数据结构算法——链表的各种操作,C++和Python
时隔已久,一直没更新博客,感觉很愧疚呀。
先贴上所有的代码。这个是用C++写的
#include "stdafx.h" //Author:Albert //Date: 2018.10.28 #include<iostream> using namespace std; typedef int datatype; class Node { public: int data; Node *next; }; class linkList { public: linkList();//初始化一个单链表 ~linkList();//销毁一个单链表 bool creatLinkListByInput(int n);//通过控制台输入新建一个长度为n的单链表 void dispLinkList();//把链表里储存的数据都显示出来 int getLength(); void insertNodetoEnd(datatype data); void insertNode(datatype data, int n);//在第n个数据后插入一个数据data void DeleteNode(int n);//删除第n个节点 void Reverse(); private: Node * head; }; linkList::linkList() { head = new Node; head->data = 0; head->next = NULL; } linkList::~linkList() { delete head; } bool linkList::creatLinkListByInput(int n) { Node *pnew, *ptemp; ptemp = head; if (n < 0) { cout << "error" << endl; return false; } for (int i = 0;i < n;i++) { pnew = new Node; cout << "请输入第" << i + 1 << "个值:"; cin >> pnew->data; pnew->next = NULL; ptemp->next = pnew; ptemp = pnew; } return true; } void linkList::dispLinkList() { Node *p; p = head; if (p!=NULL) { while (p->next!=NULL) { p = p->next; cout << p->data << endl; } } else { cout << "这是一个空链表" << endl; } } int linkList::getLength() { int n=0; Node *p; p = head; while (p->next!=NULL) { n++; p = p->next; } return n; } void linkList::insertNodetoEnd(datatype data) { Node *pnew=new Node; pnew->data = data; pnew->next = NULL; Node *p=head; while (p->next != NULL) { p = p->next; } p->next = pnew; } void linkList::insertNode(datatype data, int n) { Node *p = head; Node *pnew = new Node; for (int i = 0;i < n;i++) { p = p->next; } //此时p指向的是第n个数据 pnew->data = data; pnew->next = p->next; p->next = pnew; } void linkList::DeleteNode(int n) { Node *p = head; Node *ppre = new Node; for (int i = 0;i < n;i++) { ppre = p; p = p->next; } //ppre是要删除的节点的前一个节点 ppre->next = p->next; delete p; } void linkList::Reverse() { Node *plast = head->next; Node *p = plast->next; Node *ptmp = new Node; plast->next = NULL; while (p->next != NULL) { ptmp = p; p = p->next; ptmp->next = plast; plast= ptmp; } p->next = plast; head->next = p; } int main() { linkList a; //新建一个长度为3的单链表 a.creatLinkListByInput(3); a.dispLinkList(); cout << "链表长度为:" << a.getLength() << endl; cout << "在尾部插入一个1:" << endl; a.insertNodetoEnd(1); a.dispLinkList(); cout << "链表长度为:" << a.getLength() << endl; cout << "在第2个数据后插入1:" << endl; a.insertNode(1,2); a.dispLinkList(); cout << "链表长度为:" << a.getLength() << endl; cout << "删除第4个数据" << endl; a.DeleteNode(4); a.dispLinkList(); cout << "链表长度为:" << a.getLength() << endl; cout << "将链表逆置" << endl; a.Reverse(); a.dispLinkList(); return 0; }
1、新建一个单链表
bool linkList::creatLinkListByInput(int n) { Node *pnew, *ptemp; ptemp = head; if (n < 0) { cout << "error" << endl; return false; } for (int i = 0;i < n;i++) { pnew = new Node; cout << "请输入第" << i + 1 << "个值:"; cin >> pnew->data; pnew->next = NULL; ptemp->next = pnew; ptemp = pnew; } return true; }
这个代码还是我看了别人的之后才写的。在控制台输入一系列数据,返回是否新建成功。
其中最关键的一处就是定义一个head节点。这个节点不储存数据,head->next才是第一个储存的数据。
这样的话就比较好写循环里的内容了,后面的调用也很方便。
用图画一下就很容易理解了。

显示整个链表数据,得到链表长度什么的,不用多说啦。直接遍历就行。
2、插入节点。
void linkList::insertNode(datatype data, int n) { Node *p = head; Node *pnew = new Node; for (int i = 0;i < n;i++) { p = p->next; } //此时p指向的是第n个数据 pnew->data = data; pnew->next = p->next; p->next = pnew; }
先遍历到到第n个节点
然后

3、删除一个节点
void linkList::DeleteNode(int n) { Node *p = head; Node *ppre = new Node; for (int i = 0;i < n;i++) { ppre = p; p = p->next; } //ppre是要删除的节点的前一个节点 ppre->next = p->next; delete p; }
把它画出来就是

4、单链表的逆置
void linkList::Reverse() { Node *plast = head->next; Node *p = plast->next; Node *ptmp = new Node; plast->next = NULL; while (p->next != NULL) { ptmp = p; p = p->next; ptmp->next = plast; plast= ptmp; } p->next = plast; head->next = p; }
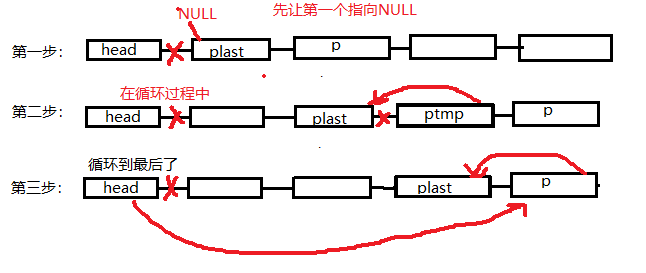
这里ptmp的作用就是为了防止p->next=plast从而导致无法往下遍历。
我见还有一种用ppre,p,pnex三个指针的。思想跟这个差不多。
感觉自己菜的要死,只能从头再开始学啦。
还有几个问题
链表中环的检测:用的快慢指针的思想。
两个有序链表的合并:遍历,主要是别让指针指乱了。
删除链表倒数第n个节点。如果链表长度知道,就很简单了,转化为整数就好。如果长度不知道,我觉得,就用迭代可以有。
求链表中的中间节点,用快慢针呀。
这几个问题我没时间一个一个的写啦。以后遇到了在一个一个的写。
此外还有循环链表和双向链表,他们都各有千秋,懂的单链表,这都很简单了。
以下为我看了Python写的之后的追加
最近贼以下把它封装成一个类,嘿嘿嘿。面向对象编程感觉条理贼清晰

#!/user/bin/python3 # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- #@author:Albert #@time:2018/11/3 class Node(object): def __init__(self,x): self.data=x self.next=None class Linklist(): def __init__(self,l): self.head=Node(0) self.changeLinklistTo(l) def changeLinklistTo(self,l): p=self.head for i in l: p.next=Node(i) p=p.next def display(self): p=self.head.next while(p): print(p.data) p=p.next def reverse(self):#翻转整个链表 cur,prev=self.head.next,None while cur: cur.next,prev,cur=prev,cur,cur.next self.head.next=prev def swapPairs(self):#交换相邻的两个链表节点位置 pre=self.head while pre.next and pre.next.next: a=pre.next b=pre.next.next pre.next,b.next,a.next=b,a,b.next #此处多重赋值是先计算右边,然后统一赋给左边 pre=a def hasCycle(self):#检测单链表环,用的快慢针的思想 fast=slow=self.head.next while fast and slow and fast.next: slow=slow.next fast=fast.next.next if fast is slow: return True return False a=Linklist([1,2,3,4,5,6]) a.display() a.reverse() print("A has been reversed") a.display() a.swapPairs() print("A has been swapped") a.display() print("A has cycle? : ",a.hasCycle())



