JavaSE知识-07(面向对象-构造方法&静态static)
目录
构造方法Constructor概述和格式
- 构造方法概述和作用
- 给对象的数据(属性)进行初始化
- 构造方法格式特点
- a:方法名与类名相同(大小也要与类名一致)
- b:没有返回值类型,连void都没有
- c:没有具体的返回值return;
构造方法的重载
- 重载:方法名相同,与返回值类型无关(构造方法没有返回值),只看参数列表
- 构造方法注意事项
- a:如果我们没有给出构造方法,系统将自动提供一个无参构造方法。
- b:如果我们给出了构造方法,系统将不再提供默认的无参构造方法。
- 注意:这个时候,如果我们还想使用无参构造方法,就必须自己给出。建议永远自己给出无参构造方法
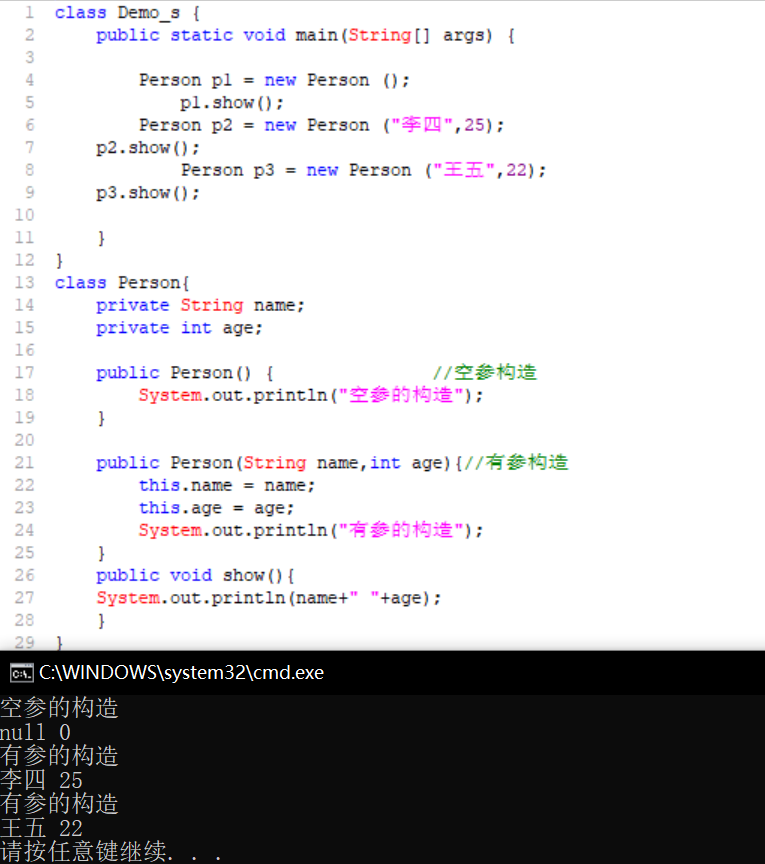
- 注意:这个时候,如果我们还想使用无参构造方法,就必须自己给出。建议永远自己给出无参构造方法
给成员变量赋值的两种方式的区别, 学生类的代码及测试
- setXxx()方法 推荐
- 修改属性值
- 构造方法
- 给对象中属性进行初始化
class Demo_S2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p1 = new Person("张三",23); //构造方法
System.out.println(p1.getName() +" "+ p1.getAge());
p1 = new Person("张天一",23); //这种方式看运行结果貌似是改名了,其实是将原对象变成垃圾
System.out.println(p1.getName() +" "+ p1.getAge() +"......getXxx()获取属性值输出"); //获取到的属性值也可以做其它操作
p1.show();
System.out.println("--------------------");
Person p2 = new Person(); //空参构造创建对象
p2.setName("李四");
p2.setAge(24); //setXxx()方法
System.out.println(p2.getName() +" "+ p2.getAge());
p2.setName("李鬼");
System.out.println(p2.getName() +" "+ p2.getAge());
}
}
class Person {
private String name;
private int age; //如果为public, 上面可直接println(p1.age)输出年龄
public Person (String name,int age){ //有参构造
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public Person() { //空参构造
}
public void setName(String name){
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age){
this.age = age;
}
public String getName(){
return name;
}
public int getAge(){
return age;
}
public void show(){
System.out.println(name +" "+ age +"......show()显示属性值输出");
}
}

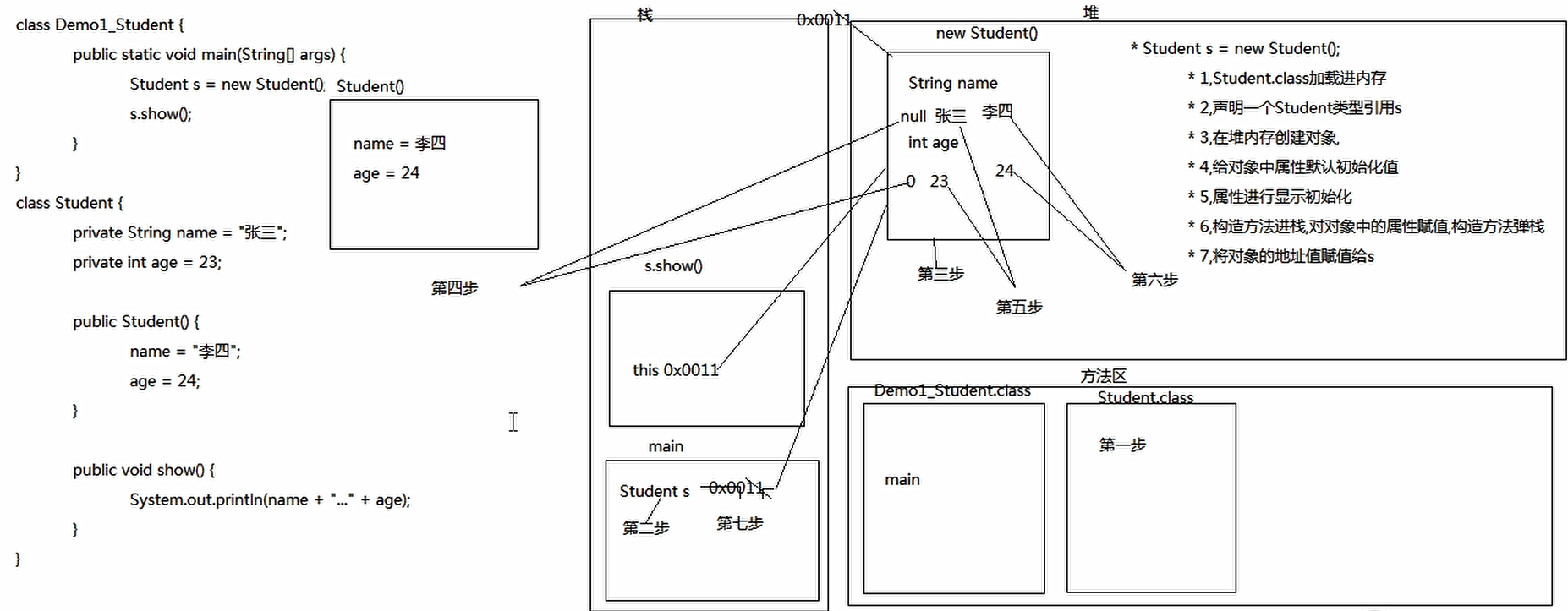
创建一个对象的步骤
定义长方形类,求周长和面积
class Test1_Rectangle { //Rectangle矩形
public static void main(String[] args) {
//第一种方式:使用构造方法赋值
Rectangle r = new Rectangle(10,20);
System.out.println(r.getLength()); //周长
System.out.println(r.getArea()); //面积
//第二种方式:使用set方法赋值
Rectangle r2 = new Rectangle();
r2.setWidth(10);
r2.setHigh(20);
System.out.println(r2.getLength()); //周长
System.out.println(r2.getArea()); //面积
}
}
/*
成员变量:
宽width,高high
空参有参构造
成员方法:
setXxx和getXxx
求周长:getLength()
求面积:getArea()
*/
class Rectangle {
private int width; //宽
private int high; //高
public Rectangle(){} //空参构造
public Rectangle(int width,int high) {
this.width = width; //有参构造
this.high = high;
}
public void setWidth(int width) {//设置宽
this.width = width;
}
public int getWidth() { //获取宽
return width;
}
public void setHigh(int high) { //设置高
this.high = high;
}
public int getHigh() { //获取高
return high;
}
public int getLength() { //获取周长
return 2 * (width + high);
}
public int getArea() { //获取面积
return width * high;
}
}
定义员工类
class Test2_Employee { //employee员工
public static void main(String[] args) {
Employee e = new Employee("令狐冲","9527",20000);
e.work();
}
}
/*
* 姓名name,工号id,工资salary
* 构造方法,
* 空参和有参的
* getXxx()setXxx()方法,
* 以及一个显示所有成员信息的方法。并测试。
* work
*/
class Employee {
private String name; //姓名
private String id; //工号
private double salary; //工资
public Employee() {} //空参构造
public Employee(String name, String id, double salary) {//有参构造
this.name = name;
this.id = id;
this.salary = salary;
}
public void setName(String name) { //设置姓名
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() { //获取姓名
return name;
}
public void setId(String id) { //设置id
this.id = id;
}
public String getId() { //获取id
return id;
}
public void setSalary(double salary) { //设置工资
this.salary = salary;
}
public double getSalary() { //获取工资
return salary;
}
public void work() {
System.out.println("我的姓名是:" + name + ",我的工号是:" + id + ",我的工资是:" + salary
+ ",我的工作内容是敲代码");
}
}
static关键字
- static关键字的特点
- a:随着类的加载而加载
- b:优先于对象存在
- c:被类的所有对象共享
- 举例:咱们班级的学生应该共用同一个班级编号。
- 其实这个特点也是在告诉我们什么时候使用静态?
- 如果某个成员变量是被所有对象共享的,那么它就应该定义为静态的。
- 举例:
- 饮水机(用静态修饰)
- 水杯(不能用静态修饰)
- 共性用静态,特性用非静态
- d:可以通过类名调用
- 其实它本身也可以通过对象名调用。
- 推荐使用类名调用。
- 静态修饰的内容一般我们称其为:与类相关的,类成员
class Demo1_Static {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p3 = new Person();
p3.name = "福原爱老师"; //调用姓名属性并赋值
p3.country = "台湾"; //调用国籍属性并赋值
p3.speak();
Person p1 = new Person(); //创建对象
p1.name = "苍老师"; //调用姓名属性并赋值
p1.country = "日本"; //调用国籍属性并赋值
p1.speak();
Person p2 = new Person();
p2.name = "小泽老师"; //调用姓名属性并赋值
// p2.country = "日本"; //调用国籍属性并赋值
p2.speak();
Person p4 = new Person();
p4.name = "黄老师"; //调用姓名属性并赋值
// p2.country = "日本"; //调用国籍属性并赋值
p4.speak();
//Person.country = "日本"; //静态多了一种调用方式,可以通过类名.
//System.out.println(Person.country);
}
}
class Person {
String name; //姓名
static String country; //国籍
public void speak() { //说话的方法
System.out.println(name + "..." + country);
}
}
class Demo2_Static {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Demo d = new Demo();
//d.print1();
//Demo d = new Demo();
//System.out.println(d.num1);
System.out.println(Demo.num1);
//Demo.print2();
}
}
/*
* A:static的注意事项
* a:在静态方法中是没有this关键字的
* 如何理解呢?
* 静态是随着类的加载而加载,this是随着对象的创建而存在。
* 静态比对象先存在。
* b:静态方法只能访问静态的成员变量和静态的成员方法
* 静态方法:
* 成员变量:只能访问静态变量
* 成员方法:只能访问静态成员方法
* 非静态方法:
* 成员变量:可以是静态的,也可以是非静态的
* 成员方法:可是是静态的成员方法,也可以是非静态的成员方法。
* 简单记:
* 静态只能访问静态。
*/
class Demo {
int num1 = 10; //非静态的成员变量
static int num2 = 20; //静态的成员变量
/*public void print1() { //非静态的成员方法,既可以访问静态的成员也可以访问非静态的
System.out.println(num1);
System.out.println(num2);
}*/
public static void print2() { //静态的成员方法
//System.out.println(this.num1);//静态的成员方法不能访问非静态的,错误: 无法从静态上下文中引用非静态 变量 num1
System.out.println(num2);
}
}
静态变量和成员变量的区别
- 静态变量也叫类变量 成员变量也叫对象变量
- A:所属不同
- 静态变量属于类,所以也称为为类变量
- 成员变量属于对象,所以也称为实例变量(对象变量)
- B:内存中位置不同
- 静态变量存储于方法区的静态区
- 成员变量存储于堆内存
- C:内存出现时间不同
- 静态变量随着类的加载而加载,随着类的消失而消失
- 成员变量随着对象的创建而存在,随着对象的消失而消失
- D:调用不同
- 静态变量可以通过类名调用,也可以通过对象调用
- 成员变量只能通过对象名调用
工具类中使用静态
/**
这是一个数组工具类,里面封装了查找数组最大值,打印数组,数组反转的方法
*/
public class ArrayTool {
//如果一个类中所有的方法都是静态的,需要再多做一步,私有构造方法,目的是不让其他类创建本类对象
//直接用类名.调用即可
private ArrayTool(){
}
//1,获取最大值
public static int getMax(int[] arr) {
int max = arr[0]; //记录第一个元素
for (int i = 1;i < arr.length ;i++ ) { //从第二个元素开始遍历
if (max < arr[i]) { //max与数组中其他的元素比较
max = arr[i]; //记录住较大的
}
}
return max; //将最大值返回
}
//2,数组的遍历
public static void print(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 0;i < arr.length ;i++ ) { //遍历数组
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
}
//3,数组的反转
public static void revArray(int[] arr) {
for (int i = 0;i < arr.length / 2 ;i++ ) { //循环次数是元素个数的一半
int temp = arr[i];
arr[i] = arr[arr.length-1-i];
arr[arr.length-1-i] = temp;
}
}
}
class Demo1_ArrayTool {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] arr = {33,11,22,66,55,44};
/*ArrayTool at = new ArrayTool();
int max = at.getMax(arr); //获取最值
System.out.println(max);
System.out.println("---------------");
at.print(arr); //打印
System.out.println();
System.out.println("---------------");
System.out.println("反转后:");
at.revArray(arr); //反转
at.print(arr); */
ArrayTool.print(arr); //静态不用创建对象,直接用类名.调用即可
}
}
Math类的随机数功能

class Demo4_random {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//double d =Math.random();
//System.out.println(d);
//生成10个1-100的随机数
for (int i=0;i<10 ;i++ ){
System.out.println((int)(Math.random()*100)+1);
}
}
}





