Docker基础技术:Linux Namespace(下)
好,下面我们就介绍一下还剩下的这两个Namespace。
User Namespace
User Namespace主要是用了CLONE_NEWUSER的参数。使用了这个参数后,内部看到的UID和GID已经与外部不同了,默认显示为65534。那是因为容器找不到其真正的UID所以,设置上了最大的UID(其设置定义在/proc/sys/kernel/overflowuid)。
要把容器中的uid和真实系统的uid给映射在一起,需要修改 /proc/<pid>/uid_map 和 /proc/<pid>/gid_map 这两个文件。这两个文件的格式为:
ID-inside-ns ID-outside-ns length
其中:
- 第一个字段ID-inside-ns表示在容器显示的UID或GID,
- 第二个字段ID-outside-ns表示容器外映射的真实的UID或GID。
- 第三个字段表示映射的范围,一般填1,表示一一对应。
比如,把真实的uid=1000映射成容器内的uid=0
1 2 | $ cat /proc/2465/uid_map 0 1000 1 |
再比如下面的示例:表示把namespace内部从0开始的uid映射到外部从0开始的uid,其最大范围是无符号32位整形
1 2 | $ cat /proc/$$/uid_map 0 0 4294967295 |
另外,需要注意的是:
- 写这两个文件的进程需要这个namespace中的CAP_SETUID (CAP_SETGID)权限(可参看Capabilities)
- 写入的进程必须是此user namespace的父或子的user namespace进程。
- 另外需要满如下条件之一:1)父进程将effective uid/gid映射到子进程的user namespace中,2)父进程如果有CAP_SETUID/CAP_SETGID权限,那么它将可以映射到父进程中的任一uid/gid。
这些规则看着都烦,我们来看程序吧(下面的程序有点长,但是非常简单,如果你读过《Unix网络编程》上卷,你应该可以看懂):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 | #define _GNU_SOURCE#include <stdio.h>#include <stdlib.h>#include <sys/types.h>#include <sys/wait.h>#include <sys/mount.h>#include <sys/capability.h>#include <stdio.h>#include <sched.h>#include <signal.h>#include <unistd.h>#define STACK_SIZE (1024 * 1024)static char container_stack[STACK_SIZE];char* const container_args[] = { "/bin/bash", NULL};int pipefd[2];void set_map(char* file, int inside_id, int outside_id, int len) { FILE* mapfd = fopen(file, "w"); if (NULL == mapfd) { perror("open file error"); return; } fprintf(mapfd, "%d %d %d", inside_id, outside_id, len); fclose(mapfd);}void set_uid_map(pid_t pid, int inside_id, int outside_id, int len) { char file[256]; sprintf(file, "/proc/%d/uid_map", pid); set_map(file, inside_id, outside_id, len);}void set_gid_map(pid_t pid, int inside_id, int outside_id, int len) { char file[256]; sprintf(file, "/proc/%d/gid_map", pid); set_map(file, inside_id, outside_id, len);}int container_main(void* arg){ printf("Container [%5d] - inside the container!\n", getpid()); printf("Container: eUID = %ld; eGID = %ld, UID=%ld, GID=%ld\n", (long) geteuid(), (long) getegid(), (long) getuid(), (long) getgid()); /* 等待父进程通知后再往下执行(进程间的同步) */ char ch; close(pipefd[1]); read(pipefd[0], &ch, 1); printf("Container [%5d] - setup hostname!\n", getpid()); //set hostname sethostname("container",10); //remount "/proc" to make sure the "top" and "ps" show container's information mount("proc", "/proc", "proc", 0, NULL); execv(container_args[0], container_args); printf("Something's wrong!\n"); return 1;}int main(){ const int gid=getgid(), uid=getuid(); printf("Parent: eUID = %ld; eGID = %ld, UID=%ld, GID=%ld\n", (long) geteuid(), (long) getegid(), (long) getuid(), (long) getgid()); pipe(pipefd); printf("Parent [%5d] - start a container!\n", getpid()); int container_pid = clone(container_main, container_stack+STACK_SIZE, CLONE_NEWUTS | CLONE_NEWPID | CLONE_NEWNS | CLONE_NEWUSER | SIGCHLD, NULL); printf("Parent [%5d] - Container [%5d]!\n", getpid(), container_pid); //To map the uid/gid, // we need edit the /proc/PID/uid_map (or /proc/PID/gid_map) in parent //The file format is // ID-inside-ns ID-outside-ns length //if no mapping, // the uid will be taken from /proc/sys/kernel/overflowuid // the gid will be taken from /proc/sys/kernel/overflowgid set_uid_map(container_pid, 0, uid, 1); set_gid_map(container_pid, 0, gid, 1); printf("Parent [%5d] - user/group mapping done!\n", getpid()); /* 通知子进程 */ close(pipefd[1]); waitpid(container_pid, NULL, 0); printf("Parent - container stopped!\n"); return 0;} |
上面的程序,我们用了一个pipe来对父子进程进行同步,为什么要这样做?因为子进程中有一个execv的系统调用,这个系统调用会把当前子进程的进程空间给全部覆盖掉,我们希望在execv之前就做好user namespace的uid/gid的映射,这样,execv运行的/bin/bash就会因为我们设置了uid为0的inside-uid而变成#号的提示符。
整个程序的运行效果如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | hchen@ubuntu:~$ iduid=1000(hchen) gid=1000(hchen) groups=1000(hchen)hchen@ubuntu:~$ ./user #<--以hchen用户运行Parent: eUID = 1000; eGID = 1000, UID=1000, GID=1000 Parent [ 3262] - start a container!Parent [ 3262] - Container [ 3263]!Parent [ 3262] - user/group mapping done!Container [ 1] - inside the container!Container: eUID = 0; eGID = 0, UID=0, GID=0 #<---Container里的UID/GID都为0了Container [ 1] - setup hostname!root@container:~# id #<----我们可以看到容器里的用户和命令行提示符是root用户了uid=0(root) gid=0(root) groups=0(root),65534(nogroup) |
虽然容器里是root,但其实这个容器的/bin/bash进程是以一个普通用户hchen来运行的。这样一来,我们容器的安全性会得到提高。
我们注意到,User Namespace是以普通用户运行,但是别的Namespace需要root权限,那么,如果我要同时使用多个Namespace,该怎么办呢?一般来说,我们先用一般用户创建User Namespace,然后把这个一般用户映射成root,在容器内用root来创建其它的Namesapce。
Network Namespace
Network的Namespace比较啰嗦。在Linux下,我们一般用ip命令创建Network Namespace(Docker的源码中,它没有用ip命令,而是自己实现了ip命令内的一些功能——是用了Raw Socket发些“奇怪”的数据,呵呵)。这里,我还是用ip命令讲解一下。
首先,我们先看个图,下面这个图基本上就是Docker在宿主机上的网络示意图(其中的物理网卡并不准确,因为docker可能会运行在一个VM中,所以,这里所谓的“物理网卡”其实也就是一个有可以路由的IP的网卡)
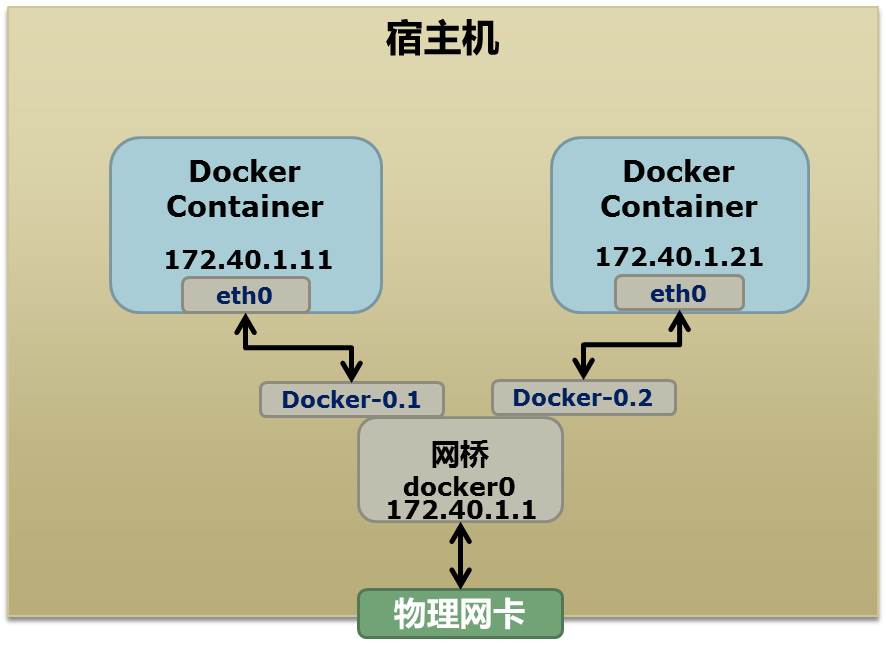
上图中,Docker使用了一个私有网段,172.40.1.0,docker还可能会使用10.0.0.0和192.168.0.0这两个私有网段,关键看你的路由表中是否配置了,如果没有配置,就会使用,如果你的路由表配置了所有私有网段,那么docker启动时就会出错了。
当你启动一个Docker容器后,你可以使用ip link show或ip addr show来查看当前宿主机的网络情况(我们可以看到有一个docker0,还有一个veth22a38e6的虚拟网卡——给容器用的):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | hchen@ubuntu:~$ ip link show1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state ... link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:002: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc ... link/ether 00:0c:29:b7:67:7d brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff3: docker0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 ... link/ether 56:84:7a:fe:97:99 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff5: veth22a38e6: <BROADCAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc ... link/ether 8e:30:2a:ac:8c:d1 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff |
那么,要做成这个样子应该怎么办呢?我们来看一组命令:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 | ## 首先,我们先增加一个网桥lxcbr0,模仿docker0brctl addbr lxcbr0brctl stp lxcbr0 offifconfig lxcbr0 192.168.10.1/24 up #为网桥设置IP地址## 接下来,我们要创建一个network namespace - ns1# 增加一个namesapce 命令为 ns1 (使用ip netns add命令)ip netns add ns1 # 激活namespace中的loopback,即127.0.0.1(使用ip netns exec ns1来操作ns1中的命令)ip netns exec ns1 ip link set dev lo up ## 然后,我们需要增加一对虚拟网卡# 增加一个pair虚拟网卡,注意其中的veth类型,其中一个网卡要按进容器中ip link add veth-ns1 type veth peer name lxcbr0.1# 把 veth-ns1 按到namespace ns1中,这样容器中就会有一个新的网卡了ip link set veth-ns1 netns ns1# 把容器里的 veth-ns1改名为 eth0 (容器外会冲突,容器内就不会了)ip netns exec ns1 ip link set dev veth-ns1 name eth0 # 为容器中的网卡分配一个IP地址,并激活它ip netns exec ns1 ifconfig eth0 192.168.10.11/24 up# 上面我们把veth-ns1这个网卡按到了容器中,然后我们要把lxcbr0.1添加上网桥上brctl addif lxcbr0 lxcbr0.1# 为容器增加一个路由规则,让容器可以访问外面的网络ip netns exec ns1 ip route add default via 192.168.10.1# 在/etc/netns下创建network namespce名称为ns1的目录,# 然后为这个namespace设置resolv.conf,这样,容器内就可以访问域名了mkdir -p /etc/netns/ns1echo "nameserver 8.8.8.8" > /etc/netns/ns1/resolv.conf |
上面基本上就是docker网络的原理了,只不过,
- Docker的resolv.conf没有用这样的方式,而是用了上篇中的Mount Namesapce的那种方式
- 另外,docker是用进程的PID来做Network Namespace的名称的。
了解了这些后,你甚至可以为正在运行的docker容器增加一个新的网卡:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | ip link add peerA type veth peer name peerB brctl addif docker0 peerA ip link set peerA up ip link set peerB netns ${container-pid} ip netns exec ${container-pid} ip link set dev peerB name eth1 ip netns exec ${container-pid} ip link set eth1 up ; ip netns exec ${container-pid} ip addr add ${ROUTEABLE_IP} dev eth1 ; |
上面的示例是我们为正在运行的docker容器,增加一个eth1的网卡,并给了一个静态的可被外部访问到的IP地址。
这个需要把外部的“物理网卡”配置成混杂模式,这样这个eth1网卡就会向外通过ARP协议发送自己的Mac地址,然后外部的交换机就会把到这个IP地址的包转到“物理网卡”上,因为是混杂模式,所以eth1就能收到相关的数据,一看,是自己的,那么就收到。这样,Docker容器的网络就和外部通了。
当然,无论是Docker的NAT方式,还是混杂模式都会有性能上的问题,NAT不用说了,存在一个转发的开销,混杂模式呢,网卡上收到的负载都会完全交给所有的虚拟网卡上,于是就算一个网卡上没有数据,但也会被其它网卡上的数据所影响。
这两种方式都不够完美,我们知道,真正解决这种网络问题需要使用VLAN技术,于是Google的同学们为Linux内核实现了一个IPVLAN的驱动,这基本上就是为Docker量身定制的。
Namespace文件
上面就是目前Linux Namespace的玩法。 现在,我来看一下其它的相关东西。
让我们运行一下上篇中的那个pid.mnt的程序(也就是PID Namespace中那个mount proc的程序),然后不要退出。
1 2 3 4 | $ sudo ./pid.mnt [sudo] password for hchen: Parent [ 4599] - start a container!Container [ 1] - inside the container! |
我们到另一个shell中查看一下父子进程的PID:
1 2 | hchen@ubuntu:~$ pstree -p 4599pid.mnt(4599)───bash(4600) |
我们可以到proc下(/proc//ns)查看进程的各个namespace的id(内核版本需要3.8以上)。
下面是父进程的:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | hchen@ubuntu:~$ sudo ls -l /proc/4599/nstotal 0lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 4月 7 22:01 ipc -> ipc:[4026531839]lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 4月 7 22:01 mnt -> mnt:[4026531840]lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 4月 7 22:01 net -> net:[4026531956]lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 4月 7 22:01 pid -> pid:[4026531836]lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 4月 7 22:01 user -> user:[4026531837]lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 4月 7 22:01 uts -> uts:[4026531838] |
下面是子进程的:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 | hchen@ubuntu:~$ sudo ls -l /proc/4600/nstotal 0lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 4月 7 22:01 ipc -> ipc:[4026531839]lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 4月 7 22:01 mnt -> mnt:[4026532520]lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 4月 7 22:01 net -> net:[4026531956]lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 4月 7 22:01 pid -> pid:[4026532522]lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 4月 7 22:01 user -> user:[4026531837]lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 4月 7 22:01 uts -> uts:[4026532521] |
我们可以看到,其中的ipc,net,user是同一个ID,而mnt,pid,uts都是不一样的。如果两个进程指向的namespace编号相同,就说明他们在同一个namespace下,否则则在不同namespace里面。
这些文件还有另一个作用,那就是,一旦这些文件被打开,只要其fd被占用着,那么就算PID所属的所有进程都已经结束,创建的namespace也会一直存在。比如:我们可以通过:mount –bind /proc/4600/ns/uts ~/uts 来hold这个namespace。
另外,我们在上篇中讲过一个setns的系统调用,其函数声明如下:
1 | int setns(int fd, int nstype); |
其中第一个参数就是一个fd,也就是一个open()系统调用打开了上述文件后返回的fd,比如:
1 2 | fd = open("/proc/4600/ns/nts", O_RDONLY); // 获取namespace文件描述符setns(fd, 0); // 加入新的namespace |




