time/datetime/random/string/os/sys/shutil/zipfile/tarfile - 总结
time 模块:
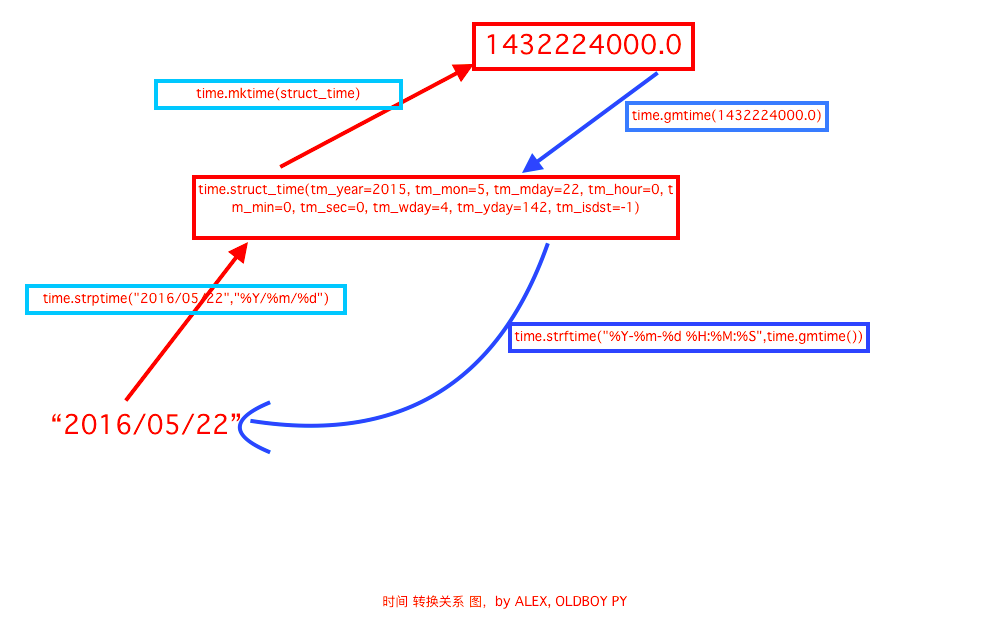
time.time() #时间戳 time.localtime() #当前时间对象元组 time.localtime(123123) #根据时间戳的时间对象 time.mktime(time.localtime()) #把时间对象转成时间戳 time.gmtime() #0时区,我们是东8区,比我们晚8h的时间对象元组 time.sleep(2) #单位s 睡一会 time.asctime() #美国表示时间字符串 'Sat Feb 24 13:23:36 2018' time.ctime() #美国表示时间字符串 time.ctime(213123) #美国表示时间字符串 time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S',time.localtime()) #时间对象转化成字符串'2018-02-24 13:41:42' time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S %A',time.localtime()) # %a %A %b %B %p %U %w %z %Z 表示不同的含义 time.strptime('2018-2-24','%Y-%m-%d') #将字符串转化成时间对象 time.mktime(time.strptime('2018-2-24','%Y-%m-%d')) #字符串->时间对象->时间戳
datetime 模块
datetime.datetime.now() #年月日时分秒对象 datetime.datetime.now().year datetime.datetime.now().timetuple() == time.localtime() #时间对象 datetime.date.fromtimestamp(time.time()) #根据时间戳快速的拿到年月日 datetime.date.fromtimestamp(time.time()).timetuple() #时间对象的时分秒会丢 时间运算: datetime.datetime.now()-datetime.timedelta(days=3) # - + days hours minutes seconds 没有年,月 时间替换: datetime.datetime.now().replace(year=2016,month=12,day=12,hour=12) # 年月日时 没有,分 秒
random 模块
random.randint(1,3) #[1-3]的随机数 random.randrange(1,3) #[1-3)的随机数 random.random() #[0-1)的浮点数 random.choice('abcdefg1234!@#$') #字符串中的随机一个 random.sample('abcdefg12345!@#$%',5) #随机产生5 d=list(range(10)) random.shuffle(d) #洗牌,将列表打乱 ''.join(random.sample(string.ascii_lowercase+string.digits+string.punctuation,6)) #随机数
string 模块
string.digits #[0-9]的字符串 string.ascii_letters #[a-z][A-Z]的字符串 string.ascii_lowercase #[a-z] string.ascii_uppercase #[A-Z] string.punctuation #特殊字符
os 模块
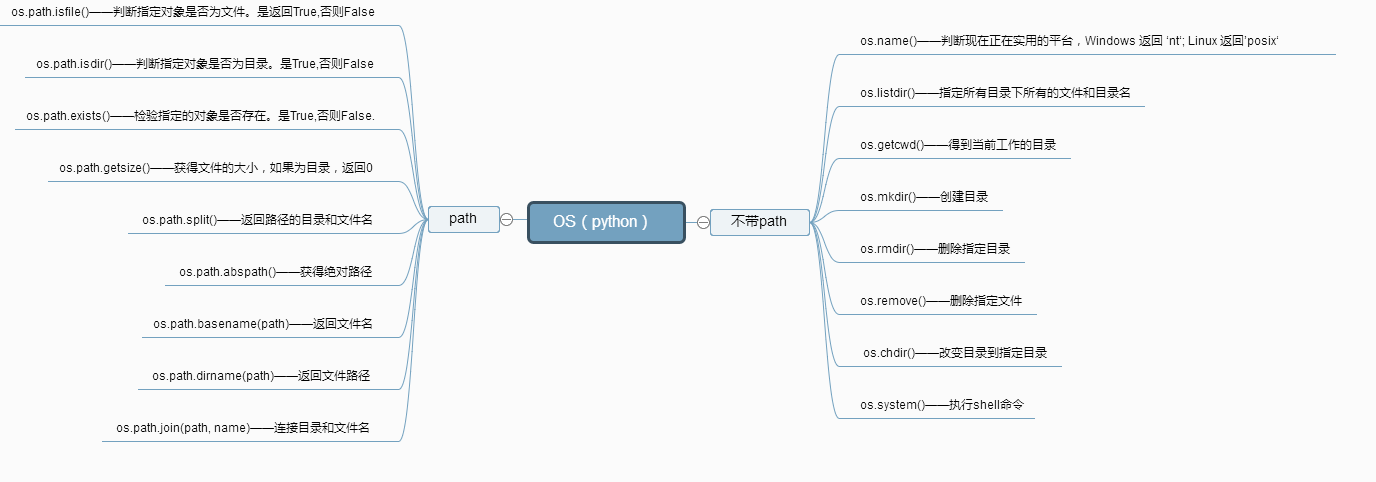
os.getcwd() #获取当前工作目录 os.listdir() #当前工作目录下的文件和目录名 os.remove('') #当前目录下删除一个文件 os.removedirs('') #删除空目录 os.system('ls') #运行shell命令 os.environ #操作系统所在的环境变量 os.getenv('USERNAME') #读取操作系统环境变量USERNAME的值 os.environ.setdefault('HOME','/home/alex') #设置环境变量的值仅程序运行时有效 os.linesep #当前平台使用的终止符 windows:\r\n linux mac:\n os.name #当前使用的平台 windows:nt linux mac:posix os.rename(old, new) #重命名 os.makedirs('./test1/test2') #创建多级目录 os.mkdir('test') #创建单个目录 os.stat(file) #获取文件属性 http://www.runoob.com/python/os-stat.html os.chmod('test_new.txt',stat.S_IREAD) #修改文件权限http://www.runoob.com/python/os-chmod.html os.chdir(dirname) #改变工作目录到dirname os.get_terminal_size() #获取当前终端大小 os.kill(10884,signal.SIGILL) #杀死进程 os.path.isfile() #判断是否是文件 os.path.isdir() #判断是否是目录 os.path.isabs() #判断是否是绝对路径 os.path.exists() #判断路劲文件是否真的存在 os.path.split() #当前目录下分割 os.path.splitext() #将文件的后缀名给分隔开 os.path.dirname() #获取目录名 os.path.abspath() #获取绝对路径 os.path.basename() #获取文件名 os.path.getsize(filename) #获取文件大小 os.path.join(dir,filename) #结合目录名和文件名
sys 模块
sys.argv #命令行参数List,第一个元素是程序本身路径 print(sys.argv) python exec.py luffy == ['exec.py', 'luffy']
sys.exit(n)=exit() #退出程序,正常退出时exit(0) sys.version #获取python解释程序的版本信息 sys.maxsize #最大的Int值 sys.path #python所在环境变量 模块搜索时的搜索路径 sys.platform #返回操作系统的平台 sys.stdout.write('ab') #标准输出 sys.stdin.readline()[:-1] #标准输入 sys.getrecursionlimit() #获取最大递归层次 1000 sys.setrecursionlimit(1000) #设置最大递归层次 sys.getdefaultencoding() #获取python解释器默认编码 utf-8 sys.getfilesystemencoding() #获取内存数据存到文件里的默认编码 utf-8
shutil 模块
shutil.copyfileobj(open('ok.txt','r'),open('ok1.txt','w')) #将文件内容拷贝到另一个文件中,目标文件可以不存在 shutil.copyfile('ok.txt','ok3.txt') #拷贝文件内容,目标文件可以不存在 shutil.copymode('ok.txt','ok2.txt') #仅拷贝权限,目标文件必须存在 mode os.chmod('ok.txt',stat.S_IREAD) shutil.copystat('ok.txt','ok2.txt') #仅拷贝文件状态信息,目标文件必须存在 mode atime, mtime, flags os.stat('ok.txt') shutil.copy('ok.txt','ok5.txt') #拷贝文件内容和权限,目标文件可以不存在 shutil.copy2('ok.txt','ok6.txt') #拷贝文件内存和权限和状态信息,目标文件可以不存在 shutil.copytree('test1','test3',ignore=shutil.ignore_patterns('*.rar','*.py')) #递归的去拷贝文件夹,文件,目标目录不能存在,ignore 可忽略拷贝哪些文件,拷贝了文件的内容,权限,状态信息 shutil.rmtree('test4') #递归的去删除文件 shutil.move('test2','test22') #递归的去移动文件 其实就是重命名 shutil.move('./test5/test2','./test5/test22') shutil.make_archive('bao','zip') #创建当前目录下的压缩包 返回路径 shutil.make_archive('bao1','zip',root_dir='./test5') #创建root_dir下的压缩包 shutil.make_archive('./test6/bao2','tar',root_dir='./test5') #创建root_dir下的压缩包 存放在./test6下面 shutil 对压缩包的处理是调用 ZipFile 和 TarFile 两个模块来进行的,详细:
zipfile 模块 压缩&解压缩
# 压缩 z = zipfile.ZipFile('laxi.zip', 'w') z.write('a.log') z.write('data.data') z.close() # 解压 z = zipfile.ZipFile('laxi.zip', 'r') z.extractall(path='.') z.close()
tarfile 模块 压缩&解压缩
import tarfile # 压缩 >>> t=tarfile.open('/tmp/egon.tar','w') >>> t.add('/test1/a.py',arcname='a.bak') >>> t.add('/test1/b.py',arcname='b.bak') >>> t.close() # 解压 >>> t=tarfile.open('/tmp/egon.tar','r') >>> t.extractall('/egon') >>> t.close()
