Node.js - 模块系统, 函数
模块是Node.js 应用程序的基本组成部分,文件和模块是一一对应的。换言之,一个 Node.js 文件就是一个模块,这个文件可能是JavaScript 代码、JSON 或者编译过的C/C++ 扩展。
Node.js 提供了 exports 和 require 两个对象,其中 exports 是模块公开的接口,require 用于从外部获取一个模块的接口,即所获取模块的 exports 对象。如果函数没有exports标识。当require文件之后将不能访问函数
所以创建一个模块很简单.
//hello.js
exports.sayHi = function() {
console.log('Hi, this is hello.js.');
}
//main.js
var hi = require('./hello');
hi.sayHi();
我们也可以把函数封装起来。用module.exports导出。我们修改hello.js文件。如下
//hello.js
function Hello(){
this.sayHi = function(){
console.log('Hi , this is Hello module');
}
this.setName = function(name){
console.log('Hello ' + name);
}
}
module.exports = Hello;
//main.js
var Hi = require('./hello');
var hello = new Hi();
hello.setName('Allen');
hello.sayHi();
我们可看到如下结果:
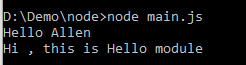
模块接口的唯一变化是使用 module.exports = Hello 代替了exports.sayHi = function(){}。 在外部引用该模块时,其接口对象就是要输出的 Hello 对象本身,而不是原先的 exports。
由于Node.js中存在4类木块(原生模块和3中文件模块),尽管require 方法很简单。但是内部却做了很多事情。加载的优先级也有不同。
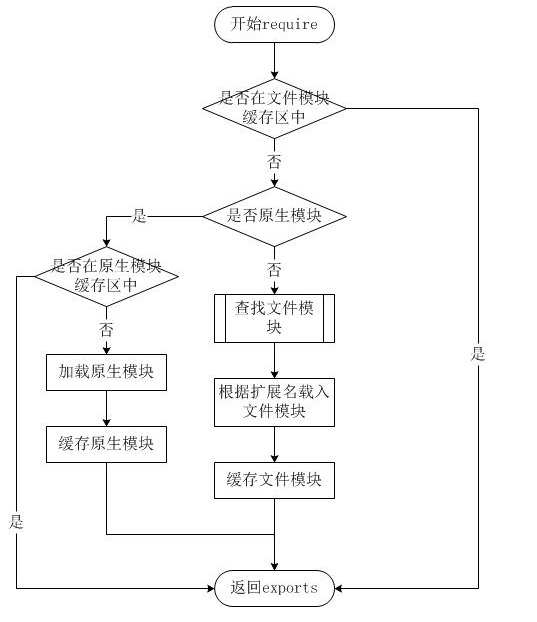
我们可以看到Node的加载策越。则都是先从缓存中加载。如果不在缓存区。当获得加载之后也会缓存进文件模块。已提高加载效率
从文件模块缓存中加载
尽管原生模块与文件模块的优先级不同,但是都会优先从文件模块的缓存中加载已经存在的模块。
从原生模块加载
原生模块的优先级仅次于文件模块缓存的优先级。require 方法在解析文件名之后,优先检查模块是否在原生模块列表中。以http模块为例,尽管在目录下存在一个 http/http.js/http.node/http.json 文件,require("http") 都不会从这些文件中加载,而是从原生模块中加载。
原生模块也有一个缓存区,同样也是优先从缓存区加载。如果缓存区没有被加载过,则调用原生模块的加载方式进行加载和执行。
从文件加载
当文件模块缓存中不存在,而且不是原生模块的时候,Node.js 会解析 require 方法传入的参数,并从文件系统中加载实际的文件,这里有一些细节值得知晓。
require方法接受以下几种参数的传递:
- http、fs、path等,原生模块。
- ./mod或../mod,相对路径的文件模块。
- /pathtomodule/mod,绝对路径的文件模块。
- mod,非原生模块的文件模块。
函数
在前面的接我们都有提到过函数。函数一般分为普通和匿名函数。我们来看一个例子
//函数
function hello(name){
console.log('我就是一个函数 : ' + name);
}
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
//匿名函数
function afterhello(func,value){
func();
}
//当我们执行afterhello是我们可以传入hello函数。hello函数也将被执行.afterhello(hello,'test')
//这里我们我们可以用匿名函数实现
afterhello(function(name){
console.log('匿名函数 : ' + name)
},'test');



