Keystone Federation Identity
转自 http://wsfdl.com/openstack/2016/01/14/Keystone-Federation-Identity.html
Keystone federation identity 涉及很多概念,安装配置复杂,官网的文档又不够清晰,下面 4 篇文章在安装配置方面阐述的非常详细。
- Configure Keystone to Keystone Federation
- Configure Keystone to Testshib Federation with SAML
- Configure Keystone federation with Kerberos
- Configure Keystone federation with multi-IDP
1. Federation Identity 简介
关于 federation identity,维基百科的定义如下:
A federated identity is the means of linking a person's electronic identity and attributes, stored across multiple distinct identity management systems(IDM).
在多个认证管理系统互相信任的基础上,federation identity 允许多个认证管理系统联邦认证各个系统的用户身份。它最重要的一个功能就是实现单点登录(Single Sign On),用户仅需认证一次,便可访问这些互相授信的资源。比如 A 公司员工需使用 AWS 公有云,出于安全考虑,不希望在 AWS 的 IAM 创建员工账户信息,通过 federation identity 打通二者之间的用户授权和认证,A 公司员工只需在本公司完成身份认证即可访问 AWS 资源。我们把 A 公司称之为 Identity Provider(IDP), AWS 称之为 Service Provider(SP)。
- Service Provider: 服务提供方,它只提供服务,依赖 Identity Provider 认证用户身份
- Identity Provider: 断言(assertion)方,用于认证用户身份
- Assertion Protocol: 认证(断言)协议,Service Provider 和 Identity Provider 完成认证用户身份所用的协议,常用有 SAML, OpenID, Oauth 等
以 SAML 协议为例,典型的认证流程分为 Redirect Bindings 和 Artifact/POST Bindings 两种。
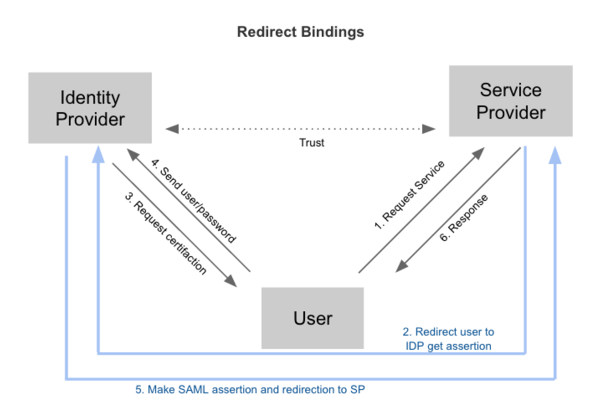
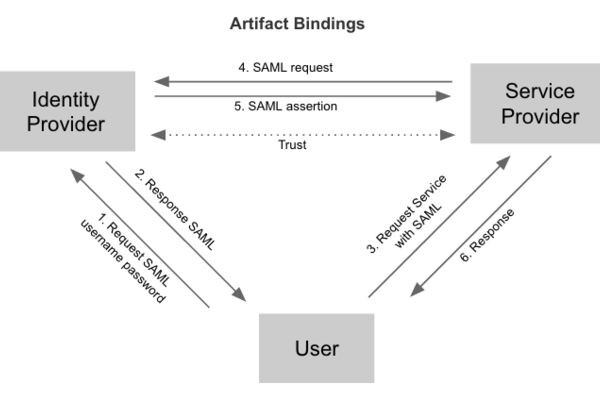
Federation identity 具有以下优点:
- 支持 SSO 单点登录
- 避免向 Service Provider 暴露用户信息,提高安全性
- 避免用户注册多个账号,增加用户负担
Keystone Federation 的原理
Federation identity 为 hybrid cloud 在用户管理层面提供了良好的解决方案。Keystone 从 Icehouse 开始逐步增加 federation identity 的功能,Icehouse 支持 Keystone 作为 Service Provider,Juno 版本新增了 Identity Provider,支持 SAML 和 OpenID 两种认证协议。OpenStack 作为云服务的解决方案,对外提供计算、存储和网络等服务,多数场景下 Keystone 常常作为服务端,对接其它的 Identity Provider,所以本节着重阐述 Service Provider 的原理和流程。首先先介绍 3 类重要的 API。
- Identity Provider API: /OS-FEDERATION/identity_providers
管理 Keystone 信任的 Identity Providers。 - Protocol API: /OS-FEDERATION/identity_providers/{idp_id}/protocols
管理 Keystone 和某个 Identity Provider 之间认证的协议,通常为 oidc(OpenID) 或 saml2(SAML)。 -
Mapping API: /OS-FEDERATION/mappings
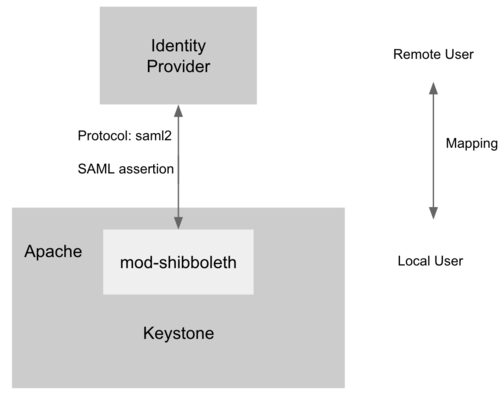
管理 Identity Provider 里的用户和 Keystone 里的用户之间的映射规则,通过该 API,管理员可以管理 IDP 中用户访问 Service 的权限。比如 IDP 有用户 A,B,通过配置 mapping rule,可以允许 A 有权限而 B 无权限访问。![Keystone Federation]()
为了支持 Service Provider,Keystone 必须运行在 Apache HTTPD 上,mod-shibboleth 作为 apache plugin 支持 SAML 认证协议,完成了 Keystone 和 IDP 之间用户的身份认证,流程如下。
- 用户访问 /OS-FEDERATION/identity_providers/{identity_provider}/protocols/{protocol}/auth,Apache 捕获该 URL 并触发 mod-shibboleth 重定向至外部的 Identity Provider。
- 外部的 Identity Provider 认证用户的身份并把用户的某些身份信息返回给 Apache,Apache 再把信息传给 Keystone。
- Keystone 根据 mapping rule 把判断用户是否有访问权限,如果有访问权限,返回一个 unscoped token。用户可拿 unscoped token 查看可用的 project 并生成 scoped token,进而访问 OpenStack 的 API。
Configure Keystone as a Service Provider
本节开始介绍如何安装配置 Keystone to Keystone Federation,重点参考了 it-is-time-to-play-with-keystone-to-keystone-federation-in-kilo(原文存在 2 处配置错误,本文已给予纠正)。 我们有两个服务器,分别作为 SP 和 IDP,二者均需按照官网的手册安装 Keystone。
- Linux: Ubuntu 14.04 LTS
- OpenStack: Kilo
更新 keystone.conf 如下配置:
[auth]
methods = external,password,token,oauth1,saml2
saml2 = keystone.auth.plugins.mapped.Mapped
Apache 新增如下配置:
Listen 5000
Listen 35357
<VirtualHost *:5000>
WSGIScriptAliasMatch ^(/v3/OS-FEDERATION/identity_providers/.*?/protocols/.*?/auth)$ /var/www/cgi-bin/keystone/main/$1
......
</VirtualHost>
<VirtualHost *:35357>
WSGIScriptAliasMatch ^(/v3/OS-FEDERATION/identity_providers/.*?/protocols/.*?/auth)$ /var/www/cgi-bin/keystone/admin/$1
......
</VirtualHost>
<Location /Shibboleth.sso>
SetHandler shib
</Location>
<LocationMatch /v3/OS-FEDERATION/identity_providers/.*?/protocols/saml2/auth>
ShibRequestSetting requireSession 1
AuthType shibboleth
ShibExportAssertion Off
Require valid-user
</LocationMatch>
安装 Shibboleth:
apt-get install libapache2-mod-shib2
更新 /etc/shibboleth/attribute-map.xml 的以下配置项:
<Attribute name="openstack_user" id="openstack_user"/>
<Attribute name="openstack_roles" id="openstack_roles"/>
<Attribute name="openstack_project" id="openstack_project"/>
<Attribute name="openstack_user_domain" id="openstack_user_domain"/>
<Attribute name="openstack_project_domain" id="openstack_project_domain"/>
更新 /etc/shibboleth/shibboleth2.xml 的以下配置项:
<SSO entityID="http://idp:5000/v3/OS-FEDERATION/saml2/idp">
SAML2 SAML1
</SSO>
<MetadataProvider type="XML" uri="http://idp:5000/v3/OS-FEDERATION/saml2/metadata"/>
启动 shibboleth 并重启 apache:
shib-keygen
service apache2 restart
查看 shibboleth 是否正常运行
unbuntu@SP:~# a2enmod shib2
Module shib2 already enabled
Configure Keystone as an Identity Provider
安装 xmlsec1 和 pysaml2:
sudo apt-get install xmlsec1
sudo pip install pysaml2
更新 keystone.conf 的如下配置:
[saml]
certfile=/etc/keystone/ssl/certs/ca.pem
keyfile=/etc/keystone/ssl/private/cakey.pem
idp_entity_id=http://idp:5000/v3/OS-FEDERATION/saml2/idp
idp_sso_endpoint=http://idp:5000/v3/OS-FEDERATION/saml2/sso
idp_metadata_path=/etc/keystone/keystone_idp_metadata.xml
生成 DIP 的 metadata 并重启 apache HTTPD:
keystone-manage saml_idp_metadata > /etc/keystone/keystone_idp_metadata.xml
service apache2 restart
Test Keystone to Keystone federation
- 在 Service Provider 端执行以下脚本,创建 domain, group, mapping, idp, protocol 等。其中 idp 指向另外一个作为 Identity Provider 的 Keystone,protocol 采用了 saml2 协议,mapping 的规则为只要 IDP 中名为 bob 或者 acme 的用户都可通过认证,并且映射到 Service 端的 federated_user 用户上。
import os
from keystoneclient import session as ksc_session
from keystoneclient.auth.identity import v3
from keystoneclient.v3 import client as keystone_v3
try:
# Used for creating the ADMIN user
OS_PASSWORD = '123456'
OS_USERNAME = 'admin'
# This will vary according to the entity:
# the IdP or the SP
OS_AUTH_URL = 'http://sp:35357/v3'
OS_PROJECT_NAME = 'admin'
OS_DOMAIN_NAME = 'default'
except KeyError as e:
raise SystemExit('%s environment variable not set.' % e)
def client_for_admin_user():
auth = v3.Password(auth_url=OS_AUTH_URL,
username=OS_USERNAME,
password=OS_PASSWORD,
user_domain_name=OS_DOMAIN_NAME,
project_name=OS_PROJECT_NAME,
project_domain_name=OS_DOMAIN_NAME)
session = ksc_session.Session(auth=auth)
return keystone_v3.Client(session=session)
# Used to execute all admin actions
client = client_for_admin_user()
def create_domain(client, name):
try:
d = client.domains.create(name=name)
except:
d = client.domains.find(name=name)
return d
def create_group(client, name, domain):
try:
g = client.groups.create(name=name, domain=domain)
except:
g = client.groups.find(name=name)
return g
def create_role(client, name):
try:
r = client.roles.create(name=name)
except:
r = client.roles.find(name=name)
return r
print('\nCreating domain1')
domain1 = create_domain(client, 'domain1')
print('\nCreating group1')