数据库 - Navicat与pymysql模块
一、Navicat
在生产环境中操作MySQL数据库还是推荐使用命令行工具mysql,但在我们自己开发测试时,
可以使用可视化工具Navicat,以图形界面的形式操作MySQL数据库
官网下载:https://www.navicat.com/en/products/navicat-for-mysql
网盘下载:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1bpo5mqj
链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1Hu-x0mPuSW3g9CxNFlnAng 密码:pqe5
# 打开 双击:
# D:\navicatformysql\Navicat for MySQL\navicat
需要掌握的基本操作
掌握:
#1. 测试+链接数据库
#2. 新建库
#3. 新建表,新增字段+类型+约束
#4. 设计表:外键
#5. 新建查询
#6. 备份库/表
注意:
批量加注释:ctrl+?键
批量去注释:ctrl+shift+?键
二、pymysql
介绍:
在python程序中操作数据库呢?这就用到了pymysql模块,
该模块本质就是一个套接字客户端软件,使用前需要事先安装
pip3 install pymysql
前提:
授权加创建
grant all on *.* to 'root'@'%' identified by '123';
flush privileges;
端口:3306
ip: 192.168.1.102
mysql -uroot -p123 -h 192.168.1.102
1.pymysql基本使用

1 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 2 """ 3 端口:3306 4 ip: 192.168.1.102 5 mysql -uroot -p123 -h 192.168.1.102 6 7 """ 8 import pymysql 9 10 name = input('user>>>:').strip() # egon1 11 password = input('password>>>:').strip() # 123 12 13 # 建连接 14 conn = pymysql.connect( 15 host = '192.168.1.102', 16 port = 3306, 17 user = 'root', 18 password = '123', 19 db = 'egon', 20 charset = 'utf8' 21 ) 22 23 # 拿游标 24 cursor = conn.cursor() 25 26 # 执行sql语句 27 sql = 'select * from userinfo where name= "%s" and password = "%s"'%(name,password) 28 rows = cursor.execute(sql) 29 print(rows) 30 31 # 关闭 32 cursor.close() 33 conn.close() 34 35 # 进行判断 36 if rows: 37 print('登录成功') 38 else: 39 print('登录失败')
2.sql注入
注意:符号--会注释掉它之后的sql,正确的语法:--后至少有一个任意字符
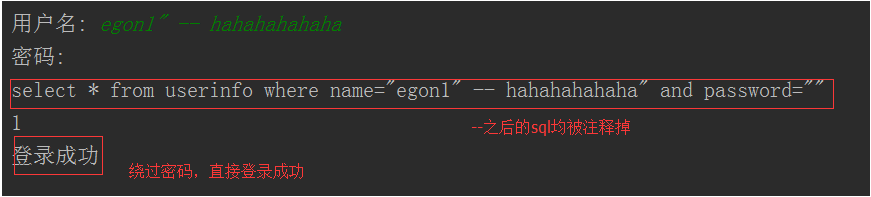
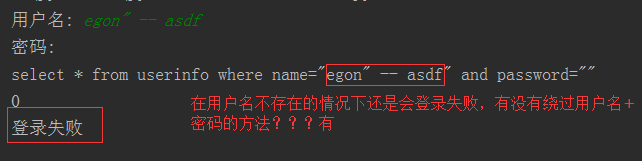
1、sql注入之:用户存在,绕过密码
egon' -- 任意字符
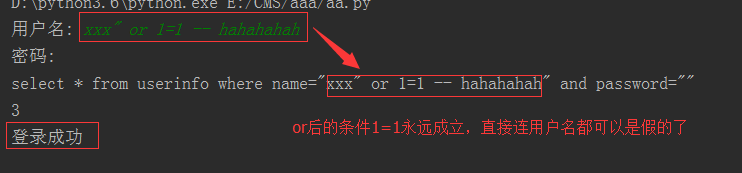
2、sql注入之:用户不存在,绕过用户与密码
xxx' or 1=1 -- 任意字符
解决办法:
# 原来是我们对sql进行字符串拼接
# sql="select * from userinfo where name='%s' and password='%s'" %(user,pwd)
# print(sql)
# res=cursor.execute(sql)
#改写为(execute帮我们做字符串拼接,我们无需且一定不能再为%s加引号了)
sql="select * from userinfo where name=%s and password=%s" #!!!注意%s需要去掉引号,因为pymysql会自动为我们加上
res=cursor.execute(sql,[user,pwd]) #pymysql模块自动帮我们解决sql注入的问题,只要我们按照pymysql的规矩来。

1 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- 2 import pymysql 3 4 name = input('name>>>:').strip() 5 password = input('password>>>:').strip() 6 conn = pymysql.connect( 7 host = '192.168.1.102', 8 port = 3306, 9 user = 'root', 10 password = '123', 11 db = 'egon', 12 charset = 'utf8' 13 ) 14 cursor = conn.cursor() 15 # sql = 'select * from userinfo where name = "%s" and password = "%s"'%(name,password) 16 # rows = cursor.execute(sql) 17 sql = 'select * from userinfo where name=%s and password = %s' 18 rows = cursor.execute(sql,(name,password)) #执行sql语句,返回sql影响成功的行数 19 print(sql) 20 print(rows) 21 cursor.close() 22 conn.close() 23 if rows: 24 print('登录成功') 25 else: 26 print('登录失败') 27 28 """ 29 name>>>:egon1" -- x #需要帐号,sql注入 -- 表示 注释掉 只需要判断user 不需要判断password 30 password>>>: 31 select * from userinfo where name = "egon1" -- x" and password = "" 32 1 33 登录成功 34 """ 35 """ 36 name>>>:xxx" or 1=1 -- xxx #不需要帐号密码,sql注入 太恐怖!! 37 password>>>: 38 select * from userinfo where name = "xxx" or 1=1 -- xxx" and password = "" 39 3 40 登录成功 41 """ 42 """ 43 解决办法: 44 sql = 'select * from userinfo where name=%s and password = %s' 45 rows = cursor.execute(sql,(name,password)) 46 """
3.pymysql模块之增删改查
增:
sql = 'insert into userinfo(name,password) values(%s,%s)'
rows = cursor.execute(sql,('lily','123'))
conn.commit() # 注意只有执行了commit() 才会更新到数据库中
批量:
rows = cursor.executemany(sql,[('alice4','123'),('alice5','123'),('alice6','123')])
print(cursor.lastrowid) # 显示插入数据前的id 走到哪
删:
sql = 'delete from userinfo where name = %s'
rows = cursor.execute(sql,('alice5'))
conn.commit()
改:
sql = 'update userinfo set name = %s where id = %s '
rows = cursor.execute(sql,('abcd',2))
conn.commit()
查:
# 元祖形式
cursor = conn.cursor()
rows = cursor.execute(sql)
print(cursor.fetchone())
print(cursor.fetchmany(3))
print(cursor.fetchall())
print(cursor.fetchone()) # None 没有数据了!
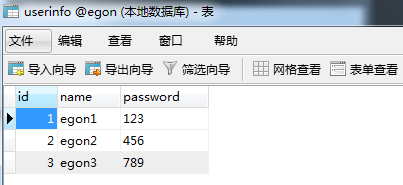
((1, 'aaabbb', '123'), (2, 'abcd', '456'), (3, 'egon3', '789'))
# 字典形式
cursor = conn.cursor(pymysql.cursors.DictCursor)
cursor.fetchone() cursor.fetchmany(2) cursor.fetchall()
[{'id': 3, 'name': 'egon3', 'password': '789'}, {'id': 6, 'name': 'alice', 'password': '123'}]
# 相对 绝对 移动游标
print(cursor.fetchone())
cursor.scroll(5,'absolute')
# cursor.scroll(5,'relative')
print(cursor.fetchmany(2))

1 """增删改""" 2 import pymysql 3 conn = pymysql.connect( 4 host = '192.168.1.102', 5 port = 3306, 6 user = 'root', 7 password = '123', 8 db = 'egon', 9 charset = 'utf8' 10 ) 11 cursor = conn.cursor() 12 # sql = 'insert into userinfo(name,password) values(%s,%s)' 13 # rows =cursor.execute(sql,('lily','123')) 14 # rows = cursor.executemany(sql,[('alice4','123'),('alice5','123'),('alice6','123')]) 15 # print(cursor.lastrowid) 16 17 # sql = 'delete from userinfo where name = %s' 18 # rows = cursor.execute(sql,('alice6')) 19 20 sql = 'update userinfo set name = %s where id = %s ' 21 rows = cursor.execute(sql,('abcd',2)) 22 print(rows) 23 24 conn.commit() 25 26 cursor.close() 27 conn.close() 28 29 if rows: 30 print('操作成功') 31 else: 32 print('失败') 33 34 35 """查""" 36 import pymysql 37 conn = pymysql.connect( 38 host = '192.168.1.102', 39 port = 3306, 40 user = "root", 41 password = '123', 42 db = 'egon', 43 charset = 'utf8' 44 ) 45 cursor = conn.cursor() 46 # cursor = conn.cursor(pymysql.cursors.DictCursor) 47 sql = 'select * from userinfo' 48 rows = cursor.execute(sql) #执行sql语句,返回sql影响成功的行数rows,将结果放入一个集合,等待被查询 49 print(rows) 50 # print(cursor.fetchone()) 51 # print(cursor.fetchone()) 52 # print(cursor.fetchmany(2)) 53 # print(cursor.fetchall()) 54 # print(cursor.fetchone()) # None 55 56 print(cursor.fetchone()) 57 cursor.scroll(5,'absolute') 58 # cursor.scroll(5,'relative') 59 print(cursor.fetchmany(2)) 60 61 cursor.close() 62 conn.close() 63 64 if rows: 65 print('操作成功') 66 else: 67 print('失败')


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号