Django - 路由层(URLconf)
一、django 静态文件配置
/mysite1/settings.py
STATIC_URL = '/static/' STATICFILES_DIRS = [ os.path.join(BASE_DIR,'static') ]
/templates/timer.html
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>timer</title> <link rel="stylesheet" href="/static/timer.css"> </head> <body> <h4>当前时间:{{ date }}</h4> </body> <script src="/static/jquery-3.2.1.min.js"></script> <script src="/static/timer.js"></script> </html>
/static/...

效果

二、简单得路由配置
URL配置(URLconf) 就像Django 所支撑网站的目录。它的本质是URL与要为该URL调用的视图函数之间的映射表;你就是以这种方式告诉Django,对于客户端发来的某个URL调用哪一段逻辑代码对应执行。
from django.urls import path,re_path from app01 import views urlpatterns = [ re_path(r'^articles/2003/$',views.special_case_2003), re_path(r'^articles/([0-9]{4})/$',views.year_archive), # year_archive(request,‘2009’) re_path(r'^articles/([0-9]{4})/([0-9]{2})/$',views.month_archive), re_path(r'^articles/([0-9]{4})/([0-9]{2})/([0-9]+)/$',views.article_detail), ]
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse def special_case_2003(request): return HttpResponse('special_case_2003') def year_archive(request,y): return HttpResponse(y) def month_archive(request,y,m): return HttpResponse(y+'-'+m) def article_detail(request,y,m,d): return HttpResponse(y+'-'+m+'-'+d)

注意:
- 若要从URL 中捕获一个值,只需要在它周围放置一对圆括号。
- 不需要添加一个前导的反斜杠,因为每个URL 都有。例如,应该是
^articles而不是^/articles。 - 每个正则表达式前面的'r' 是可选的但是建议加上。它告诉Python 这个字符串是“原始的” —— 字符串中任何字符都不应该转义
示例:
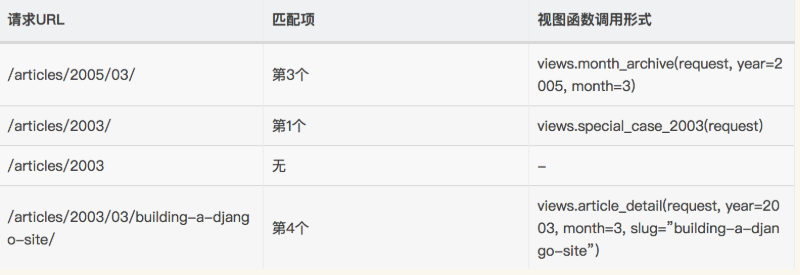
一些请求的例子: /articles/2005/03/ 请求将匹配列表中的第三个模式。Django 将调用函数views.month_archive(request, '2005', '03')。 /articles/2005/3/ 不匹配任何URL 模式,因为列表中的第三个模式要求月份应该是两个数字。 /articles/2003/ 将匹配列表中的第一个模式不是第二个,因为模式按顺序匹配,第一个会首先测试是否匹配。请像这样自由插入一些特殊的情况来探测匹配的次序。 /articles/2003 不匹配任何一个模式,因为每个模式要求URL 以一个反斜线结尾。 /articles/2003/03/03/ 将匹配最后一个模式。Django 将调用函数views.article_detail(request, '2003', '03', '03')。
三、有名分组
上面的示例使用简单的、没有命名的正则表达式组(通过圆括号)来捕获URL 中的值并以位置 参数传递给视图。在更高级的用法中,可以使用命名的正则表达式组来捕获URL 中的值并以关键字 参数传递给视图。
在Python 正则表达式中,命名正则表达式组的语法是
(?P<name>pattern),其中name是组的名称,pattern是要匹配的模式。下面是以上URLconf 使用命名组的重写:
from django.urls import path,re_path from app01 import views urlpatterns = [ re_path(r'^articles/2003/$',views.special_case_2003), re_path(r'^articles/(?P<year>[0-9]{4})/$',views.year_archive), re_path(r'^articles/(?P<year>[0-9]{4})/(?P<month>[0-9]{2})$',views.month_archive), # views.month_archive(request, year='2005', month='03') ]
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse def special_case_2003(request): return HttpResponse('special_case_2003') def year_archive(request,year): return HttpResponse(year) def month_archive(request,year,month): return HttpResponse(year+'-'+month)
这个实现与前面的示例完全相同,只有一个细微的差别:捕获的值作为关键字参数而不是位置参数传递给视图函数。例如:
/articles/2005/03/ 请求将调用views.month_archive(request, year='2005', month='03')函数,而不是views.month_archive(request, '2005', '03')。 /articles/2003/03/03/ 请求将调用函数views.article_detail(request, year='2003', month='03', day='03')。
在实际应用中,这意味你的URLconf 会更加明晰且不容易产生参数顺序问题的错误 —— 你可以在你的视图函数定义中重新安排参数的顺序。当然,这些好处是以简洁为代价;
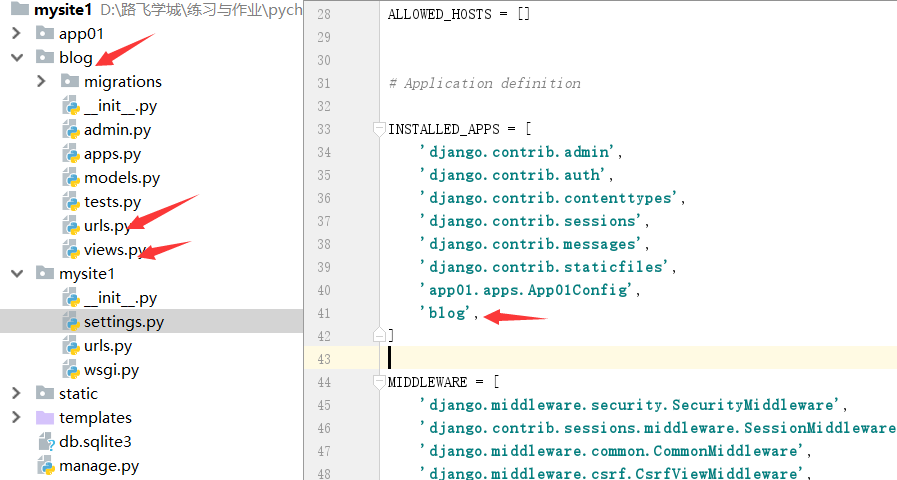
四、分发
from django.contrib import admin from django.urls import path,re_path,include urlpatterns = [ path('admin/', admin.site.urls), path('blog/',include('blog.urls')) ]
# blog.urls
from django.contrib import admin from django.urls import path,re_path,include from blog import views urlpatterns = [ path('index/',views.index) ]
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse def index(request): return HttpResponse('OKok')
补充
re_path(r'^$',views.index),

re_path(r'^',include('blog.urls')),
五、反向解析
在使用Django 项目时,一个常见的需求是获得URL 的最终形式,以用于嵌入到生成的内容中(视图中和显示给用户的URL等)或者用于处理服务器端的导航(重定向等)。人们强烈希望不要硬编码这些URL(费力、不可扩展且容易产生错误)或者设计一种与URLconf 毫不相关的专门的URL 生成机制,因为这样容易导致一定程度上产生过期的URL。
在需要URL 的地方,对于不同层级,Django 提供不同的工具用于URL 反查:
- 在模板中:使用url 模板标签。
- 在Python 代码中:使用
from django.urls import reverse()函数
在模板中
urls.py
from django.urls import path,re_path,include from app01 import views urlpatterns = [ path('login.html/',views.login,name='Log'), ]
views.py
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse def login(request): if(request.method == 'POST'): user = request.POST.get('user') pwd = request.POST.get('pwd') if(user == 'alice' and pwd == '123'): return HttpResponse('登录成功') else: return HttpResponse('<h4 style="color:red;">登录失败</h4>') else: return render(request,'login.html')
login.html
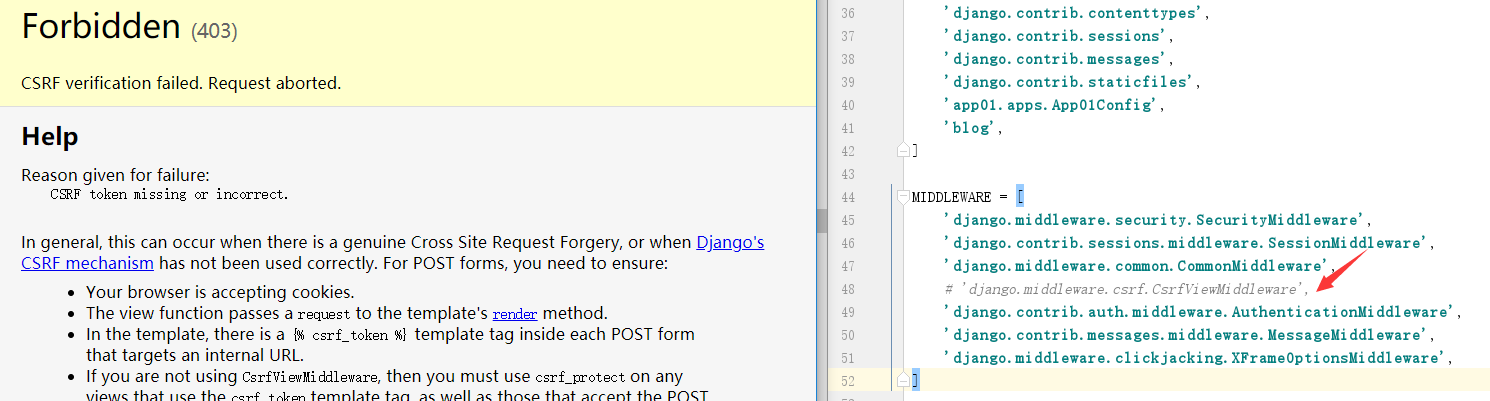
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>login</title> </head> <body> {# url 控制器 action 默认 当前 反向解析 模板语法{{ }} 和{% %} 两种 #} <form action="{% url 'Log' %}" method="post"> 用户名:<input type="text" name="user"> 密码:<input type="password" name="pwd"> <input type="submit"> </form> </body> </html>

补充:
在python中
urls.py
from django.urls import path,re_path,include from app01 import views urlpatterns = [ re_path(r'^articles/2003/$',views.special_case_2003,name='s_c_2003'), re_path(r'^articles/(?P<year>[0-9]{4})/$',views.year_archive,name='y'), re_path(r'^articles/(?P<year>[0-9]{4})/(?P<month>[0-9]{2})$',views.month_archive), path('index/',views.index,name='indexes') ]
views.py
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse # 在python 里面反向解析 不想写死url 在以后会很灵活 from django.urls import reverse def index(request): print(reverse('indexes')) # /app01/index/ return HttpResponse('OKOK') def special_case_2003(request): # request 不管用不用,一定要写 url = reverse('s_c_2003') print(url) # /app01/articles/2003/ return HttpResponse('special_case_2003') def year_archive(request,year): url = reverse('y',args=(year,)) # 这里有这正则表达式 print(url) # /app01/articles/2018/ return HttpResponse(year) def month_archive(request,year,month): return HttpResponse(year+'-'+month)

注:当命名你的URL 模式时,请确保使用的名称不会与其它应用中名称冲突。如果你的URL 模式叫做
comment,而另外一个应用中也有一个同样的名称,当你在模板中使用这个名称的时候不能保证将插入哪个URL。在URL 名称中加上一个前缀,比如应用的名称,将减少冲突的可能。我们建议使用myapp-comment而不是comment。
六、名称空间
命名空间(英语:Namespace)是表示标识符的可见范围。一个标识符可在多个命名空间中定义,它在不同命名空间中的含义是互不相干的。这样,在一个新的命名空间中可定义任何标识符,它们不会与任何已有的标识符发生冲突,因为已有的定义都处于其它命名空间中。
from django.urls import path,re_path,include urlpatterns = [ path('app01/',include(('app01.urls','app01'))), # 右面是名称空间, 命名空间的意义 path('app02/',include(('app02.urls','app02'))), ]
app01.urls:
from django.urls import path,re_path,include from app01 import views urlpatterns = [ path('index/', views.index, name='index') ]
app02.urls:
from django.urls import path, re_path, include from app02 import views urlpatterns = [ path('index/', views.index, name='index') ]
app01.views
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse from django.urls import reverse def index(request): return HttpResponse(reverse('app01:index'))
app02.views
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse from django.urls import reverse def index(request): return HttpResponse(reverse('app02:index'))
七、django2.0版的path
思考情况如下:
urlpatterns = [ re_path('articles/(?P<year>[0-9]{4})/', year_archive), re_path('article/(?P<article_id>[a-zA-Z0-9]+)/detail/', detail_view), re_path('articles/(?P<article_id>[a-zA-Z0-9]+)/edit/', edit_view), re_path('articles/(?P<article_id>[a-zA-Z0-9]+)/delete/', delete_view), ]
考虑下这样的两个问题:
第一个问题,函数 year_archive 中year参数是字符串类型的,因此需要先转化为整数类型的变量值,当然year=int(year) 不会有诸如如TypeError或者ValueError的异常。那么有没有一种方法,在url中,使得这一转化步骤可以由Django自动完成?
第二个问题,三个路由中article_id都是同样的正则表达式,但是你需要写三遍,当之后article_id规则改变后,需要同时修改三处代码,那么有没有一种方法,只需修改一处即可?
在Django2.0中,可以使用 path 解决以上的两个问题。
示例
简单例子:
from django.urls import path from app01 import views urlpatterns = [ path('articles/2003/', views.special_case_2003), path('articles/<int:year>/', views.year_archive), # year_archive(request,year) path('articles/<int:year>/<int:month>/', views.month_archive), path('articles/<int:year>/<int:month>/<slug:str_data>/', views.article_detail), ]
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse def special_case_2003(request): return HttpResponse('special_case_2003') def year_archive(request,year): print(year,type(year)) return HttpResponse(year) def month_archive(request,year,month): print(year,type(year)) print(month,type(month)) return HttpResponse(month) def article_detail(request,year,month,str_data): print(str_data,type(str_data)) return HttpResponse(str_data)
基本规则:
- 使用尖括号(
<>)从url中捕获值。 - 捕获值中可以包含一个转化器类型(converter type),比如使用
<int:name>捕获一个整数变量。如果没有转化器,将匹配任何字符串,当然也包括了/字符。 - 无需添加前导斜杠。
以下是根据 2.0官方文档 而整理的示例分析表:
path转化器
文档原文是Path converters,暂且翻译为转化器。
Django默认支持以下5个转化器:
- str,匹配除了路径分隔符(
/)之外的非空字符串,这是默认的形式 - int,匹配正整数,包含0。
- slug,匹配字母、数字以及横杠、下划线组成的字符串。
- uuid,匹配格式化的uuid,如 075194d3-6885-417e-a8a8-6c931e272f00。
- path,匹配任何非空字符串,包含了路径分隔符
注册自定义转化器
对于一些复杂或者复用的需要,可以定义自己的转化器。转化器是一个类或接口,它的要求有三点:
regex类属性,字符串类型
to_python(self, value)方法,value是由类属性regex所匹配到的字符串,返回具体的Python变量值,以供Django传递到对应的视图函数中。to_url(self, value)方法,和to_python相反,value是一个具体的Python变量值,返回其字符串,通常用于url反向引用。
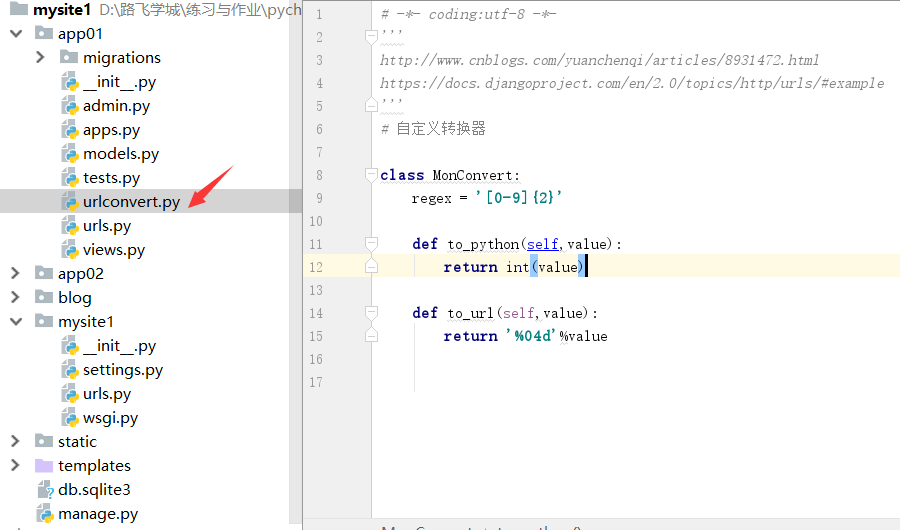
urlconvert.py
''' http://www.cnblogs.com/yuanchenqi/articles/8931472.html https://docs.djangoproject.com/en/2.0/topics/http/urls/#example ''' # 自定义转换器 class MonConvert: regex = '[0-9]{2}' def to_python(self,value): return int(value) def to_url(self,value): return '%04d'%value
urls.py (使用register_converter 将其注册到URL配置中)
from django.urls import path,register_converter from app01 import views from app01.urlconvert import MonConvert # 注册转换器 注册自定义的转换器 register_converter(MonConvert,'mm') urlpatterns = [ # 自己注册的转换器 path('articles/<mm:month>/', views.year_archive), ]
views.py
from django.shortcuts import render,HttpResponse def year_archive(request,month): print(month,type(month)) return HttpResponse(month)

总结:
django urls:
简单配置
第一站: url 路径匹配
有名分组
。。。 按关联字传参 (?P...) () 可传参
分发:
多个app
反向解析
不想写死url 别名name
名称空间
防止名字起重了 配合反向解析使用
path # django 2.0 的特性
内部数值不会转换 正则反复使用
含正则的 反向解析
https://www.cnblogs.com/yuanchenqi/articles/7629939.html

