TF的使用
激活函数
关于激活函数的介绍请参考:激活函数
这里只是记录TF提供的激活函数
import tensorflow as tf a = tf.nn.relu( tf.matmul(x, w1) + biases1 ) y = tf.nn.relu( tf.matmul(a, w2) + biases2 )
tf.cast
cast(
x,
dtype,
name=None
)
#将x的数据格式转化成dtype.例如,原来x的数据格式是bool,
#那么将其转化成float以后,就能够将其转化成0和1的序列。反之也可以
import tensorflow as tf
a = tf.Variable([1,0,0,1,1])
b = tf.cast(a,dtype=tf.bool)
sess = tf.Session()
sess.run( tf.global_variables_initializer() )
print(sess.run(b))
#[ True False False True True]
tf.greater与tf.select连用在自定义损失函数中,注意:tf.select is deprecated since v0.12 and was renamed to tf.where in v1.0
在预测商品销量时,预测多了,损失的是成本;预测少了,损失的是利润。比如一个商品成本是1元,利润是10元,少预测一个就少挣10元,而多预测一个则少挣1元。损失函数为:其中x为真实销量,y为预测值
这样用自定义的损失函数而不是均方误差才能获得最大利润
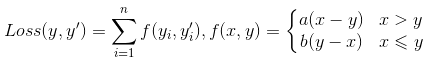
import tensorflow as tf v1 = tf.constant( [1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 4.0] ) v2 = tf.constant( [4.0, 3.0, 2.0, 1.0] ) sess = tf.InteractiveSession() print(tf.greater(v1, v2).eval()) #[False False True True] print(tf.select(tf.greater(v1, v2), v1, v2).eval() ) #[4. 3. 3. 4.] a = tf.constant([10.0]) b = tf.constant( [1.0] ) loss = tf.reduce_sum(tf.select(tf.greater(v1, v2), (v1 - v2) * a, (v2-v1) * b) ) print(loss.eval()) #44.0 #ft.greater()输入的是两个张量,比较大小,返回真假 #tf.select()有三个参数,第一个为条件,为True时,tf.select会选择第二个参数值,否则会使用第三个参数值



