【C012】Python - 基础教程学习(三)
第五章 条件、循环和其他语句
print和import的更多信息
>>> print 'Age:',42 Age: 42 >>> print 'Age;';42 Age; 42 >>> name = 'Gumby' >>> salutation = 'Mr' >>> greeting = 'Hello,' >>> print greeting,salutation,name Hello, Mr Gumby
>>> import math as foobar >>> foobar.sqrt(4) 2.0 >>> from math import sqrt as foobar >>> foobar(4) 2.0
赋值魔法
>>> x,y,z = 1,2,3
>>> print x,y,z
1 2 3
>>> x,y = y,x
>>> print x,y,z
2 1 3
>>> values = 1,2,3
>>> values
(1, 2, 3)
>>> x,y,z = values
>>> x
1
>>> y
2
>>>
>>> scoundrel = {'name':'Robin','girlfriend':'Marion'}
>>> key,value = scoundrel.popitem()
>>> key
'girlfriend'
>>> value
'Marion'
链式赋值
>>> x = y = 1 >>> x 1 >>> y 1 >>>
增量赋值
>>> x = 2 >>> x += 1 >>> x 3 >>> x *= 4 >>> x 12 >>> fnord = 'foo' >>> fnord += 'bar' >>> fnord 'foobar' >>> fnord *=2 >>> fnord 'foobarfoobar' >>>
语句块:缩排的乐趣
条件和条件语句
>>> True
True
>>> False
False
>>> True == 1
True
>>> False == 0
True
>>> True + False + 43
44
>>>
>>> bool('I think, therefore I am')
True
>>> bool(42)
True
>>> bool('')
False
>>> bool("")
False
>>> bool(0)
False
>>> bool([])
False
>>> bool({})
False
>>> bool(False)
False
>>> bool(None)
False
>>>
条件执行和if语句(if、elif、else)
name = raw_input('What is your name?')
if name.endswith('Gumby'): print 'Hello, Mr.Gumby'
num = input('Enter a number:')
if num > 0:
print 'The number is positive'
elif num < 0:
print 'The number is negative'
else:
print 'The number is zero'
嵌套代码块
name = raw_input('What is your name?')
if name.endswith('Gumby'):
if name.startswith('Mr'):
print 'Hello, Mr.Gumby'
elif name.startswith('Mrs'):
print 'Hello, Mrs.Gumby'
else:
print 'Hello, Gumby'
else:
print 'Hello, stranger'
更复杂的条件
比较运算符
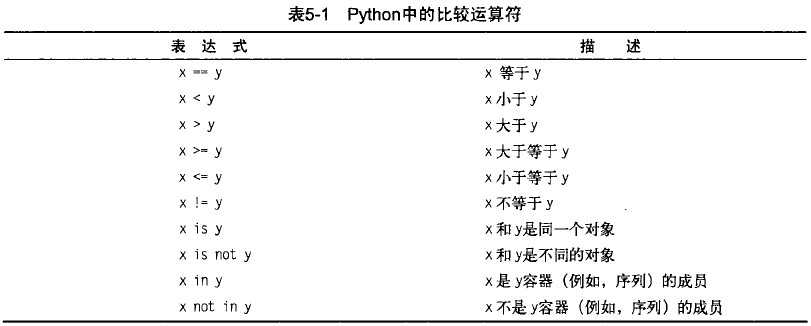
>>> 'foo' == "foo" True >>> 'foo' == 'bar' False >>> x = y = [1,2,3] >>> z = [1,2,3] >>> x == y True >>> x is y True >>> x is z False >>> x = z >>> x ==z True >>> >>> x = [1,2,3] >>> y = [2,4] >>> x is not y True >>> del x[2] >>> x [1, 2] >>> y[1] = 1 >>> y.reverse() >>> y [1, 2] >>> x == y True >>> x is y False
name = raw_input('What is your name?')
if 's' in name:
print 'Your name contains the letter "s".'
else:
print 'Your name doesn\'t contain the letter "s".'
>>> "alpha" < "beta" True >>> 'FnOrD'.lower() == 'Fnord'.lower() True >>> [1,2] < [2,1] True >>> [2,[1,4]] < [2,[1,5]] True
number = input('Enter a number between 1 and 10:')
if number <= 10 and number >= 1:
print 'Great'
else:
print 'Wrong'
断言
循环
while循环
x = 1
while x <= 1000:
print x
x += 1
name = ''
while not name:
name = raw_input('Please enter your name?')
print 'Hello, %s!' % name
for循环
words = ['this','is','an','ex','parrot']
for word in words:
print word
numbers = [0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]
for number in numbers:
print number
>>> range(0,10) [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] >>> range(10) [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] >>>
d = {'x':1,'y':2,'z':3}
for key in d:
print key, 'corresponds to', d[key]
y corresponds to 2 x corresponds to 1 z corresponds to 3
一些迭代工具
names = ['anne','beth','george','damon']
ages = [12,45,32,102]
for i in range(len(names)):
print names[i],'is',ages[i],'year old'
翻转和排序迭代
>>> sorted([4,3,6,8,3])
[3, 3, 4, 6, 8]
>>> sorted('Hello, world!')
[' ', '!', ',', 'H', 'd', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'l', 'o', 'o', 'r', 'w']
跳出循环
break
from math import sqrt
for n in range(99,0,-1):
root = sqrt(n)
if root == int(root):
print n
break
>>> range(0,10,2) [0, 2, 4, 6, 8] >>>
continue
while True/break
word = 'dummy'
while word:
word = raw_input('Please enter a word:')
print 'The word was ' + word
word = raw_input('Please enter a word:')
while word:
print 'The word was ' + word
word = raw_input('Please enter a word:')
while True:
word = raw_input('Please enter a word:')
if not word:break
print 'The word was ' + word
from math import sqrt
for n in range(92,99,1):
root = sqrt(n)
if root == int(root):
print n
break
else:
print "Didn't find it!",n
Didn't find it! 92 Didn't find it! 93 Didn't find it! 94 Didn't find it! 95 Didn't find it! 96 Didn't find it! 97 Didn't find it! 98
from math import sqrt
for n in range(99,89,-1):
root = sqrt(n)
if root == int(root):
print n
break
else:
print "Didn't find it!",n
Didn't find it! 99 Didn't find it! 98 Didn't find it! 97 Didn't find it! 96 Didn't find it! 95 Didn't find it! 94 Didn't find it! 93 Didn't find it! 92 Didn't find it! 91 Didn't find it! 90
range函数,就是不包括后面的边界~
列表推导式——轻量级循环
>>> [x*x for x in range(10)] [0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81] >>> [x*x for x in range(10) if x % 3 == 0] [0, 9, 36, 81] >>> [(x,y) for x in range(3) for y in range(3)] [(0, 0), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 0), (1, 1), (1, 2), (2, 0), (2, 1), (2, 2)]
result = []
for x in range(3):
for y in range(3):
result.append((x,y))
print result
>>> girls = ['alice','bernice','clarice'] >>> boys = ['chris','arnold','bob'] >>> [b+'+'+g for b in boys for g in girls if b[0] == g[0]] ['chris+clarice', 'arnold+alice', 'bob+bernice']
比较(Python根据缩进来判断语句关系)
result = []
for x in range(3):
for y in range(3):
result.append((x,y))
print result
[(0, 0), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 0), (1, 1), (1, 2), (2, 0), (2, 1), (2, 2)]
result = []
for x in range(3):
for y in range(3):
result.append((x,y))
print result
[(0, 0)] [(0, 0), (0, 1)] [(0, 0), (0, 1), (0, 2)] [(0, 0), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 0)] [(0, 0), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 0), (1, 1)] [(0, 0), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 0), (1, 1), (1, 2)] [(0, 0), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 0), (1, 1), (1, 2), (2, 0)] [(0, 0), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 0), (1, 1), (1, 2), (2, 0), (2, 1)] [(0, 0), (0, 1), (0, 2), (1, 0), (1, 1), (1, 2), (2, 0), (2, 1), (2, 2)]

第六章 抽象
fibs = [0,1]
num = input('How many Fibonacci numbers do you want?')
for i in range(num-2):
fibs.append(fibs[-2] + fibs[-1])
print fibs
How many Fibonacci numbers do you want?10 [0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34]
函数
def hello(name):
return 'Hello,'+name+'!'
>>> print hello('world')
Hello,world!
>>> print hello('Gumby')
Hello,Gumby!
def fibs(num):
result = [0,1]
for i in range(num-2):
result.append(result[-2]+result[-1])
return result
>>> fibs(10) [0, 1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34] >>> fibs(10)[2] 1
记录函数
def square(x):
'Calculates the square of the number x.'
return x*x
def square(x):
'Calculates the square of the number x.'
return x*x
并非真正函数的函数
def test():
print 'This is printed'
return
print 'This is not'
>>> x = test() This is printed >>> x >>> print x None >>>
参数魔法
>>> def change(n): n = 'Alex' >>> name = 'mr' >>> change(name) >>> name 'mr'
>>> def change(n): n[0] = 'Mr. Gumby' >>> names = ['Mrs. Entity','Mrs. Thing'] >>> change(names) >>> names ['Mr. Gumby', 'Mrs. Thing'] >>> >>> names = ['Mrs. Entity','Mrs. Thing'] >>> n = names >>> n[0] = 'Mr. Gumby' >>> names ['Mr. Gumby', 'Mrs. Thing'] >>>
>>> names = ['Mrs. Entity','Mrs. Thing'] >>> n = names >>> n is names True >>> n == names True >>> n = names[:] >>> n is names False >>> n == names True
指向同一对象的时候,is就是True,否则就是False



【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(二):开始使用ML.NET
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 探究高空视频全景AR技术的实现原理
· 理解Rust引用及其生命周期标识(上)
· 浏览器原生「磁吸」效果!Anchor Positioning 锚点定位神器解析
· DeepSeek 开源周回顾「GitHub 热点速览」
· 记一次.NET内存居高不下排查解决与启示
· 物流快递公司核心技术能力-地址解析分单基础技术分享
· .NET 10首个预览版发布:重大改进与新特性概览!
· .NET10 - 预览版1新功能体验(一)