论文笔记[4] GPT 1-3 梳理和对比
论文题目:
Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training
Language Models are Unsupervised Multitask Learners
Language Models are Few-Shot Learners
论文传送门: GPT1 GPT2 GPT3
论文团队:OpenAI
GPT-1
Motivation & Objectives#
-
most SOTA NLP models were trained specifically on a particular task
- Limitations:
① need large amount of annotated data, not easily available
② fail to generalize
- Limitations:
-
2 Challenges:
① which optimization objectives are most effective?
② what’s the most efficient way to transfer learned representations to target task?⇒ \Rightarrow ⇒ A semi-supervised approach using a combination of unsupervised pre-training and supervised fine-tuning
⇒ \Rightarrow ⇒ To learn a universal representation that transfers with little adaptation to a wide range of tasks -
learning a generative language model using unlabeled data and then fine-tuning the model by providing examples of specific downstream tasks
- 不清楚要使用哪种optimization objectives在学习到用于迁移的表示中最有用
- 哪种方式来transfer这些learned representations to the target task还没达成共识(a combination of making task-specific changes to the model architecture,using intricate learning schemes,adding auxiliary(辅助的) learning objectives)
Framework#
Unsupervised Language Modeling (Pre-training):#
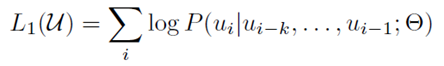
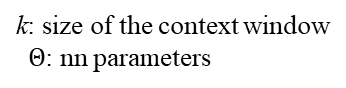
- multi-layer Transformer decoder (N = 12)
- NO Encoder-Decoder Attention Layer
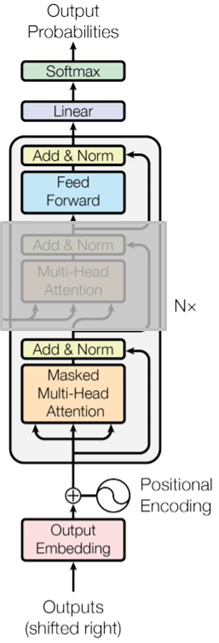
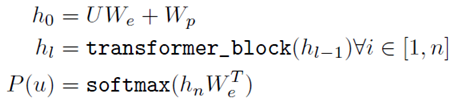
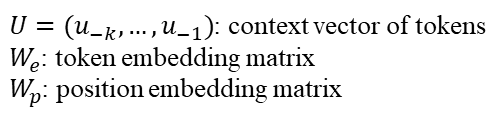

-
去掉Encoder-Decoder Attention层作为模型的主体,然后将decoder的输出经过一个softmax层,来产生目标词的输出分布。
-
h n h_{n} hn可以理解为是输出层对词汇表中各个词语的注意力权重;而 h n W e h_{n}W_{e} hnWe就是输出层对各个token的注意力大小。经过预训练的GPT中,存储了从语料中学习到的语义和语法信息。
Supervised Fine-Tuning#
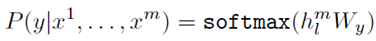
- objective to maximize
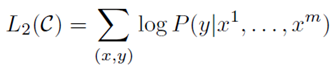
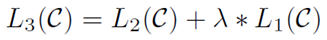
- Advatages:
① improving generalization of the supervised model
② accelerating convergence
λ \lambda λ是超参数,设置为0.5

Experiment#
- Dataset: BooksCorpus (7000 unpublished books, unseen data) large stretches of contiguous text, which helped the model learn large range dependencies
- Unsupervised Training:
- Byte Pair Encoding (BPE) vocabulary with 40,000 merges was used
- 768-dimensional state for encoding tokens
- 12 layered model, 12 attention heads
- position-wise feed forward layer: 3072-dimensional
- 117M parameters
- Supervised Fine-tuning:
- 3 epochs for most of the downstream tasks → already learnt a lot during pre-training. Thus, minimal fine-tuning was enough
- Most of the hyperparameters from unsupervised pre-training were used for fine-tuning



- Works well across datasets of different sizes, from smaller datasets such as STS-B (5.7k training examples) – to the largest one – SNLI (550k training examples)
Discussion#
-
Impact of number of layers transferred
-
Evolution of zero-shot performance on different tasks as a function of LM pre-training updates


- transformer block的个数越多,也就是语言模型越深,效果越好,说明语言模型的各个layer确实学到了不一样的东西
- 不对语言模型进行fine-tuning时,pretrain语言模型的迭代次数越多,最后的效果越好,说明语言模型的pretrain确实学到了general的东西
-
Ablation studies

-
larger datasets benefit from the auxiliary objective but smaller datasets do not
-
5.6 average score drop when using LSTM (single layer 2048 unit LSTM)
-
lack of pre-training hurts performance across all the tasks, resulting in a 14.8% decrease
Conclusion#
-
GPT-1 performed SOTA in 9 out of 12 tasks
-
decent zero-shot performance on various tasks
-
GPT-1 proved that LM served as an effective pre-training objective. The architecture facilitated transfer learning and could perform various NLP tasks with very little fine-tuning.
GPT-2
Main Idea#
-
Learning Objectives & Concepts
- learning multiple tasks using the same unsupervised model (×supervised fine-tuning)
- objective: P(output|input) → P(output|input, task) [task conditioning]
-
Zero Shot Learning and Zero Shot Task Transfer
- no examples are provided and the model understands the task based on the given instruction
- E.g. (translate to french, english text, french text)
-
LM = Unsupervised Multitask Learning
- the supervised output is a subset of the language model sequence
- E.g1. “The translation of word Machine Learning in chinese is 机器学习.”
- E.g2. “The President of the United States is Trump.”
相比于有监督的多任务学习,语言模型只是不需要显示地定义哪些字段是要预测的输出,所以,实际上有监督的输出只是语言模型序列中的一个子集
Model Architecture#

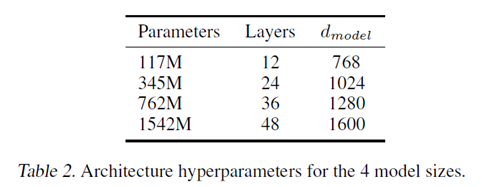
- GPT-2 has 1.5 billion parameters [GPT-1 (117M parameters)]
- 48 layers, 1600-dimension
- Larger vocabulary of 50,257 tokens
- Larger batch size of 512 and larger context window of 1024 tokens
- Layer normalisation was moved to input of each sub-block and an additional layer normalisation was added after final self-attention block
- At initialisation, the weight of residual layers was scaled by 1/√N, where N was the number of residual layers
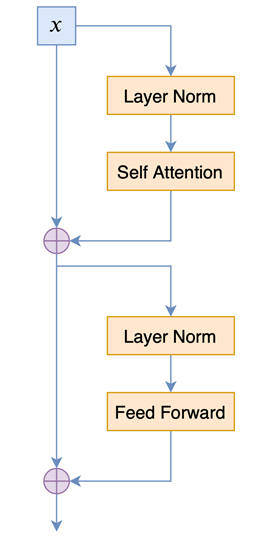
scaled by 1/√N是因为残差层的参数初始化根据网络深度进行调节。
Dataset & Experiment#
- WebText, had 40GB of text data from over 8 million documents (removed Wikipedia)

- In French to English translation task, GPT-2 performed better than most unsupervised models in zero shot setting but did not outperform the SOTA unsupervised model
- GPT-2 could not perform well on text summarization and its performance was similar or lesser than classic models trained for summarization
Generalization vs Memorization#
最近的计算机视觉研究表明,图像数据集通常都会包含一些类似的图像,例如CIFAR-10在训练集与测试集中就有3.3%的重复数据,这导致了对机器学习的泛化性能被过度高估。
- Overlapping → over-reporting of the generalization performance of machine learning systems
- Bloom filters containing 8-grams of WebText training set tokens
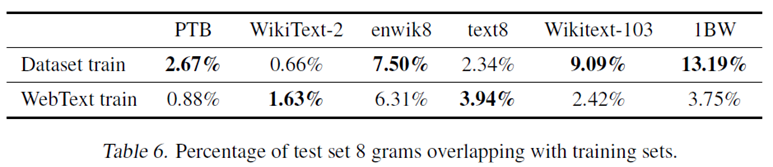
- recommend the use of n-gram overlap based de-duplication as an important verification step and sanity check during the creation of training and test splits for new NLP datasets.
- performance on training and test are similar and improve together as model size is increased → underfitting on WebText in many ways

Summary#
- achieve SOTA results on 7 out of 8 tested language modelling datasets in zero-shot
- larger dataset & more parameters improved the capability of LM to understand tasks
- How to use:

GPT-3
Introduction#
-
Limitation: although task-agnostic, still a need for task-specific datasets and fine-tuning
-
BERT, etc:
① Excessive reliance on supervised data in the field
② Overfitting to the data distribution
⇒ \Rightarrow ⇒Focusing on more general NLP model
⇒ \Rightarrow ⇒Less supervised data, no fine-tuning. -
Concepts
- In-context learning: Large language models develop pattern recognition and other skills using the text data they are trained on.
- Few-shot, one-shot and zero-shot setting: capability ↑ as capacity ↑


Model and Implementation details#
- GPT-3 has 96 layers with each layer having 96 attention heads.
- Size of word embeddings: 1600 for GPT-2 → 12888 for GPT-3
- Context window size: 1024 for GPT-2 → 2048 tokens for GPT-3
- Alternating dense and locally banded sparse attention patterns


- sparse attention:

使用交替的密集和局部带状的稀疏注意模式 (没说细节,参考论文Generating Long Sequences with Sparse Transformers). Sparse Transformer只关注k个贡献最大的状态。通过显式选择,只关注少数几个元素,与传统的注意方法相比,对于与查询不高度相关的值将被归0。
- sparse attention:
Experiment#
- Dataset (45TB): trained on a mix of 5 different corpora, each having certain weight assigned to it. High quality datasets were sampled more often, and model was trained for more than 1 epoch
- downloaded and filtered a version of CommonCrawl
- fuzzy deduplication
- added high-quality reference corpora




Discussion & Broader Impacts#

- losing coherency while formulating long sentences and repeats sequences
- does not perform very well on tasks like, fill in the blanks, some reading comprehension tasks etc.
- Unidirectionality?
- lacks the notion of task or goal-oriented prediction of tokens, suggests:
- augmentation of learning objective, use of reinforcement learning to fine tune models, etc.
- complex & costly, heavy architecture, less interpretability
- misuse of its human-like text generating capability for phishing, spamming, spreading misinformation
- gender, ethnicity, race & religion bias
Conclusion#
-
BIGGER
-
Under Few-shot setting, it surpasses the current Fine-tuning SOTA on some NLU tasks
-
performs well on downstream NLP tasks in zero-shot and few-shot setting: writing articles, summing up numbers, writing codes, etc.
-
Most impressive: generalization
几个GPT-3的demo:
Ref:
[1] GPT-1论文翻译
[2] 【论文笔记】GPT-1:Improving Language Understanding by Generative Pre-Training
[3] GPT——生成式预训练Transformer
[4] The Journey of Open AI GPT models
[5] OpenAI GPT2原理解读
[6] GPT2.0 Language Models are Unsupervised Multitask Learners 论文解读
[7] 上车!带你一文了解GPT-2模型(transformer语言模型可视化)
[8] 总结GPT1和GPT2
[9] 直觀理解 GPT-2 語言模型並生成金庸武俠小說





【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构