Nginx专题(二)-----虚拟主机、location规则、rewrite、负载均衡配置
kill命令
kill命令格式:
kill 是向进程发送信号的命令。
Nginx的信号
1)、TERM、INT 快速关闭
2)、QUIT从容关闭
3)、HUP平滑重启,重新加载配置文件
4)、USR1 重新打开日志文件
5)、USR2 平滑升级可执行程序
KILL 9 强制终止,直接杀(类似于windows中直接从任务管理器杀进程)
虚拟主机
虚拟主机使用的是特殊的软硬件技术,它把一台运行在因特网上的服务器主机分成一台台“虚拟”的主机,每台虚拟主机都可以是一个独立的网站,可以具有独立的域名,具有完整的Intemet服务器功能(WWW、FTP、Email等),同一台主机上的虚拟主机之间是完全独立的。从网站访问者来看,每一台虚拟主机和一台独立的主机完全一样。
利用虚拟主机,不用为每个要运行的网站提供一台单独的Nginx服务器或单独运行一组Nginx进程。虚拟主机提供了在同一台服务器、同一组Nginx进程上运行多个网站的功能。
配置方式
1、基于域名的虚拟主机
server {
#监听端口 80
listen 80;
#监听域名abc.com;
server_name abc.com;
location / {
# 相对路径,相对nginx根目录。也可写成绝对路径
root abc;
# 默认跳转到index.html页面
index index.html;
}
}
2、基于ip的虚拟主机
server {
listen 80;
server_name 192.168.197.142;
location / {
root ip;
index index.html;
}
}
3、基于端口的虚拟主机
server {
listen 2022;
server_name abc.com;
location / {
root /home;
index index.html;
}
}
Location语法规则
Location规则
语法规则: location [=|~|~*|^~] /uri/ {… }
首先匹配 =,其次匹配^~,其次是按文件中顺序的正则匹配,最后是交给 /通用匹配。当有匹配成功时候,停止匹配,按当前匹配规则处理请求。
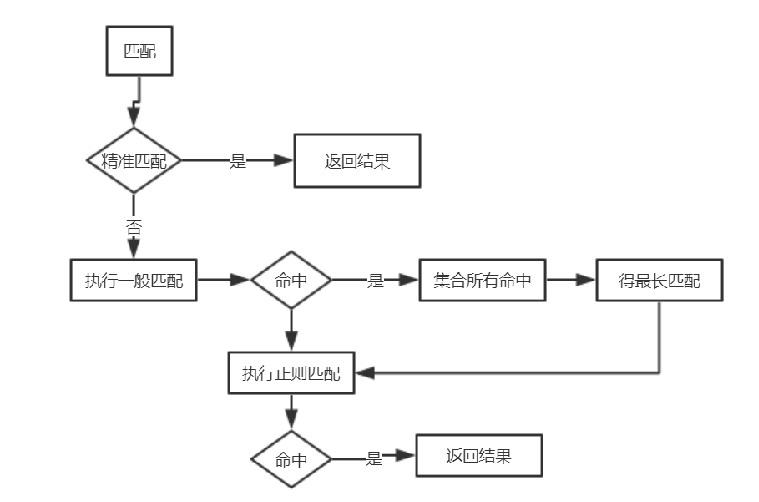
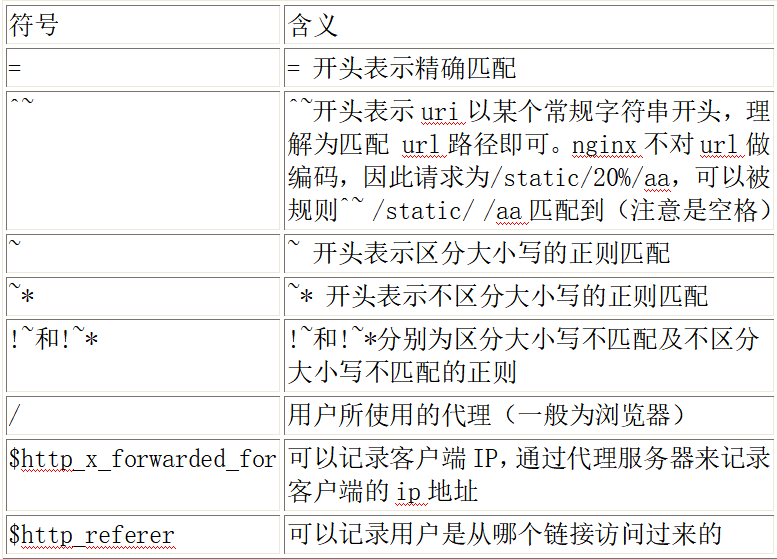
server { listen 80; server_name location.enjoy.com; location /a { rewrite ^/ /a.html break; root html/static/; } location /b/a { rewrite ^/ /b.html break; root html/static/; } location /b/d/a { rewrite ^/ /d.html break; root html/static/; } location ^~/b/c/a { rewrite ^/ /d.html break; root html/static/; } location ~ /b/d { rewrite ^/ /c.html break; root html/static/; } location ~ /b/d/a { rewrite ^/ /a.html break; root html/static/; } }
精准匹配、一般匹配、正则匹配
精准匹配-----不会被正则匹配覆盖
精准匹配以=号为标志
location = /index.htm { root /var/www/html/; index index.htm index.html; } location = /index.htm { root html/; index index.htm index.html; } #精准匹配的优先级要优于一般匹配,所以重启nginx后会打开/var/www/html下面的index.htm而不会打开html下的index.htm
普通匹配-----即使是完整匹配,也不是精准匹配
location / { root /usr/local/nginx/html; index index.htm index.html; } location /apis { root /var/www/html; index index.html; } #我们访问http://localhost/apis/,对于uri的/apis,两个location的pattern都可以匹配它们,即‘/’能够左前缀匹配,"/apis"也能够左前缀匹配。但此时最终访问的是目录/var/www/html下的文件,因为apis/匹配的更长,因此使用该目录下的文件
正则匹配
正则匹配以~符号为标志
- “~”表示区分大小写;
- “~*”表示不区分大小写
location / { root /usr/local/nginx/html; index index.html index.htm; } location ~ image { root /var/www/; index index.html; } #如果我们访问,http://localhost/image/logo.png,此时"/"与 location /匹配成功,此时"image"正则与"image/logo.png"也匹配成功?谁发挥作用呢?正则表达式的成果将会使用,会覆盖前面的匹配,图片会真正的返回/var/www/image/logo.png
root、alias
root
语法:root path
默认值:root html
配置段:http、server、location、if
示例:
location ^~ /t/ { root /www/root/html/; }
如果一个请求的URI是/t/a.html时,web服务器将会返回服务器上的/www/root/html/t/a.html的文件。
alias
语法:alias path
配置段:location
示例:
location ^~ /t/ { alias /www/root/html/new_t/; }
root、path区别总结
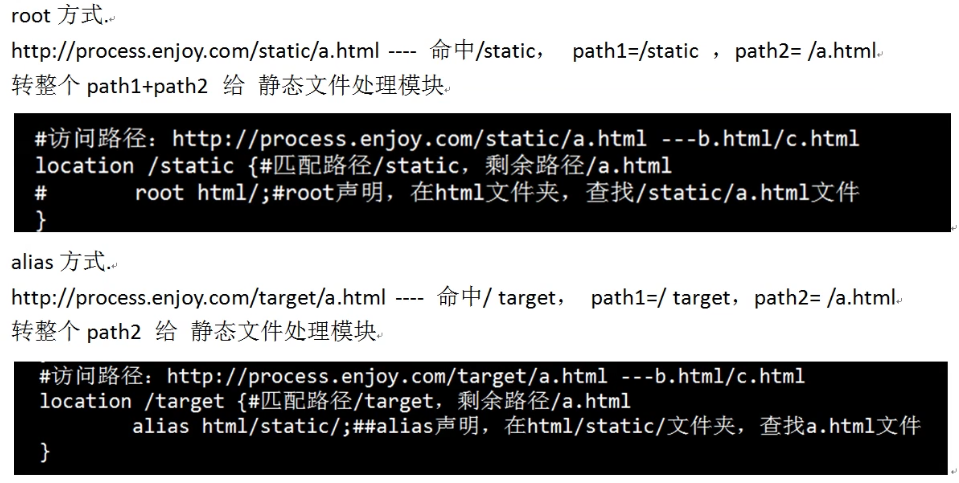
root/alias-----index命令
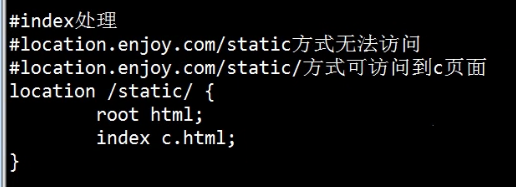
url 以 /结尾时,如:http://location.enjoy.com/static/,指的是一个目录,nginx认为用户没有指定文件;
url 不是以 / 结尾,http://location.enjoy.com/static,认为它是个文件,尝试打开这个文件,此时index命令不启用。
Root/alias时,若页面请求以/结尾,则认为path只到目录 此时启动index,找目录内的index文件。
rewrite
语法
指令语法:rewrite regex replacement[flag];
默认值:none
应用位置:server、location、if
rewrite是实现URL重定向的重要指令,他根据regex(正则表达式)来匹配内容跳转到replacement,结尾是flag标记

示例
rewrite ^/(.*) http://www.baidu.com/ permanent; # 匹配成功后跳转到百度,执行永久301跳转
常用正则
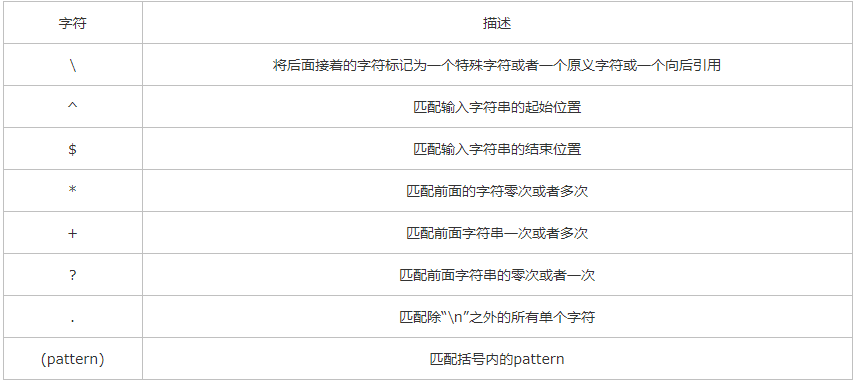
rewrite 最后一项flag参数

总结
1、名中
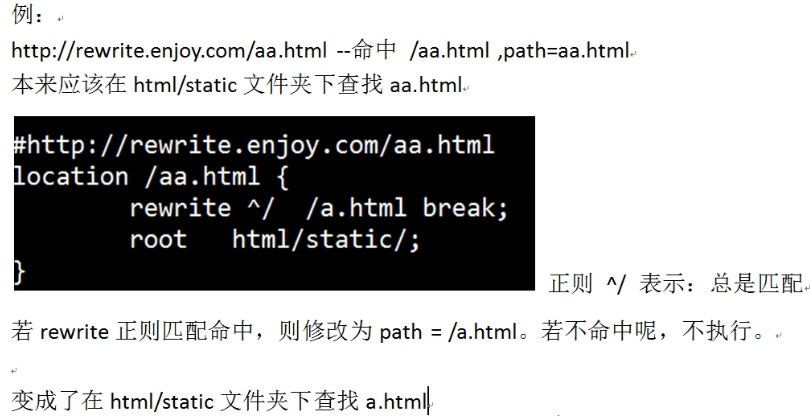
2、未命中
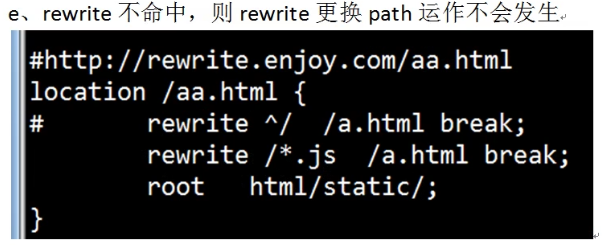
3、flag使用场景总结


proxy_pass-----反向代理
语法
格式很简单: proxy_pass URL;
其中URL包含:传输协议(http://, https://等)、主机名(域名或者IP:PORT)、uri。
示例
proxy_pass http://www.xxx.com/;
proxy_pass http://192.168.200.101:8080/uri;
proxy_pass unix:/tmp/www.sock;
配置解析
在nginx中配置proxy_pass代理转发时,如果在proxy_pass后面的url加/,表示绝对根路径;如果没有/,表示相对路径,把匹配的路径部分也给代理走。-----注:proxy_pass中带不带“/”,是针对ip+port之后有没有"/",例如proxy_pass http://a.com/aaa,这种也是带/的
假设server_name为www.xxx.com
当请求http://www.xxx.com/aming/a.html的时候,以上示例分别访问的结果是
示例1:
location /aming/
{
proxy_pass http://192.168.1.10;
...
}
结果1:http://192.168.1.10/aming/a.html
示例2:
location /aming/
{
proxy_pass http://192.168.1.10/;
...
}
结果2:http://192.168.1.10/a.html
示例3:
location /aming/
{
proxy_pass http://192.168.1.10/linux/;
...
}
结果3:http://192.168.1.10/linux/a.html
示例4:
location /aming/
{
proxy_pass http://192.168.1.10/linux;
...
}
结果4:http://192.168.1.10/linuxa.html

建议:所有的 proxy_pass 后的url都以“/”结尾。例如:
proxy_pass http://192.168.1.10/linux/;#proxy_pass也可以配置为upstream中负载的名字
负载均衡配置
nginx的upstream目前支持4种方式的分配
1、轮询(默认) 每个请求按时间顺序逐一分配到不同的后端服务器,如果后端服务器down掉,能自动剔除。
upstream nginx { server 172.17.0.4:8081; server 172.17.0.5:8081; }
每个请求按时间顺序逐一分配到不同的后端服务器,如果后端服务器down掉,能自动剔除。
2、weight 指定轮询几率,weight和访问比率成正比,用于后端服务器性能不均的情况。down 暂时不参与负载
upstream nginx { server 172.17.0.4:8081 weight=2; server 172.17.0.5:8081 weight=1; }
3、ip_hash 每个请求按访问ip的hash结果分配,这样每个访客固定访问一个后端服务器,可以解决session的问题。
upstream nginx { ip_hash; server 172.17.0.4:8081; server 172.17.0.5:8081; }
反向代理实战
需求
实现一个nginx配置: Static域名的请求,读取静态文件 Api的域名,请求tomcat 其中, order路径路由到order服务集群 Product路径路由到product服务集

说明
172.17.0.2作为代理nginx
172.17.0.3作为静态服务器,读html文件
172.17.0.4为后台服务器1,提供web服务
172.17.0.5为后台服务器2,提供web服务
配置
172.17.0.2作为反向代理,有以下配置:
upstream nginx { #ip_hash; server 172.17.0.4:8081 weight=2; server 172.17.0.5:8081 weight=1; } server { listen 80; server_name www.enjoy.com; location /proxy { proxy_pass http://172.17.0.4:8081/nginx/; } location /nginx { proxy_pass http://nginx; } error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html; location = /50x.html { root html; } location /static { proxy_pass http://rewrite.enjoy.com/; } }
location和rewrite进阶
nginx运行阶段: rewrite 阶段、access 阶段以及 content 阶段。不按代码顺序执行,是按阶段执行,顺序如下:
先执行命中的所有rewrite层指令(下面的set),再执行access,再执行content(下面的echo)
示例:
location = / { set $a 32; echo $a; set $a 64; echo $a; }
也就是说,会首先执行set指令,执行完之后才会去执行echo语句。
posted on 2020-03-04 23:08 阿里-马云的学习笔记 阅读(399) 评论(0) 编辑 收藏 举报



