列车调度(Train)
列车调度(Train)
Description
Figure 1 shows the structure of a station for train dispatching.
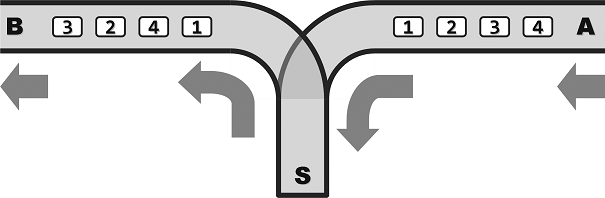
Figure 1
In this station, A is the entrance for each train and B is the exit. S is the transfer end. All single tracks are one-way, which means that the train can enter the station from A to S, and pull out from S to B. Note that the overtaking is not allowed. Because the compartments can reside in S, the order that they pull out at B may differ from that they enter at A. However, because of the limited capacity of S, no more that m compartments can reside at S simultaneously.
Assume that a train consist of n compartments labeled {1, 2, …, n}. A dispatcher wants to know whether these compartments can pull out at B in the order of {a1, a2, …, an} (a sequence). If can, in what order he should operate it?
Input
Two lines:
1st line: two integers n and m;
2nd line: n integers separated by spaces, which is a permutation of {1, 2, …, n}. This is a compartment sequence that is to be judged regarding the feasibility.
Output
If the sequence is feasible, output the sequence. “Push” means one compartment goes from A to S, while “pop” means one compartment goes from S to B. Each operation takes up one line.
If the sequence is infeasible, output a “no”.
Example 1
Input
5 2
1 2 3 5 4
Output
push
pop
push
pop
push
pop
push
push
pop
pop
Example 2
Input
5 5
3 1 2 4 5
Output
No
Restrictions
1 <= n <= 1,600,000
0 <= m <= 1,600,000
Time: 2 sec
Memory: 256 MB
- 原理与要点:栈的简单应用。初始栈为空,循环遍历出栈顺序的数组。
- 如果当前栈顶元素小于应该出栈的元素,则顺次把后面的数字入栈,记录入栈
- 如果当前栈顶元素等于应该出栈的元素,则出栈,遍历数组的指针后移 ,记录出栈
- 如果当前栈顶元素大于应该出栈的元素,则说明该出栈顺序不可能实现,输出No,然后结束程序 - 遇到的问题:无
- 时间和空间复杂度: 时间复杂度\(O(n)\),空间复杂度\(O(n)\)
#include "iostream"
#include "cstdio"
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 4e6 + 10;
int a[maxn];
int st[maxn];
const int SZ = 1<<20; //快速io
struct fastio{
char inbuf[SZ];
char outbuf[SZ];
fastio(){
setvbuf(stdin,inbuf,_IOFBF,SZ);
setvbuf(stdout,outbuf,_IOFBF,SZ);
}
}io;
int main() {
int n, m;
scanf("%d %d", &n, &m);
int now = 1;
int top = 0, tot = 0;
int x;
st[0] = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
scanf("%d", &x);
while (now <= x) {
st[++top] = now++;
a[tot++] = 0;
}
if (top > m) {
printf("No\n");
return 0;
}
if (st[top] == x) {
top--;
a[tot++] = 1;
} else {
printf("No\n");
return 0;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < tot; i++) {
if (a[i]) {
printf("pop\n");
} else {
printf("push\n");
}
}
return 0;
}

