利用Spring的Profile加载指定数据源
开发、测试、生产都有各自的数据库,这样需要配置的数据源不一样。
每次部署时修改配置过于繁琐,此时,可以使用Spring的Profile来配置多个数据源,运行前指定需要加载的数据源即可。
采用spring结合junit做演示,使用oracle和mysql做数据源区别演示,Profile名指定为oracle和mysql,junit测试时,使用@ActiveProfiles("mysql"),@ActiveProfiles("oracle")来指定需要加载的数据源。
实际工作开发、测试、生产用的同一种数据库,指定Profile名称不同,运行是指定需要加载的Profile即可。
在spring配置文件applicationContext.xml中配置oracle和mysql数据源
applicationContext-profile.xml,在其中配置Spring JdbcTemplate,junit测试查询数据库用。
<beans profile="oracle"> <!-- properties file --> <bean id="propertyConfigurer" class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer"> <property name="locations"> <list> <value>classpath:oracle.properties</value> </list> </property> </bean> <!-- 配置连接池 --> <bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource"> <property name="driverClass" value="${oracle.driver}"/> <property name="jdbcUrl" value="${oracle.url}"/> <property name="user" value="${oracle.username}"/> <property name="password" value="${oracle.password}"/> </bean> </beans> <beans profile="mysql"> <!-- properties file --> <!--<bean id="propertyConfigurer" class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer"> <property name="locations"> <list> <value>classpath:mysql.properties</value> </list> </property> </bean>--> <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:mysql.properties"/> <!-- 配置连接池 --> <bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource"> <property name="driverClass" value="${mysql.driver}"/> <property name="jdbcUrl" value="${mysql.url}"/> <property name="user" value="${mysql.username}"/> <property name="password" value="${mysql.password}"/> </bean> </beans> <beans> <bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate"> <property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property> </bean> </beans>
oracle.properties
oracle.driver=oracle.jdbc.driver.OracleDriver
oracle.url=jdbc:oracle:thin:@localhost:1521:orcl
oracle.username=scott
oracle.password=tiger
mysql.properties
mysql.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
mysql.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test
mysql.username=root
mysql.password=root
OracleProfileTest.java
import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; import org.springframework.test.context.ActiveProfiles; import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; import javax.sql.rowset.JdbcRowSet; import java.util.Map; /** * @ClassName ProfileTest * @Description TODO * @Author AlphaJunS * @Date 2020/4/2 20:06 * @Version 1.0 */ @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration(locations = {"classpath*:applicationContext-profile.xml"}) @ActiveProfiles("oracle") public class OracleProfileTest { @Autowired private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; @Test public void oracleTest() { String sql = "select * from emp where empno = 7900"; Map<String, Object> map = jdbcTemplate.queryForMap(sql); System.out.println(map); } }
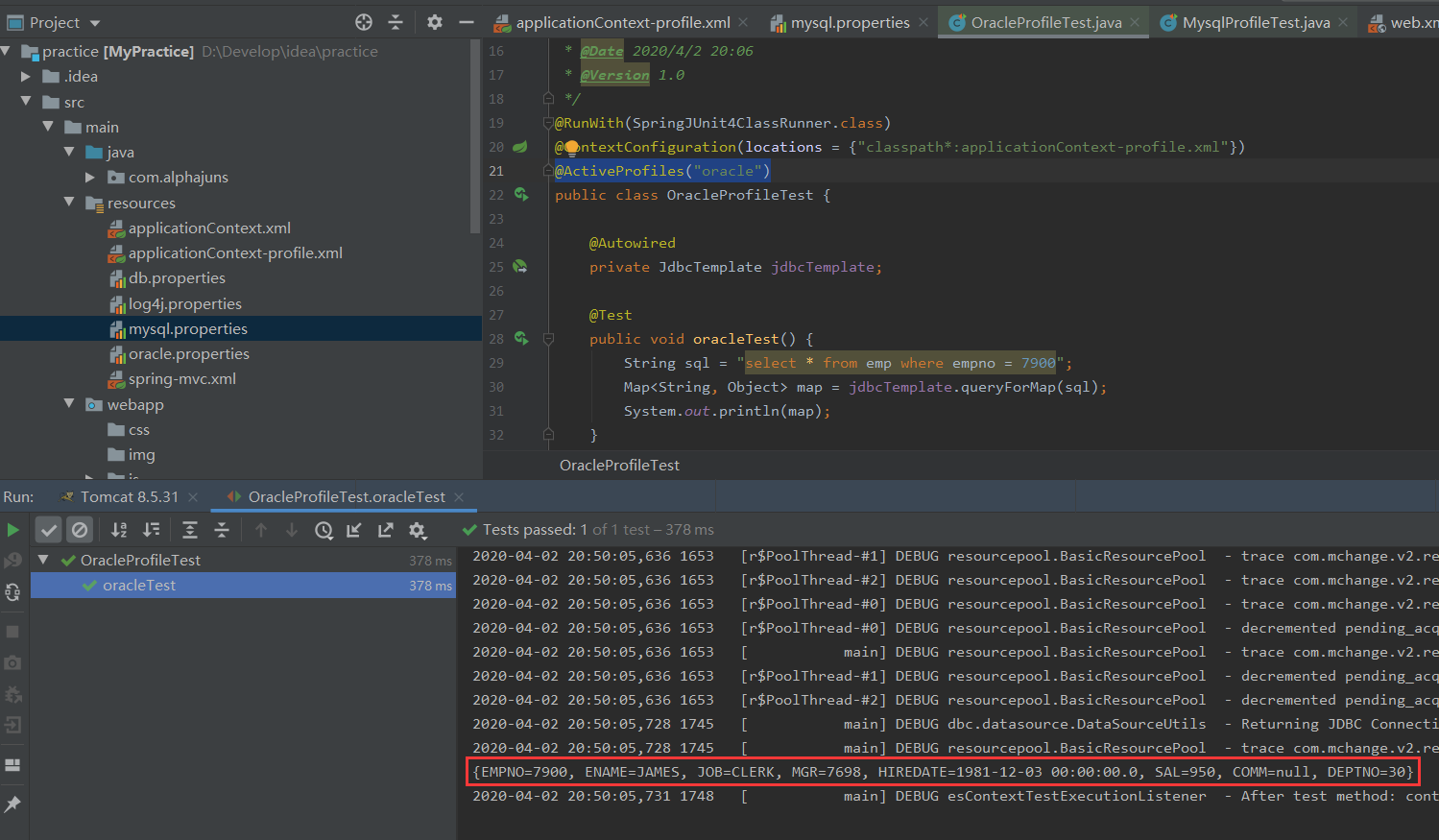
MysqlProfileTest.java
import org.junit.Test; import org.junit.runner.RunWith; import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; import org.springframework.test.context.ActiveProfiles; import org.springframework.test.context.ContextConfiguration; import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringJUnit4ClassRunner; import java.util.Map; /** * @ClassName MysqlProfileTest * @Description TODO * @Author AlphaJunS * @Date 2020/4/2 20:14 * @Version 1.0 */ @RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration(locations = {"classpath*:applicationContext-profile.xml"}) @ActiveProfiles("mysql") public class MysqlProfileTest { @Autowired private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate; @Test public void mysqlTest() { String sql = "select * from test where id = 1"; Map<String, Object> map = jdbcTemplate.queryForMap(sql); System.out.println(map); } }

其中配置profile时,可以引入数据库配置文件的方式有多种。
配置方法1
<bean id="configProperties" class="org.springframework.beans.factory.config.PropertiesFactoryBean"> <property name="locations"> <list> <value>classpath:value.properties</value> </list> </property> </bean>
配置方法2 <util:properties id="configProperties" location="classpath:value.properties"></util:properties>
配置方式3 <context:property-placeholder location="classpath:mysql.properties"/>
激活指定Profile
junit使用@ActiveProfiles("oracle")
web.xml中配置初始化参数使用spring.profiles.default、spring.profiles.active

参考帖子:
使用PropertyPlaceholderConfigurer指定配置文件和@Value 注解获取properties值


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号