Java 局部内部类、匿名内部类详解
文章目录
外部类与内部类
众所周知,每个java文件必须有一个与这个java文件同名的外部类,这个外部类可以是public或default的。而除了这个同名外部类,还可以有与这个同名外部类平级的其他外部类,但它们必须是default的。
而内部类是指在外部类的内部再定义一个类。
内部类的分类
我们所说的内部类,官方的叫法是嵌套类(Nested Classes)。嵌套类包括静态内部类(Static Nested Classes)和内部类(Inner Classes)。而内部类分为成员内部类,局部内部类(Local Classes)和匿名内部类(Anonymous Classes)。
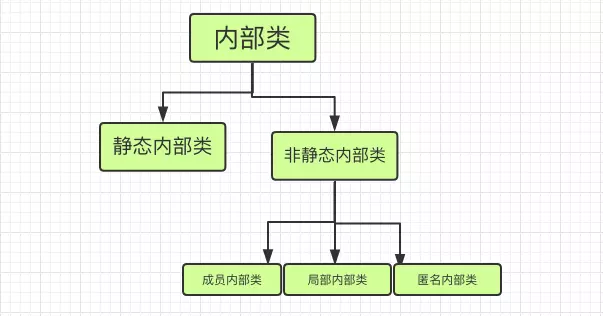
但按我的理解来看,应该这么画图:
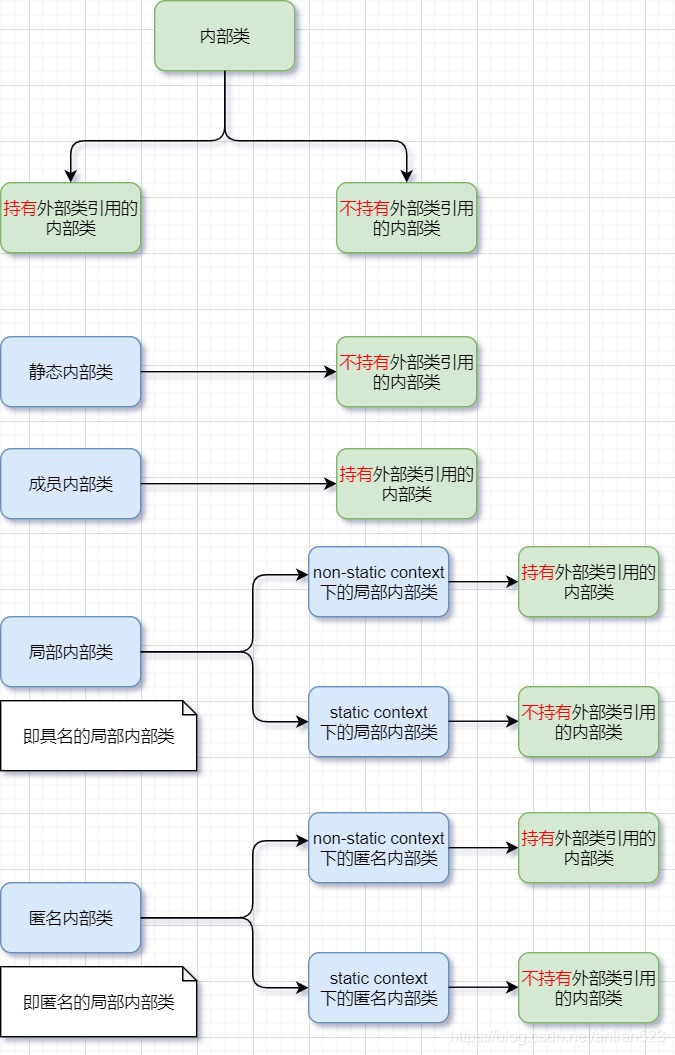
而从使用方法来讲,则应该把静态内部类和成员内部类归在一起,因为这两种是可以通过outer.staticInner或者outer.memberInner这种.语法来使用类名的。与之相对,局部内部类和匿名内部类是无法通过.语法来使用类名,这是因为这二者的使用范围会被限定到某个作用域之内(即在某对{...}大括号之中),也是因为这二者不是作为外部类的成员(既不是静态成员,也不是实例成员)。
- 非静态内部类的对象创建时,会依赖到外部类对象(持有外部类对象引用)。但具体的说,是指在non-static context这种上下文中。更具体的说,成员内部类一定会持有外部类对象引用,局部内部类(具名或匿名)却不一定。
- 内部类可以访问外部类的私有方法,和私有成员。
- 局部内部类不管是具名还是匿名的,其类定义前不可以加上
static(究其原因是局部内部类不属于外部类的成员,只有成员才有静态和非静态之分)。同样,其成员和方法也不可以加上static。 - 局部内部类包括匿名内部类,即局部内部类中分别两种:具名的、匿名的。匿名的就叫匿名内部类了。
- 具名的局部内部类的类定义不可以加上访问权限限定词。
public protected private都不可以。
局部内部类
局部内部类分为两种:1.通过继承抽象类或实现接口或普通类来定义新类(将用这种举例,因为这种更具有实用价值) 2.直接定义一个新类(虽然感觉这样做没什么用)。如果是匿名内部类则只有第1种。
首先给一个interface:
public interface Destination {
String readLabel();
}
局部内部类访问外部类成员(non-static context)
当局部内部类的类定义处于一个非静态上下文时,局部内部类可以访问外部类的私有成员(静态或非静态)或私有方法(静态或非静态):(对于具名的还是匿名的都成立)
public class test3 {
private int num = 1;
private static int snum = 2;
private String returnString(){
return "outer string";
}
private static String sreturnString(){
return "static outer string";
}
public Destination destination() {//这里是非静态方法,属于非静态context
class PDestination implements Destination {
private String label;
//内部类访问外部类私有成员,这里改成snum也可以
private int i = num;
private PDestination() {
//内部类访问外部类私有方法,这里改成sreturnString也可以
label = returnString();
}
public String readLabel() { return label; }
}
return new PDestination();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
test3 t = new test3();
Destination d = t.destination();
}
}
局部内部类访问外部类成员(static context)
public class test3 {
private int num = 1;
private static int snum = 2;
private String returnString(){
return "outer string";
}
private static String sreturnString(){
return "static outer string";
}
public static void testNamed(){//静态方法内,具名的局部内部类
class PDestination implements Destination {
private String label = "named inner";
public String readLabel() { return label; }
public void test(){
sreturnString();
//non-static method returnString() cant be refenrenced from a static context
//returnString();//无法通过编译
}
}
}
public static void testNoNamed() {//静态方法内,匿名内部类
Destination d = new Destination(){
private String label = "no named inner";
public String readLabel() { return label; }
public void test(){
sreturnString();
//non-static method returnString() cant be refenrenced from a static content
//returnString();//无法通过编译
}
};
}
public static Destination d = new Destination(){//作为静态成员,的匿名内部类
private String label = "no named inner";
public String readLabel() { return label; }
public void test(){
sreturnString();
//non-static method returnString() cant be refenrenced from a static content
//returnString();//无法通过编译
}
};
public static void main(String[] args) {
test3 t = new test3();
}
}
经过测试发现,当局部内部类(具名或匿名)的类定义属于static context时,是不可以访问外部类的非静态成员或方法。道理很简单,static context是类相关的,此时可能没有对象,当然不能访问非静态的东西,也就是说,这种情况下局部内部类对象没有持有外部类对象的引用。上面测试了三种static context的情况:
- 静态方法内,具名的局部内部类
- 静态方法内,匿名内部类
- 作为静态成员,的匿名内部类
外部类访问局部内部类成员
在局部内部类的作用域内(指包裹内部类的那个{...}内),内部类之外,是可以随意访问内部类对象的私有成员的。(注意,构造器可以直接访问;但方法和成员则必须通过内部类对象的.语法来访问哦;但一旦出了作用域,除了接口规定好的方法外,其他的方法和成员都无法访问,因为编译器只认为对象是一个Destination对象):(对于具名的还是匿名的都成立)
public class Parcel5 {
public Destination destination(String s) {
class PDestination implements Destination {
private String label;
private PDestination(String whereTo) {
label = whereTo;
}
public String readLabel() { return label; }
}
//访问了内部类私有的构造器
return new PDestination(s);
}
public String getLabel(String s) {
class PDestination implements Destination {
private String label;
private PDestination(String whereTo) {
label = whereTo;
}
public String readLabel() { return label; }
}
//访问了内部类对象的私有成员
return new PDestination(s).label;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Parcel5 p = new Parcel5();
Destination d = p.destination("Tasmania");
//System.out.println(d.label); cant resolve symbol label
//new PDestination("");
System.out.println(p.getLabel("private string"));
}
}
给内部类成员赋值
当然,上面例子也可以改成,方法参数直接给内部类成员赋值:
public class Parcel5 {
public Destination destination(String s) {
class PDestination implements Destination {
//private String label = s; //定义字段时同时初始化
//也可以把下面四行注释掉,上面这行注释取消掉
private String label;
PDestination(){
label = s;
}
public String readLabel() { return label; }
}
return new PDestination();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Parcel5 p = new Parcel5();
Destination d = p.destination("Tasmania");
}
}
局部内部类还可以访问局部变量,在jdk1.8以前这个局部变量必须加上final,由于本人jdk是1.8,新特性支持不需要加final了(注意形参也是局部变量,所以上面的例子也不需要加final)(虽然不用加final,但编译器会自动加上只是我们看不见,以保证变量初始化以后不会变,但是通常最好加上 final 作为一种暗示)。(对于具名的还是匿名的都成立)
public class Parcel5 {
public Destination destination(String s) {
int temp = 123;//局部变量
class PDestination implements Destination {
private String label = s;
private int num = temp;//访问局部变量
public String readLabel() {
return label;
}
}
return new PDestination();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Parcel5 p = new Parcel5();
Destination d = p.destination("Tasmania");
System.out.println(d.readLabel());
}
}
匿名内部类
使用匿名内部类的情况只能是:创建的匿名内部类继承某个类。
- 继承一个外部类,或静态内部类,或成员内部类,都可以。
- 继承一个抽象类abstract class。
- 实现一个接口interface。
然后通过new表达式返回的引用被自动向上转型为对其父类的引用。既然是父类引用指向子类对象,只不过这个子类有点特殊,它没有名字。所以其父类被当做“接口”使用:
- 如果是普通类,那么通过覆盖非静态方法,可以实现多态。
- 如果是抽象类,那么实现其抽象方法。
- 如果是接口,那么实现其所有方法。
当获得匿名内部类对象后,只能调用其父类已经定义好的方法,所以才说其父类被当做“接口”使用。
简单示例如下:
public interface Contents {
int value();
}
public class Parcel7 {
public Contents contents() {
return new Contents() { // 调用父类的默认构造器
private int i = 11;
public int value() { return i; }
}; // 需要分号
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Parcel7 p = new Parcel7();
Contents c = p.contents();
}
}
在上面例子中调用了父类的默认构造器,如果父类的构造器是有参数的:
public class Wrapping {
private int i;
public Wrapping(int x) { i = x; }//父类的有参构造器
public int value() { return i; }
}
public class Parcel8 {
public Wrapping wrapping(int x) {
// Base constructor call:
return new Wrapping(x) { // 直接传递这个参数给父类的有参构造器
public int value() {
return super.value() * 47;//调用父类的value方法
}
};
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Parcel8 p = new Parcel8();
Wrapping w = p.wrapping(10);
}
}
由于匿名内部类没有名字,自然也没有构造器了。但可以通过实例初始化块来起到构造器的作用:
public class Parcel10 {
public Destination destination(String dest, float price) {
return new Destination() {
private int cost;
// Instance initialization for each object 这里就是实例初始化块
{
cost = Math.round(price);
if(cost > 100)
System.out.println("Over budget!");
}
private String label = dest;
public String readLabel() { return label; }
};
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Parcel10 p = new Parcel10();
Destination d = p.destination("Tasmania", 101.395F);
}
}
局部内部类、匿名内部类比较
- 匿名内部类没有名字,也就没有构造器,只有通过实例初始化块。
- 相比具名的局部内部类,匿名内部类有些受限,因为只能继承或实现一个类或接口。
- 当我们需要一个命名的构造器或者需要重载构造器(重载构造器自然需要名字),需要使用具名的局部内部类。
- 当我们需要在作用域中一次定义,多次创建对象时,则需要使用具名的局部内部类。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号