java8 stream流操作的flatMap(流的扁平化)
来源于 https://blog.csdn.net/Mark_Chao/article/details/80810030
flatMap的用法和含义住要通过一个案例来讲解,
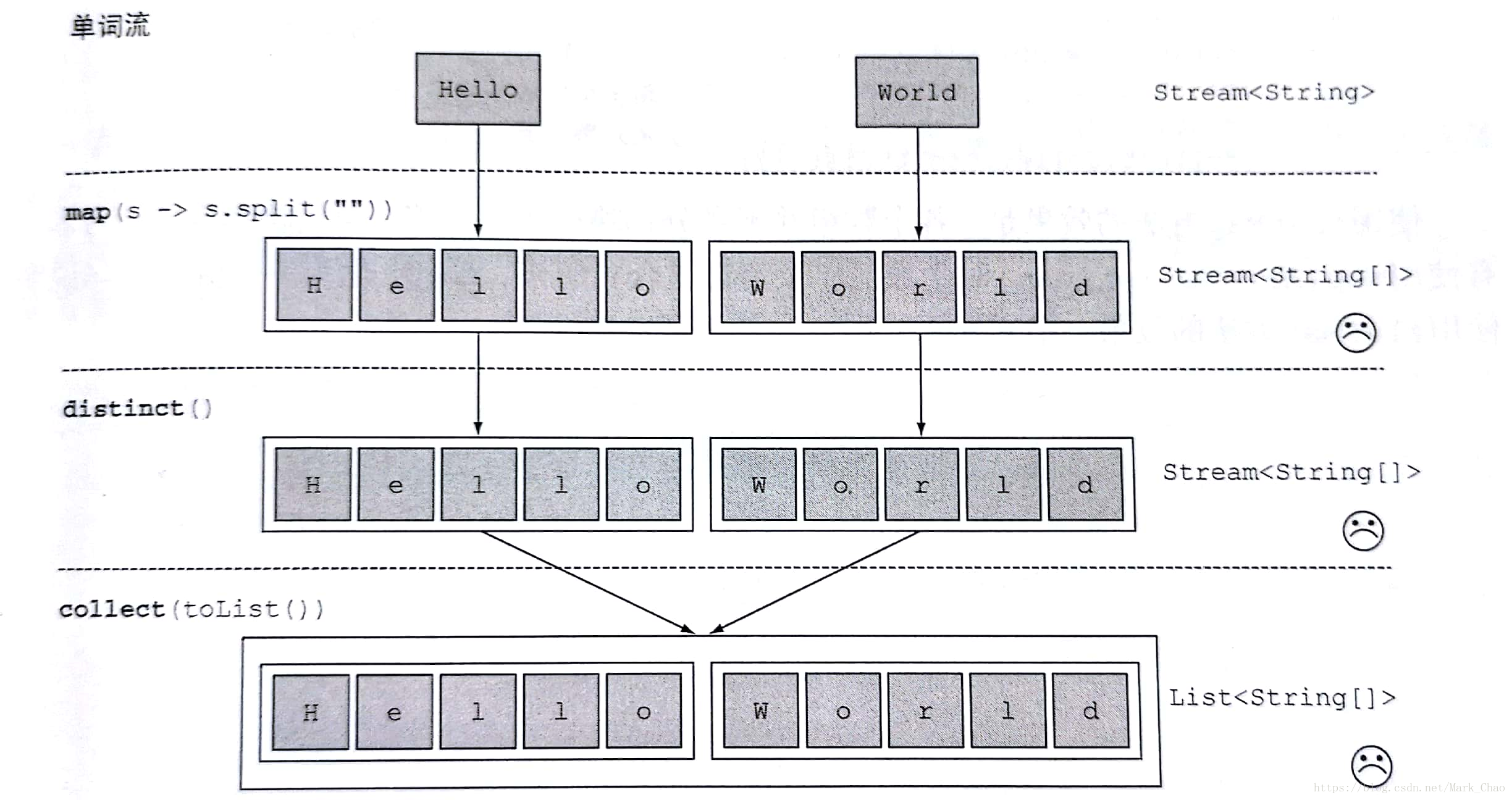
案例:对给定单词列表 ["Hello","World"],你想返回列表["H","e","l","o","W","r","d"]
第一种方式
-
String[] words = new String[]{"Hello","World"};
-
List<String[]> a = Arrays.stream(words)
-
.map(word -> word.split(""))
-
.distinct()
-
.collect(toList());
-
a.forEach(System.out::print);
代码输出为:[Ljava.lang.String;@12edcd21[Ljava.lang.String;@34c45dca
(返回一个包含两个String[]的list)
这个实现方式是由问题的,传递给map方法的lambda为每个单词生成了一个String[](String列表)。因此,map返回的流实际上是Stream<String[]> 类型的。你真正想要的是用Stream<String>来表示一个字符串。
下方图是上方代码stream的运行流程
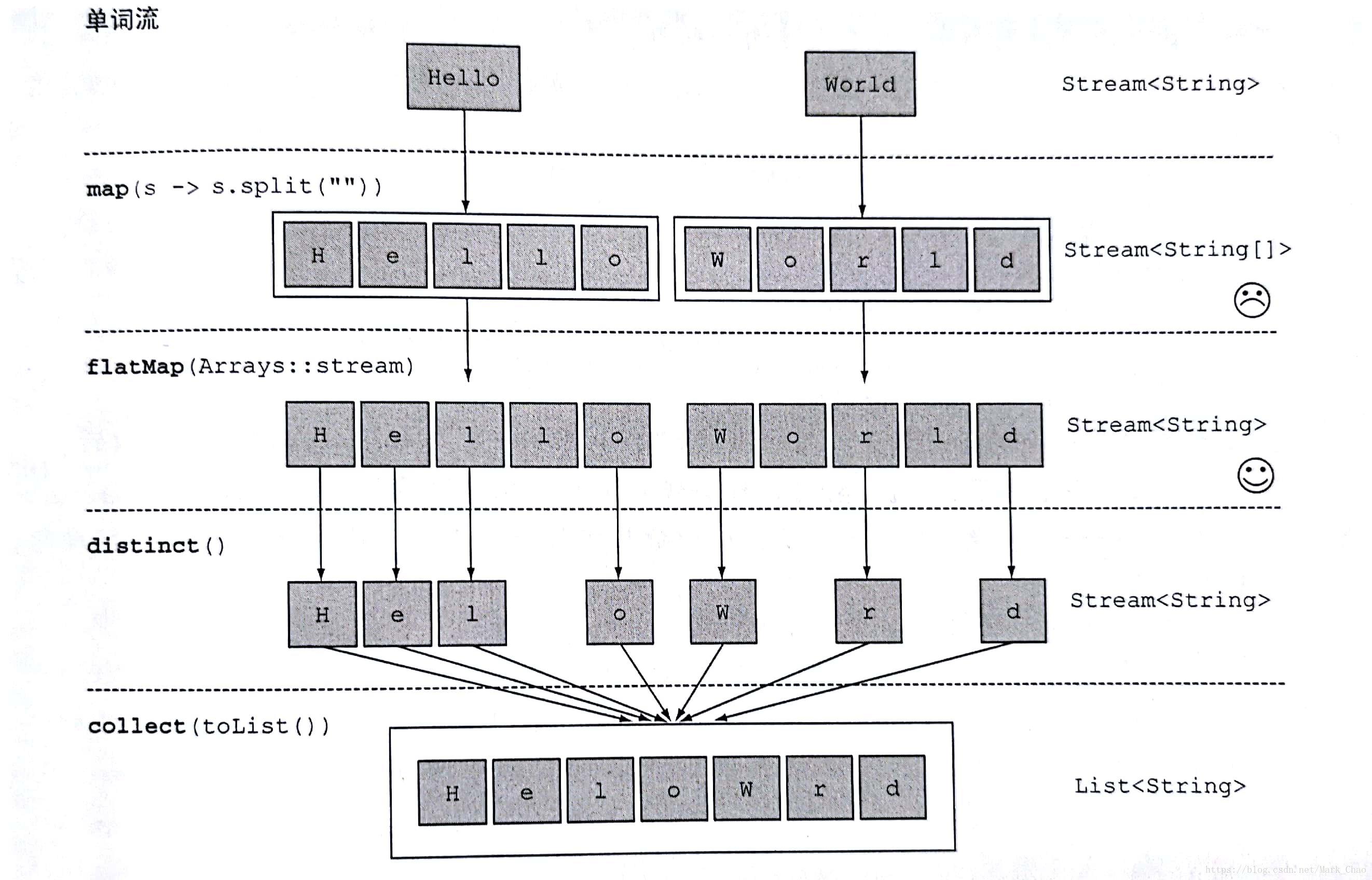
第二种方式:flatMap(对流扁平化处理)
-
String[] words = new String[]{"Hello","World"};
-
List<String> a = Arrays.stream(words)
-
.map(word -> word.split(""))
-
.flatMap(Arrays::stream)
-
.distinct()
-
.collect(toList());
-
a.forEach(System.out::print);
结果输出:HeloWrd
使用flatMap方法的效果是,各个数组并不是分别映射一个流,而是映射成流的内容,所有使用map(Array::stream)时生成的单个流被合并起来,即扁平化为一个流。
下图是运用flatMap的stream运行流程,
用空常来坐坐
https://www.cnblogs.com/alexgl2008/