就可以想象mod_php, embed等SAPI的实现机制。 :)


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号