如何在抽象类中注入bean
抽象类是无法实例化的,因此无法使用@Service等这种注解直接将抽象类交给ioc容器管理,但是项目中往往需要有很多子类公用抽象父类的模板方法,那么怎么实现呢?
错误演示
1、抽象类
@Component public abstract class BaseService { @Autowired Dao dao; }
2、子类
@Component public class MyService extends BaseService{ public void print(){ //运行时为null System.out.print(dao.toString()); } }
在我们实例化子类对象的时候,抽象父类不能实例化,因为spring注入的是实例对象,而不是类,所以spring不会将dao自动装配注入到一个实例中。
解决方法
一、使用ApplicationContextAware
1、工程图
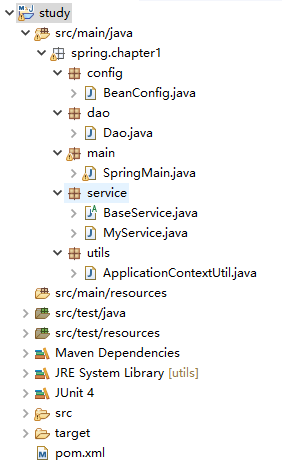
jar包只需要引入spring-context即可。
2、ApplicationContextUtil
package spring.chapter1.utils; import org.springframework.beans.BeansException; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext; import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextAware; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component public class ApplicationContextUtil implements ApplicationContextAware { private static ApplicationContext applicationContext; @Override public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException { ApplicationContextUtil.applicationContext = applicationContext; } public static Object getObject(String id) { Object object = null; object = applicationContext.getBean(id); return object; } public static ApplicationContext getSpringContext() { return applicationContext; } }
3、抽象类
package spring.chapter1.service; import spring.chapter1.dao.Dao; import spring.chapter1.utils.ApplicationContextUtil; public abstract class BaseService { Dao dao; public BaseService() { this.dao = (Dao) ApplicationContextUtil.getObject("dao"); } }
4、子类
package spring.chapter1.service; import org.springframework.context.annotation.DependsOn; import org.springframework.stereotype.Component; @Component /** * 因为BaseService中构造器需要使用applicationContextUtil这个bean,所以需要加@DependsOn这个注解。 *注解作用:1、保证applicationContextUtil总是在MyService之前实例化 * 2、保证applicationContextUtil总是在MyService销毁之后销毁 */ @DependsOn("applicationContextUtil") public class MyService extends BaseService{ public MyService() { super(); } public void print(){
dao.process();
}
}
5、Dao(一个demo组件,模拟调用某个bean的方法而已)
package spring.chapter1.dao;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class Dao {
public void process() {
System.out.println("抽象父类中成功注入dao");
}
}
6、bean配置类(定义bean扫描策略)
package spring.chapter1.config; import org.springframework.context.annotation.ComponentScan; import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration; @Configuration @ComponentScan(value = "spring.chapter1") public class BeanConfig { }
7、测试类
package spring.chapter1.main; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext; import spring.chapter1.config.BeanConfig; import spring.chapter1.service.MyService; public class SpringMain { @Test public void test() { AnnotationConfigApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(BeanConfig.class); MyService myService = (MyService) context.getBean("myService"); myService.print(); } }
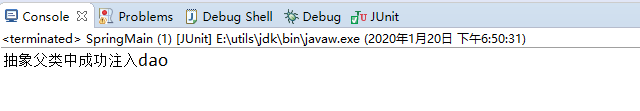
运行结果:
二、子类bean为父类注入bean
1、抽象类
public abstract class BaseService { Dao dao; }
2、子类
@Component public class myService extends BaseService{ //Autowired修饰方法时,根据方法参数类型判断实例化哪个类 @Autowired public void printDao(Dao dao){ super.dao = dao;//父类属性注入 } public void print(){ System.out.print(dao.toString()); } }
通过这种方式,抽象类就可以获取到bean,并进行使用了。
posted on 2020-01-20 18:28 阿里-马云的学习笔记 阅读(21612) 评论(2) 编辑 收藏 举报



